Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2015–2051) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a severe complication of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and its management remains a challenge. Approximately one third of the patients may develop a progressive ILD or show persistent inflammatory joint activity despite of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Favorable results with the antifibrotic nintedanib (NINTE) in RA-ILD patients with pulmonary progressive fibrosis (PPF) in pulmonary function had been reported. However, data on articular response is limited, although NINTE seems to have no efficacy on the articular domain. Therefore, NINTE should be administered combined with DMARDs. Our objective was to assess the evolution of joint and pulmonary outcomes in RA-ILD patients with PPF treated of NINTE and DMARDs in clinical practice.
Methods: National Spanish multicenter study of RA-ILD patients treated with NINTE due to PPF. the main outcome measures were joint activity and forced vital capacity (FVC) evolution of different groups of treatment according to DMARDs category (biological [bDMARDs] or synthetic [sDMARDs]) were the main outcome measures.
Results: A total of 74 patients (43 men/31 women) were collected, mean age of 69±9 years. Median [IQR] ILD duration up to antifibrotic initiation was 51 [22-78] months. NINTE was used a) combined with bDMARDs (n=47, 33 abatacept, 10 rituximab); b) combined with sDMARDs (n=29, 7 leflunomide, 6 methotrexate, 4 JAK inhibitor, 8 mycophenolate, 2 hydroxychloroquine, 1 azathioprine and 1 cyclophosphamide); c) combined with both bDMARDs and sDMARDs (n=9); and d) monotherapy (only glucocorticoids) (n=13). To avoid interference, we select only those who are on either biological or synthetic DMARDs. Main baseline characteristics of patients are shown in Table. After 12 months of follow-up, joint activity was controlled in 81% of patients (87% in the group of NINTE+ only bDMARDs and 83% in the group of NINTE+ only sDMARDs, p=0.82). In addition, no significant decline in mean FVC or DLCO values was observed, with no statistically significant differences between the 2 groups of treatment (Figure).
Conclusion: In our series of RA-ILD patients with PPF treated with NINTE, articular inflammation could be managed either with bDMARDs or sDMARDs, with similar pulmonary function evolution.
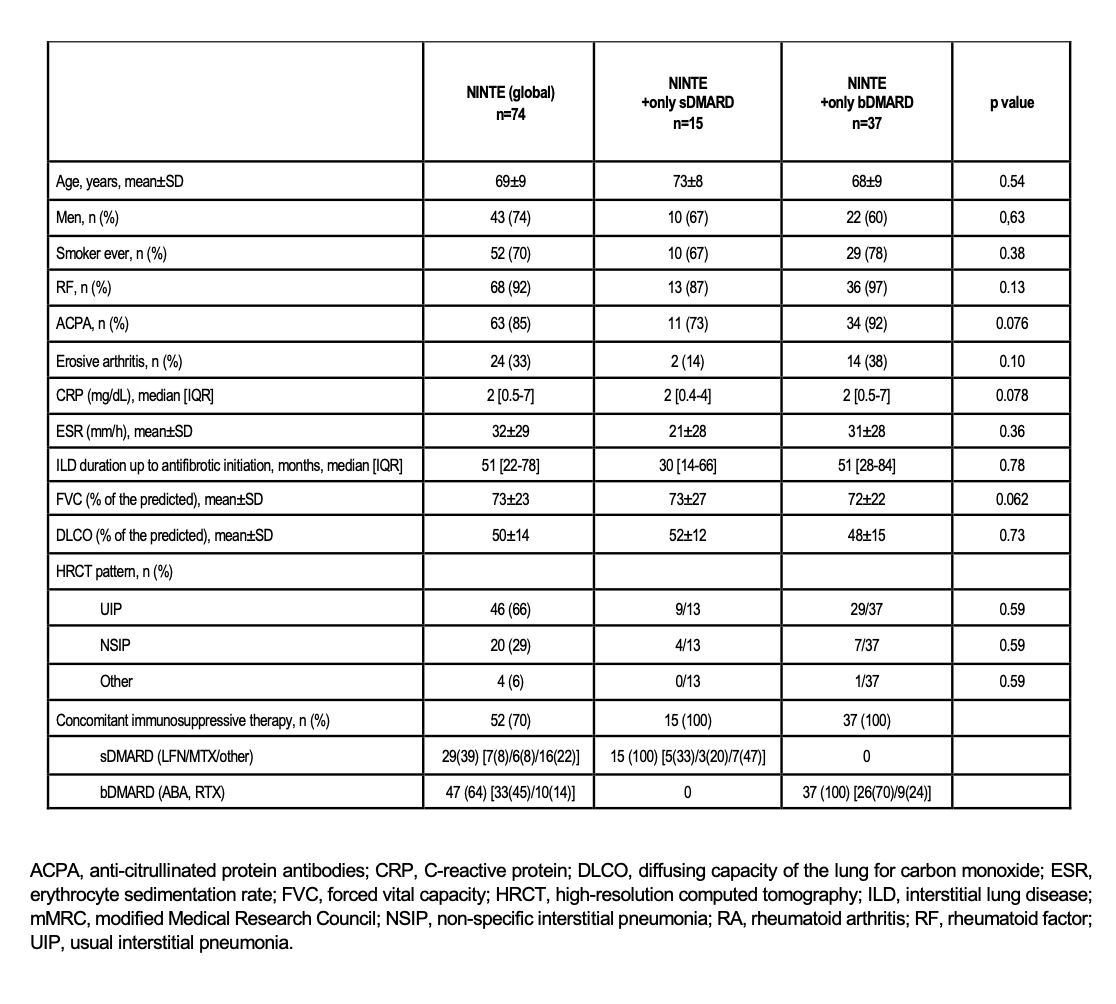 Table. Main general clinical features of RA-ILD patients at nintedanib initiation.
Table. Main general clinical features of RA-ILD patients at nintedanib initiation.
.jpg) Figure. Evolution of pulmonary function in 74 patients with RA-ILD according to the combination of nintedanib with only biologic or only synthetic DMARDs.
Figure. Evolution of pulmonary function in 74 patients with RA-ILD according to the combination of nintedanib with only biologic or only synthetic DMARDs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Serrano-Combarro A, Loarce J, Atienza-mateo B, Vegas Revenga N, Martín López M, Castañeda S, Melero-González R, Mena Vázquez N, Carrasco-Cubero C, Diez-Morrondo C, Castro-Corredor D, Vazquez Rodriguez T, García-Valle A, Bonilla G, Rodríguez Lopez M, Braña I, Andujar P, Rojas Herrera S, Sarmiento-Monroy J, Ferrer D, Ferraz Amaro I, Blanco R. Effectiveness of Nintedanib combined with different DMARDs in joint and pulmonary domains of Rheumatoid Arthritis – Interstitial Lung Disease. National multicenter study of 74 patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-nintedanib-combined-with-different-dmards-in-joint-and-pulmonary-domains-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-interstitial-lung-disease-national-multicenter-study-of-74-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-nintedanib-combined-with-different-dmards-in-joint-and-pulmonary-domains-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-interstitial-lung-disease-national-multicenter-study-of-74-patients/
