Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2338–2376) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
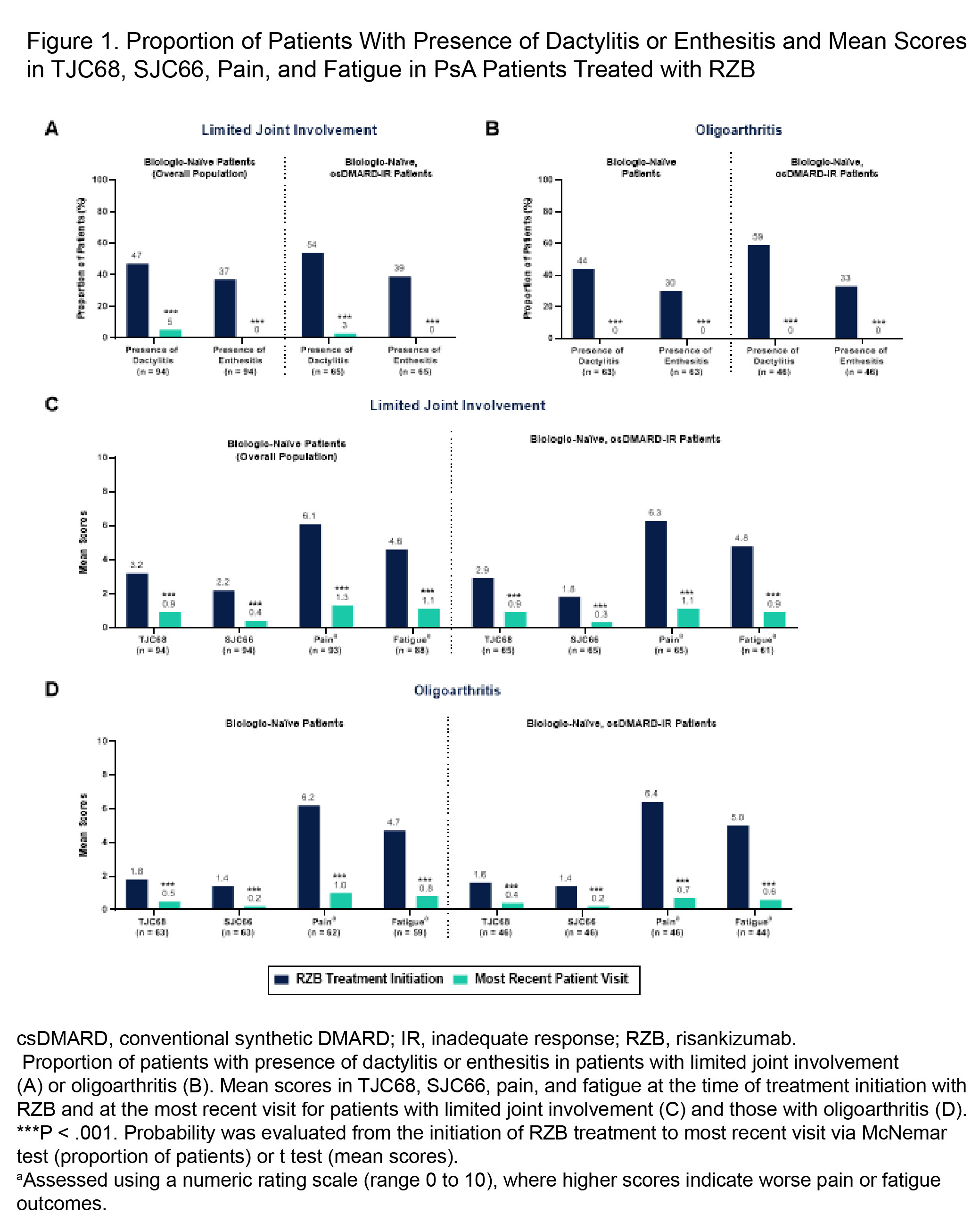
Background/Purpose: This study evaluated real-world effectiveness and patient- and physician-satisfaction with risankizumab (RZB) for biologic-naïve PsA patients with limited joint involvement or oligoarthritis.
