Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2338–2376) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: While traditional analysis relies on statistical software such as SPSS, emerging tools like ChatGPT introduce the possibility of performing statistical tests, interpreting results, and generating figures via natural language prompts. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) are accessible inflammatory markers increasingly used in the monitoring of chronic diseases like Spondyloarthritis. This study aims to compare traditional statistical analysis using SPSS (V.20.0) with AI-based analysis using ChatGPT (Model 4o) in longitudinal NLR and PLR data, evaluating their consistency, usability, and impact on research efficiency.
Methods: We performed a retrospective observational study of 85 Spondyloarthritis patients treated with Secukinumab from 2016 to 2023. NLR and PLR were recorded at baseline and every six months for four years. The Friedman test was applied to assess variation over time using both SPSS v25 and ChatGPT’s 4o built-in Python environment (Advanced Data Analysis). Results, narrative outputs, and figures were compared
Results: Patients showed a mean age of 53.6 years; 66% had axial Spondyloarthritis and 34% Psoriatic Arthritis, with balanced sex distribution. Common comorbidities included smoking (41.2%), Hypertension (27.1%), Diabetes (21.2%), and Dyslipidaemia (28.2%). Both platforms detected a decreasing trend in NLR and PLR over time. Neither test showed statistically significant differences across timepoints (NLR p = 0.41, PLR p = 0.62 in both SPSS and ChatGPT). Outputs were numerically identical, with ChatGPT also providing clinical context and suggestions for graphical representation. While SPSS required software setup and manual processing, ChatGPT offered a simplified, efficient alternative with real-time interpretation.
Conclusion: ChatGPT with integrated statistical capabilities provides a reliable, efficient alternative for exploratory data analysis in clinical research. Its results matched those from SPSS while offering added value in interpretability and ease of use. Although not a replacement for regulated statistical tools in all contexts, its potential to accelerate early-stage research and support non-specialists is notable.
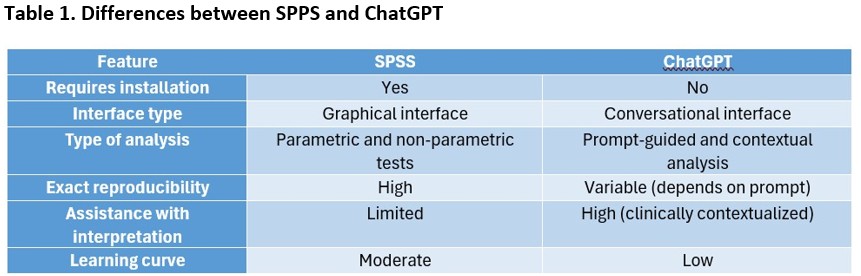 Table 1. Differences between ChatGPT and SPSS.
Table 1. Differences between ChatGPT and SPSS.
.jpg) Figures 1 and 2. Trend of NLR and PLR over time.
Figures 1 and 2. Trend of NLR and PLR over time.
.jpg) Table 2. Study of the variation in NLR and PLR Ratios and their related variables (with ChatGPT and SPSS).
Table 2. Study of the variation in NLR and PLR Ratios and their related variables (with ChatGPT and SPSS).
Disclosures: J. Sequí-Sabater: None; P. Beltrán Martin-Lorente: None; S. Pastor Navarro: None; M. Lopez Gonzalez: None; M. Sanchez-Wonenburger: None; D. CASADO POVEDA: None; A. Martínez Cristóbal: None.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sequí-Sabater J, Beltrán Martin-Lorente P, Pastor Navarro S, Lopez Gonzalez M, Sanchez-Wonenburger M, CASADO POVEDA D, Martínez Cristóbal A. ChatGPT or SPSS? A comparison between AI-based and Traditional Statistical Analysis of Longitudinal Inflammatory Marker Data in Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/chatgpt-or-spss-a-comparison-between-ai-based-and-traditional-statistical-analysis-of-longitudinal-inflammatory-marker-data-in-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/chatgpt-or-spss-a-comparison-between-ai-based-and-traditional-statistical-analysis-of-longitudinal-inflammatory-marker-data-in-spondyloarthritis/
