Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2338–2376) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
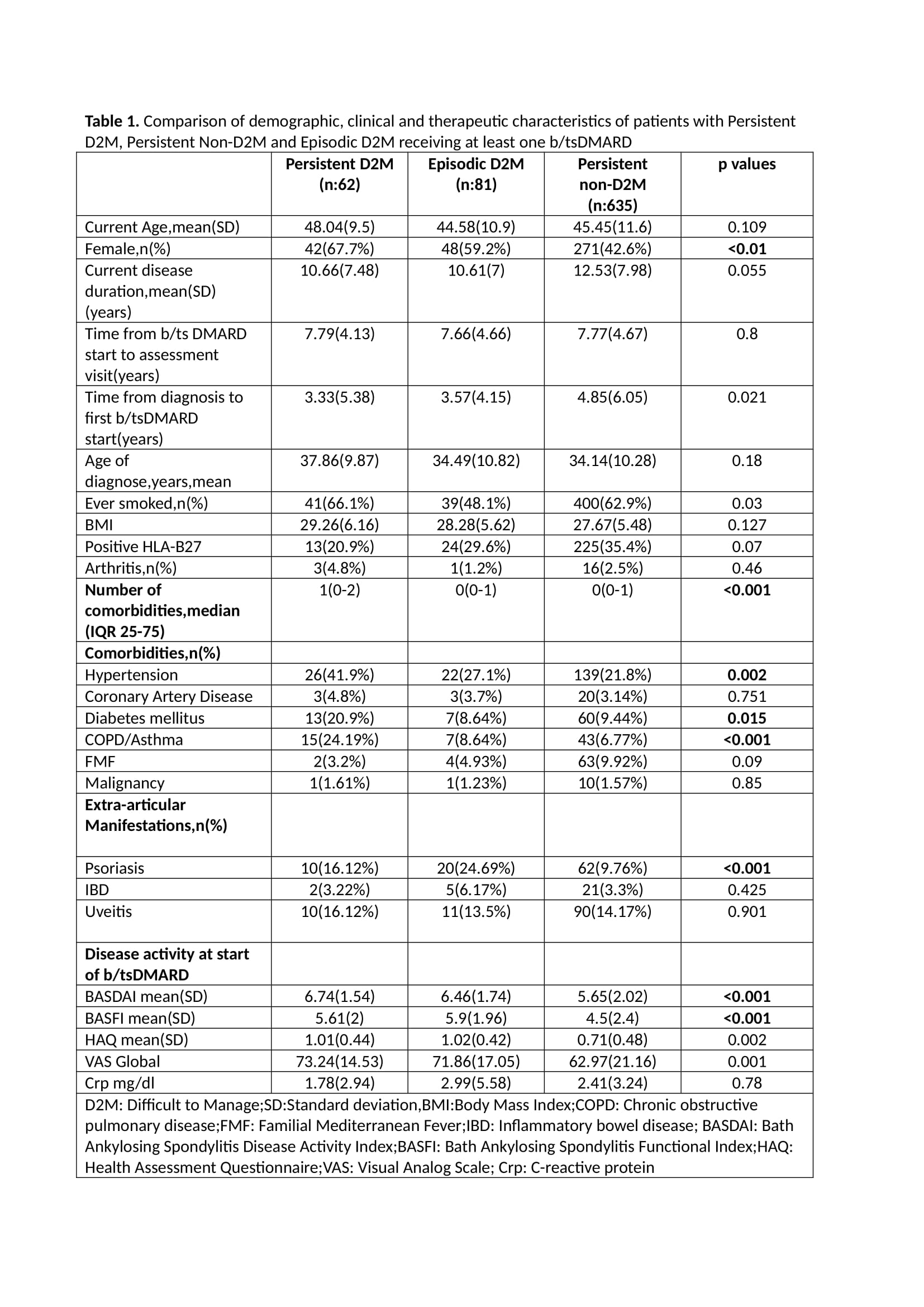
Background/Purpose: The concept of difficult-to-manage axial spondyloarthritis (D2M-axSpA)[1], may vary over time. Transitions between D2M and non-D2M classifications throughout the disease course remain unclear. This study evaluates the consistency of the D2M-axSpA classification over time and identifies differences of non-D2M and persistent and episodic D2M-axSpA cases at the b/tsDMARD initiation.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional assessment patients with axSpA who were on b/tsDMARD for at least one year and visited our rheumatology clinic between April-December 2023. Patients were assessed at two timepoints for fullfillment of D2M-axSpA: first visit at the study inclusion period and second visit between 6-12 months after the first visit. Using these two-timepoint data patients were categorized into three groups as follows:’persistent D2M’ (D2M-axSpA’ patients at both assessments), ‘persistent non-D2M'(non-D2M-axSpA’ patients at both assessments), ‘episodic D2M-axSpA’ (D2M-axSpA in only one of the assessments). Demographic, clinical and disease activity indices as well as comorbidities of the patients at the initiation of b/ts DMARD were evaluated and compared between groups. The factors associated with D2M-axSpA status on univariate analysis with significance at the 0.20 level were entered into a multivariable model. Backward elimination method was used at a significance of 0.05 level.
Results: Overall 888 patients were included in this assessment . From the initial D2M-axSpA patients(n=119), 52.1% were persistent-axSpA, 33.6% were episodic D2M-axSpA. 14.2% (17/119) did not attend follow-up visits. Of the initial non-D2M-axSpA (n=769), 82.5% were persistent non-D2M-axSpA, 5.33%were episodic D2M-axSpA, and 12.09% did not participate in follow-up visits (Figure 1). Persistent D2M-axSpA patients were more often female and had higher rates of hypertension, COPD/asthma, and diabetes mellitus. BASDAI and VAS global scores were significantly higher in the persistent D2M-group at b/tsDMARD initiation (Table 1). In the multivariable logistic regression analysis, a higher BASDAI score at the initiation of b/tsDMARD therapy was identified as a significant factor associated with the development of D2M-axSpA (either episodic or persistent) among patients initially classified as non-D2M (OR: 1.48 [1.15–1.91], p = 0.002) (Table 2).
Conclusion: Our study revealed that 33.6% of patients initially diagnosed with D2M-axSpA eventually transitioned to a non-D2M state and overall 10% of the population has transitioned from one category to another. Persistent D2M-axSpA patients were more often female and had a higher prevalence of comorbidities. Physicians should be aware that D2M-axSpA criteria fullfilments may change over time, with factors that potentially affecting subjective measures like BASDAI, HAQ, and VAS global scores.References:1. Poddubnyy D, B.X., et al ., Arthritis Rheumatol, 2024. 76.
.jpg) Figure 1. Temporal changes in D2M AxSpA and Non-D2M AxSpA patients
Figure 1. Temporal changes in D2M AxSpA and Non-D2M AxSpA patients
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kart bayram G, Akdemir M, Ekici M, Ayan G, Fırlatan Yazgan B, Ünaldı E, Bulat B, Kuştaş A, Akdoğan A, Karadağ O, Apraş Bilgen Ş, Ertenli A, Kiraz S, Kalyoncu U, Kılıç L. Classification of “Difficult-to-Manage Axial Spondyloarthritis”: A Real-World Cohort Study Evaluating the ASAS 2024 Criteria Over Time [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/classification-of-difficult-to-manage-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-real-world-cohort-study-evaluating-the-asas-2024-criteria-over-time/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/classification-of-difficult-to-manage-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-real-world-cohort-study-evaluating-the-asas-2024-criteria-over-time/

.jpg)