Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2227–2264) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: First-degree family history of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a relevant factor in genetic predisposition and early diagnosis of the disease. Objectives: 1)Estimate the frequency of family history (FH) in consecutive patients with arthralgia and its association with the final diagnosis of RA. 2) Analyze the differences between patients diagnosed with RA, according to the presence or absence of FH. 3) Compare the characteristics of patients with arthralgia without a diagnosis of RA, differentiating those with and without FH.
Methods: This was an observational study where patients with arthralgia were admitted to the Reuma-check program. At baseline, laboratory tests (ESR, CRP, RF, and ACPA), ultrasonography (US), and X-ray were performed. Sociodemographic, clinical, and clinimetry data (28-joint count – HAQ), including first-degree family history of RA, were also collected. Each evaluator was blinded to the results of the other studies (fig1). Once the circuit was completed, the diagnosis of RA was established. Descriptive statistics and logistic regression were performed.
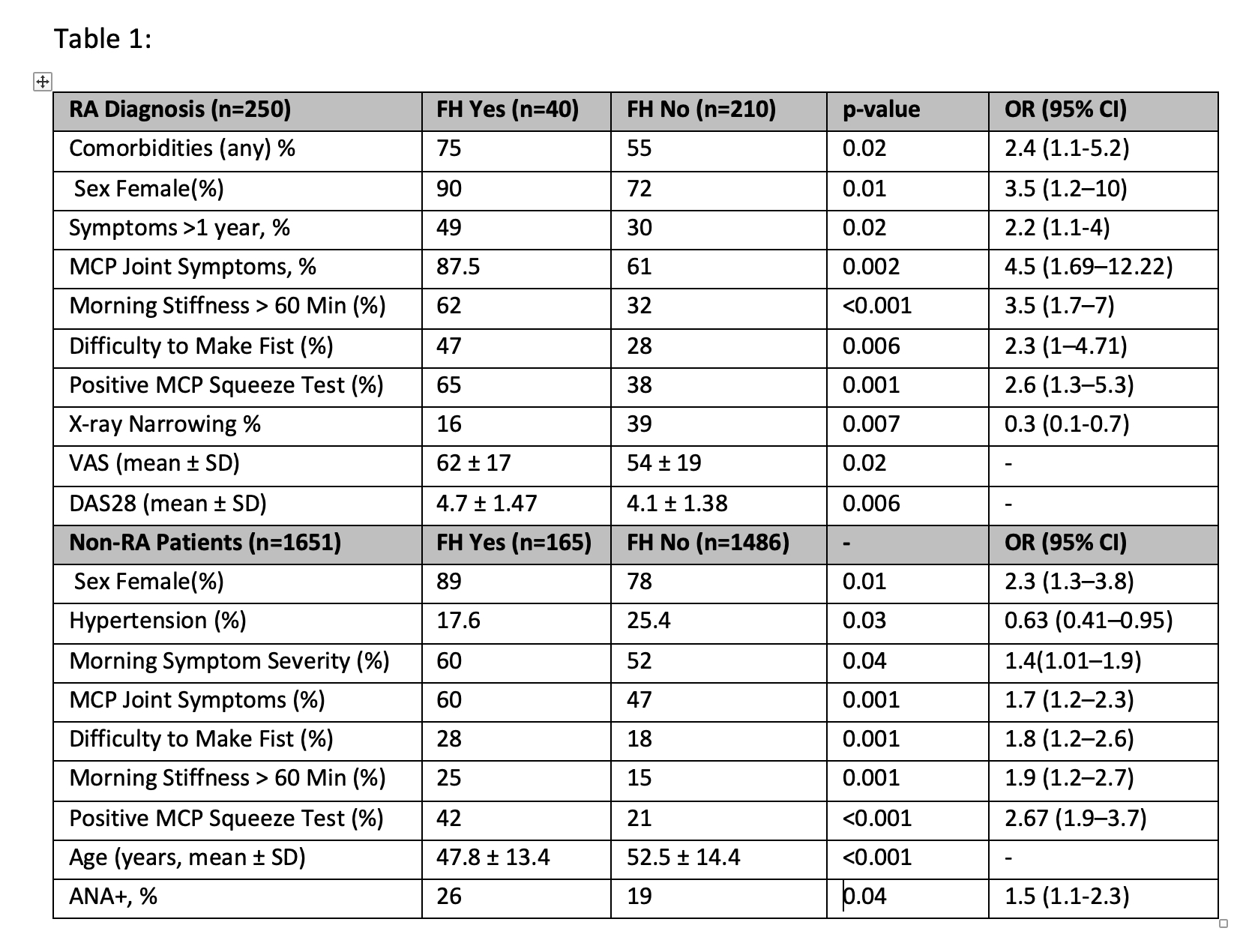
Results: A total of 1900 patients with arthralgia were evaluated: 77% were women, with a mean age of 52 years (SD 14). 10.8% (n=205; 95% CI: 9.5%-12.3%) had FH. Patients with FH showed a higher prevalence of RA (19.5% vs. 12.2%; OR: 1.75; 95% CI: 1.2-2.55; p=0.005). Patients diagnosed with RA (n=250) and FH (16%, n=40) presented distinct characteristics compared to those without FH, showing a more severe RA, Significant differences in univariate analysis between patients diagnosed with RA with and without FH are shown in Table 1. Significant variables in the univariate analysis were included in the multivariate logistic regression model. The results showed that involvement of metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints presented an independent association in patients with RA and FH (OR = 4.24, 95% CI: 1.35–13.31, p = 0.013).In patients with arthralgia without a diagnosis of RA (n=1651), those with FH (10%, n=165) showed more severe features in the univariate analysis (Table 1). Logistic regression showed an independent association with positive MCP squeeze (OR: 2.26; 95% CI: 1.57-3.27; p< 0.001), female sex (OR: 1.92; 95% CI: 1.14-3.21; p=0.013) and Youngest age at consultation (OR: 0.8 CI: 0.78-0.9; p=0.001).
Conclusion: The frequency of FH is 11% in patients with arthralgia and is associated with a higher risk of RA diagnosis. Patients with RA and FH present distinct severity characteristics. In patients with arthralgia without a diagnosis of RA, the presence of FH is associated with more severe clinical features of arthralgia.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
García Salinas R, Arguello J, Ruta S, Perez R, Magri S. Impact of Family History of RA in Patients Evaluated for Arthralgia: A Comprehensive Analysis of the Reuma-check Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-family-history-of-ra-in-patients-evaluated-for-arthralgia-a-comprehensive-analysis-of-the-reuma-check-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-family-history-of-ra-in-patients-evaluated-for-arthralgia-a-comprehensive-analysis-of-the-reuma-check-cohort/

.jpg)