Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2052–2078) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Dysphagia remains a key contributor to mortality in IBM due to its connection with aspiration pneumonia and malnutrition (Shelly et al., 2021). Compared to other IIMs, IBM increases the odds of acquiring aspiration pneumonia and non-oral means of nutrition 3-fold (Ma et al., 2023). Yet, dysphagia kinematics in IBM are ill-defined, possibly leading to under-detection, misdiagnosis, and inappropriate dysphagia treatment (Ambrocio et al., 2023). Our study aimed to profile the kinematics underlying dysphagia in IBM using standardized and validated assessment methods and identify clinical predictors of dysphagia severity.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, cross-sectional study involving 15 adults with IBM (9 males) suspected of dysphagia. They had a mean age of 72.7 years (SD=5.9) and met the European Neuromuscular Center diagnostic criteria (Lilleker et al., 2024) and ACR classification (Lundberg et al., 2017). Their mean IBM Functional Rating Scale (IBMFRS) score and disease duration were 26.9 (SD=5.5) and 8.5 years (SD=3.8), respectively. Participants underwent a modified barium swallow study following the Modified Barium Swallow Impairment Profile (MBSImP) protocol, including 12 bolus tasks ranging from thin to highly thick liquids and a solid (Martin-Harris et al., 2008). We analyzed the images using MBSImP ratings, yielding Overall Impression (OI), Oral Total (OT), and Pharyngeal Total (PT) scores across 17 oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal kinematic components. We compared participants’ OI, OT, and PT scores with data from age- and sex-matched healthy controls in a normative database (Garand et al., 2022). Mann-Whitney U tests compared OI, OT, and PT scores between groups. We analyzed dysphagia severity using the Dynamic Imaging Grade of Swallowing Toxicity (DIGEST) (Hutcheson et al., 2022). Univariate ordinal logistic regressions estimated the impact of OT and PT scores, age, sex, IBMFRS scores, and disease duration on DIGEST grades.
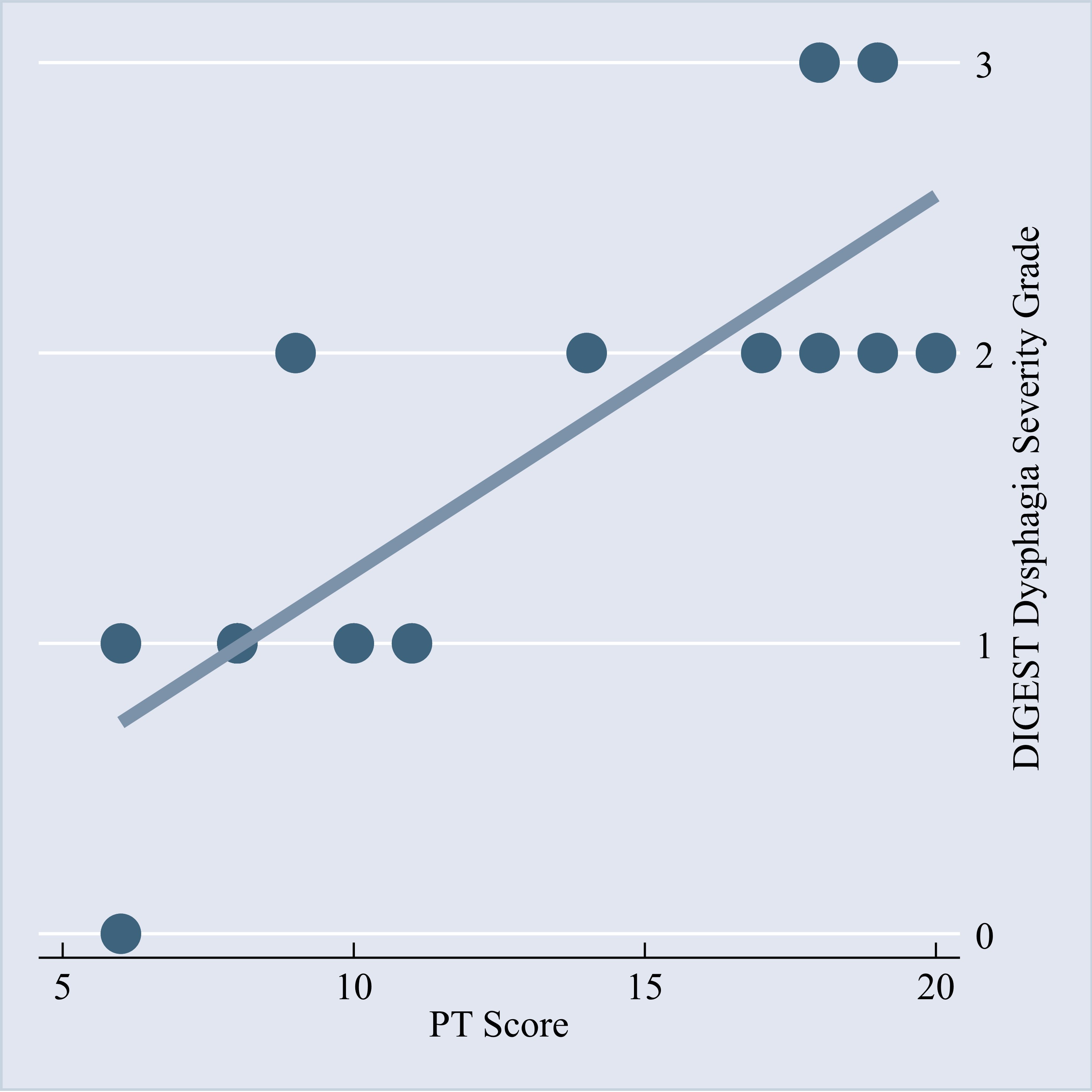
