Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (sJIA) and Adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) are rare, chronic, autoinflammatory diseases distinct from other forms of chronic inflammatory arthritis. Potential life-threatening complications include macrophage activation syndrome (MAS)/secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) and interstitial lung disease (ILD). Despite advances in targeted therapies, there remain patients with refractory disease. JAK inhibitors offer a promising new treatment option, with case reports and series suggesting efficacy and safety in treating refractory sJIA and AOSD, but the amount of information on ruxolitinib is limited. We present a case series of three patients with sJIA and two with AOSD who were treated with ruxolitinib at a single center.
Methods: We queried the electronic medical record (EMR) of a large tertiary health system for patients who received ruxolitinib within the past ten years for diagnosed sJIA or AOSD. Nine patients were identified, five older than 16 and four younger at the time of diagnosis (Figure 1). Then via record review, we confirmed that ruxolitinib was specifically used for treating sJIA or AOSD, excluding three adults who were treated for T cell lymphoma (2) and graft vs host disease (1). One patient was excluded for receiving one dose of ruxolitinib hours before dying from systemic organ failure. For the remaining five patients (3 sJIA, 2 AOSD), we collected data on demographics, previous medications used, laboratory abnormalities, disease complications and clinical outcomes.
Results: All five patients were treated with other medications prior to starting ruxolitnib including systemic steroids (5), conventional DMARDs (4), biologics (5), and other JAK inhibitors (3). Three of five patients had adverse effects to other medications prior to starting ruxolitinib.Disease complications prior to the use of ruxolitinib included: MAS/HLH (3), ILD confirmed by CT (1), pericarditis and pleural effusion (1), and opportunistic infection (1). All patients had refractory disease prior to starting ruxolitinib. The mean length of treatment with ruxolitinib was 30.8 months (median 12 months, range 7-91 months).Since starting ruxolitinib, 4 of 5 demonstrated clinical response to therapy according to clinical documentation and remained on ruxolitinib with good disease control and no adverse effects at the time of last follow-up. One is on monotherapy and three on combination therapy. One patient discontinued ruxolitinib in the context of severe MAS with concern that ruxolitinib could have contributed to a GI bleed, though there were other risk factors. Inflammatory markers, cytokines, and chemokines improved in some patients, though lab acquisition was inconsistent between patients (Table 1).
Conclusion: Ruxolitinib represents an alternative treatment employed for refractory sJIA or AOSD that in our case series led to a favorable outcome regarding safety and efficacy. Our ability to evaluate response was limited by the data available in an EMR chart review. This series highlights the need for more rigorous study of ruxolitinib as a possibly safe and effective treatment strategy for treatment-refractory sJIA and AOSD.
 Patients included in the series were those treated with Ruxolitinib for at least one day for diagnoses of sJIA or AOSD, with or without MAS/HLH. sJIA, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis; AOSD, Adult Onset Still’s Disease; MAS, Macrophage Activation Syndrome; HLH, Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis; GVHD, Graft-Versus-Host Disease.
Patients included in the series were those treated with Ruxolitinib for at least one day for diagnoses of sJIA or AOSD, with or without MAS/HLH. sJIA, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis; AOSD, Adult Onset Still’s Disease; MAS, Macrophage Activation Syndrome; HLH, Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis; GVHD, Graft-Versus-Host Disease.