Methods: Data were drawn from the Adelphi Spondyloarthritis VI Disease Specific Programme™ collected from June 2023 to June 2024 focusing on biologic-naïve patients with PsA who received RZB 150 mg and had limited joint involvement (≥ 1 to ≤ 8 TJC or SJC ≥ 1 to ≤ 8 ; 1–16 total active joints) or oligoarthritis (≥ 1 to ≤ 4 TJC or ≥ 1 to ≤ 4 SJC; 1–8 total active joints) at treatment initiation. Patients were located in the US and Europe (France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the UK). Data were collected from cross-sectional questionnaires completed by physicians (treatment effectiveness and satisfaction) and their consulting patients (satisfaction) during recent visits. Outcomes were evaluated in the overall population of patients naïve to biologics with limited joint involvement and 3 subgroups: (1) patients naïve to biologics with limited joint involvement and an inadequate response to ≥ 1 conventional synthetic DMARD (csDMARD-IR), (2) patients with oligoarthritis naïve to biologics, and (3) patients with oligoarthritis naïve to biologics and csDMARD-IR.
Results: In the overall population, there were 94 biologic-naïve patients were included (23% [n = 22] from the US, 77% [n = 72] from Europe); mean age 43.3 years old, 40% female, 16.1% BSA affected by PsO at treatment initiation. Mean RZB treatment duration was 9.3 months in the overall population; mean TJC and SJC at treatment initiation was 3.2 and 2.2, respectively. Baseline characteristics were similar across the subgroups. Improvements in the presence of dactylitis and enthesitis and mean changes in TJC68, SJC66, pain, and fatigue were reported from treatment initiation to most recent visit for all groups (P ≤ .001 for all) (Figure 1). High rates of complete resolution of dactylitis (89%) and enthesitis (100%), TJC68 ≤ 1 (69%), SJC66 ≤ 1 (79%), and clinically meaningful improvements in pain (94%) and fatigue (76%) were observed with RZB in the overall population (Figure 2A). Effectiveness results were consistent in the csDMARD-IR subgroup (n = 65) with limited joint involvement (Figures 1-2). Patients with oligoarthritis who presented with dactylitis or enthesitis at treatment initiation, including 100% of both the biologic-naïve (n = 63) and csDMARDs-IR (n = 46) subgroups, demonstrated complete resolution of dactylitis and enthesitis. Clinically meaningful improvements were also seen in TJC68 ≤ 1 (69% and 73%), SJC66 ≤ 1 (82% for both), pain (95% and 98%), and fatigue (82% and 89%) in the biologic-naïve and csDMARD-IR oligoarthritis subgroups, respectively (Figure 2B). In the overall population, high patient (100%, n = 18) and physician (98%, n = 94) satisfaction rates were reported for the ability of RZB to control the disease.
Conclusion: In biologic-naïve patients with PsA and limited joint involvement or oligoarthritis, RZB treatment demonstrated effectiveness and high levels of satisfaction among patients and physicians in real-world clinical practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ostor A, Walsh J, Saffore C, Ye X, Patel M, Biljan A, Vora J, Truman I, Edwards M, Milligan G, Tillett W. Real-World Effectiveness and Satisfaction in Biologic-Naïve Patients With Psoriatic Arthritis and Limited Joint Involvement Treated With Risankizumab in the United States and Europe [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-effectiveness-and-satisfaction-in-biologic-naive-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-limited-joint-involvement-treated-with-risankizumab-in-the-united-states-and-europe/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-effectiveness-and-satisfaction-in-biologic-naive-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-limited-joint-involvement-treated-with-risankizumab-in-the-united-states-and-europe/

.jpg)