Results: Compared to controls, the IBM group had significantly higher (worse) OI scores for tongue motion, soft palate elevation, pharyngeal stripping, pharyngoesophageal segment opening, pharyngeal residue, and esophageal clearance, each p< .05, with large effects ranging from r=.51-.91 (Table 1). The IBM group had significantly higher (worse) OT (p=.001, r=.62) and PT (p=.013, r=.50) scores than controls, with large effects (Table 2). One participant had a normal DIGEST grade, but the rest spanned from mild to severe dysphagia. Only PT scores predicted DIGEST grades, with higher PT scores significantly linked to greater dysphagia severity, p=.031, OR=2.16 (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Participants with IBM exhibited kinematic deficits across swallowing phases. Surrogate kinematic markers for pressure generation and bolus propulsion mechanics were most impaired, which may be valuable for predicting dysphagia severity in IBM. Our study demonstrates the use of robust swallowing metrics to quantify and obtain a nuanced phenotypic dysphagia profile for IBM, representing an improvement over prior studies. Such findings facilitate targeted dysphagia treatment, precise symptom monitoring, and early identification of people with IBM at risk of dysphagia.
.jpg) Figure 1. DIGEST Dysphagia Severity Grade Regression.
Figure 1. DIGEST Dysphagia Severity Grade Regression.
The scatter plot shows the interaction between each participant’s PT score and DIGEST dysphagia severity grade, while the line represents the overall trend of the fitted regression model. This trend illustrates that higher (worse) PT scores are generally associated with higher (worse) DIGEST dysphagia severity grades. DIGEST severity grade interpretation: 0=normal, 1=mild, 2=moderate, 3=severe.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ambrocio K, Kothari V, Aggarwal R, Miles A, Coyle J, Alhassan E, Stinnett S, Lacomis D, Sayce L, (Focht) Garand K. Kinematics Underlying IBM-induced Dysphagia [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/kinematics-underlying-ibm-induced-dysphagia/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/kinematics-underlying-ibm-induced-dysphagia/

.jpg)