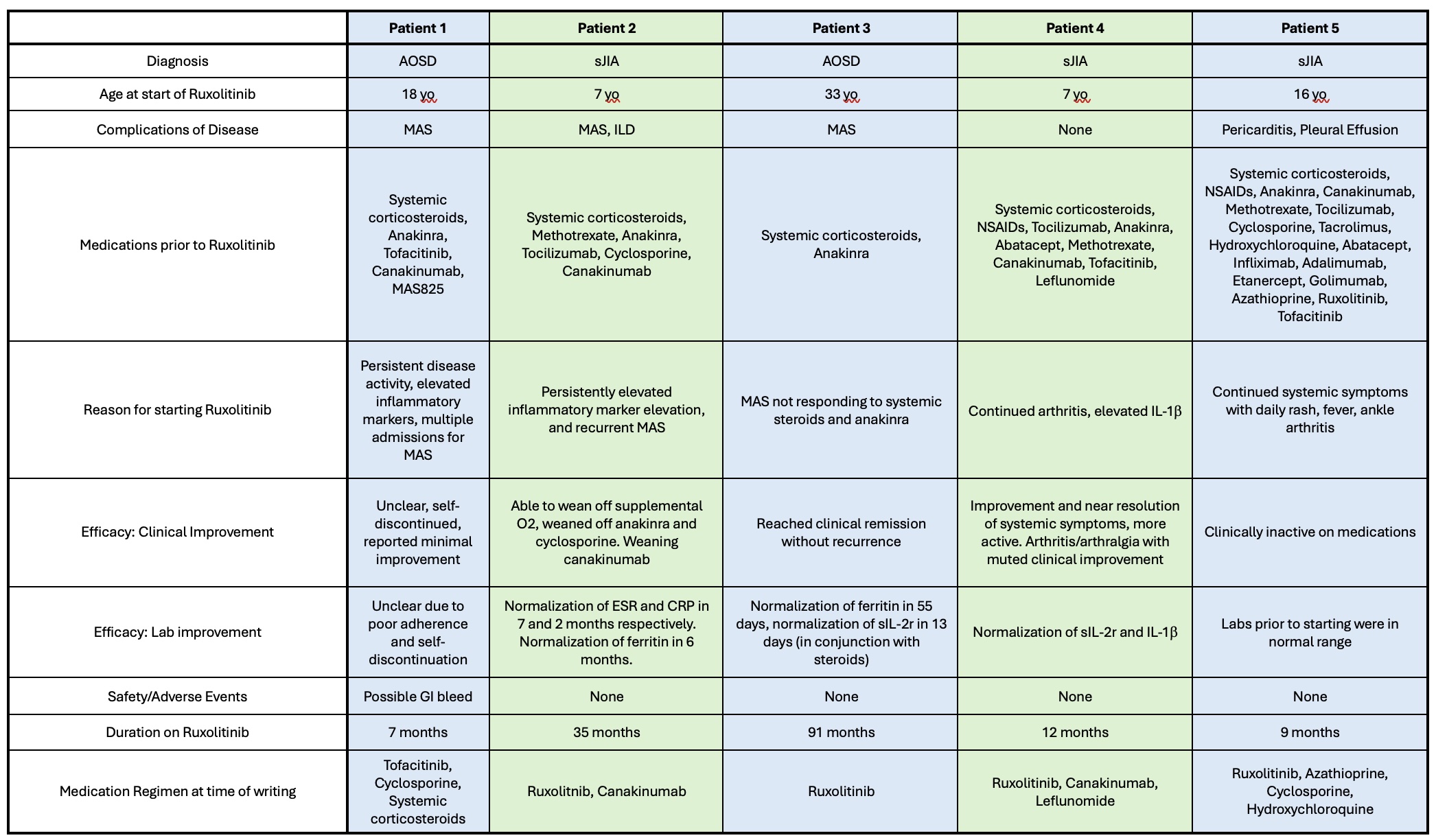
.jpg) Clinical characteristics of patients included in series. sJIA, systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis, AOSD, Adult Onset Still’s Disease; MAS, Macrophage Activation Syndrome; ILD, Interstitial Lung Disease; ESR, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate, CRP, C-reactive protein
Clinical characteristics of patients included in series. sJIA, systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis, AOSD, Adult Onset Still’s Disease; MAS, Macrophage Activation Syndrome; ILD, Interstitial Lung Disease; ESR, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate, CRP, C-reactive protein
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Madison J, Grim A, Shim J. Ruxolitinib for Refractory sJIA/AOSD: A Single Center Case Series [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ruxolitinib-for-refractory-sjia-aosd-a-single-center-case-series/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ruxolitinib-for-refractory-sjia-aosd-a-single-center-case-series/
