Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Adequate immunization is essential for patients with inflammatory rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (iRMD). Autoimmunity itself and immunotherapy increase the risk of infection independent of each other. In Germany, the Standing Committee on Vaccination recommends influenza and pneumococcal vaccine for all patients above the age of 60 and for all iRMD patients above the age of 50. However, many data suggest that this vulnerable group is not sufficiently vaccinated. To explore barriers and facilitators to influenza and pneumococcal vaccine uptake in immunosuppressed adults with iRMDs.
Methods: Using claims data of a German statutory health insurance, the “VAC-MAC” – VACcination of MS/Arthritis/Colitis Patients´ project analysed vaccine uptake in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) and systemic lupus erythematous (SLE). Quantitative analyses were based on approximately 9 million individuals in Germany insured from 2013-2021. Determinants of vaccine uptake were analyzed based on insurance data of 2019 with univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis. The analysis includes both the overall patient cohort and a subset of newly vaccinated iRMD patients, defined as those who were unvaccinated for three or more consecutive seasons and received the influenza vaccine between Q3 2019 and Q2 2020. Additionally, semi-structured interviews with trained qualitative researcher were performed in 2023 with in total 30 patients, rheumatologist, and primary care physicians.
Results: We identified 229.913 patients (73% female, mean age 66±15 years) in 2019. The rate of influenza vaccination with 31% was moderate for the total iRMD group but higher with 41,.6% in the group ≥ 50 years of age and substantially higher with 47% in the group ≥ 60 years of age. The rate of pneumococcal vaccine was low with 6.0% in the total iRMD group with an insignificant increase to 6.8% in the group ≥ 50 years of age and to 8.2% in the group ≥ 60 years of age. Older age, more frequent physicians´ visits, higher number of comorbidities, health care provided by vaccination-oriented physicians and residence in the former East German states, were associated with a higher vaccination rate (figure 1). The following barriers to vaccination were identified in the qualitative survey: 1) concerns about side effects including experience of flares, 2) negative vaccination experiences, 3) insufficient medical information and proactive discussion about the need for vaccination, 4) too little or complicated information material, 5) gaps in knowledge about immunomodulation and vaccination recommendations for patients with autoimmune diseases, and 6) unclear roles and too little communication between treating rheumatologist and general practitioners.
Conclusion: Although influenza vaccination is recommended of all iRMD patients, a German health insurance dataset shows an influenza vaccination rate of only 37% of all iRMD patients in 2019. There is a substantial gap in quality of care in vaccination against pneumococci. Physicians and patient factors as well as fears and concerns about side effect of patients and physicians can serve as modifiable factors to improve quality of care for iRMD patients.
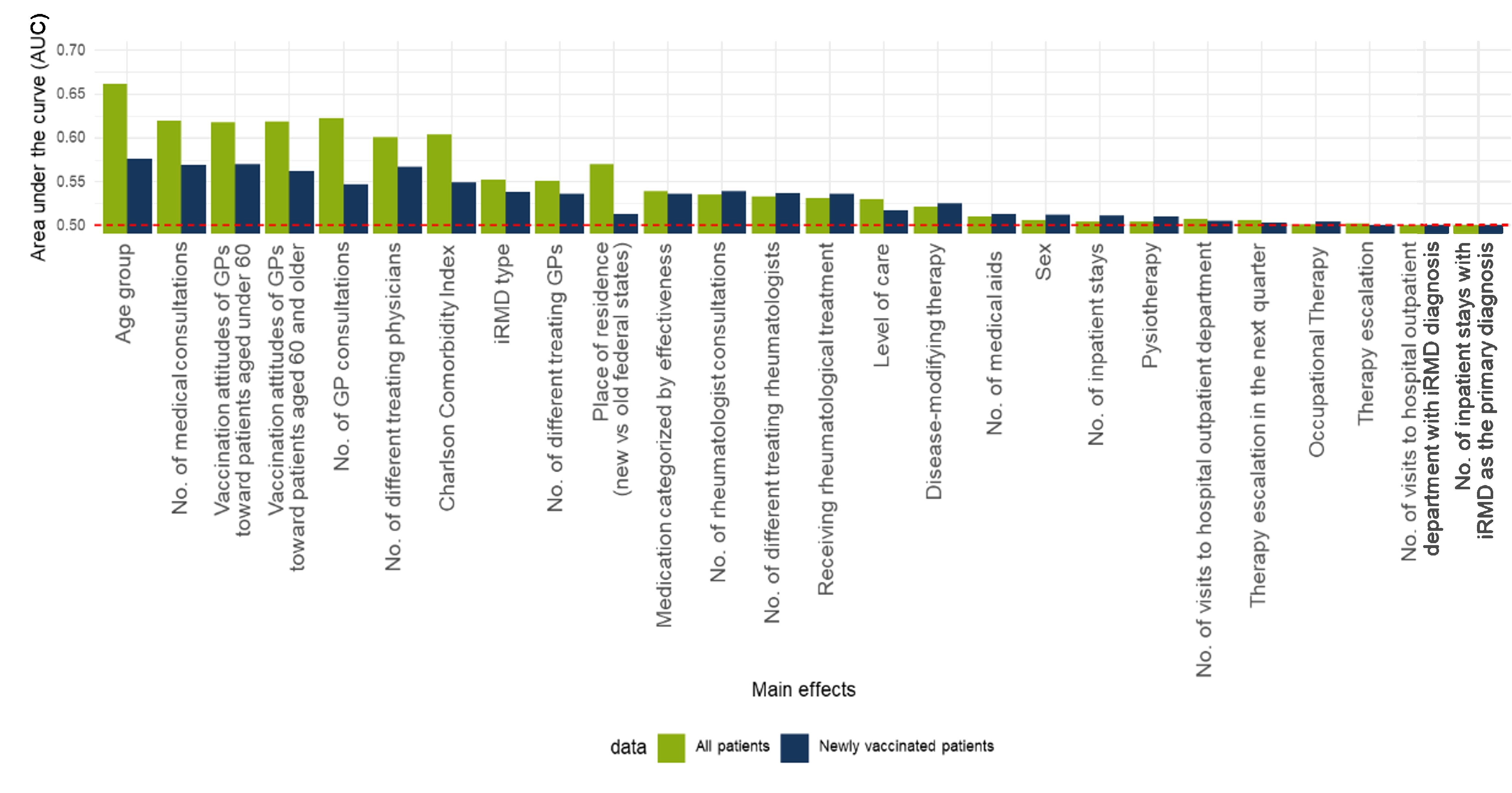 Figure 1: Area under the curve (AUC) of univariate models assessing factors influencing influenza vaccination coverage in patients with iRMD
Figure 1: Area under the curve (AUC) of univariate models assessing factors influencing influenza vaccination coverage in patients with iRMD
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zacharopoulou M, Grüter t, van de Sand H, Lauer R, Tokic M, Basten J, Denz R, Suslow A, Stallmach A, Franz A, Oganowski T, Otte I, Meyer I, Vollmar H, Timmesfeld N, Marschall U, Saam J, Hellwig K, Kiltz U. Analysis of the Determinants of Vaccine Acceptance and Hesitancy in Germany: A Mixed-Methods Approach Incorporating Health Insurance Data and Qualitative Interviews with Patients and Physicians [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-the-determinants-of-vaccine-acceptance-and-hesitancy-in-germany-a-mixed-methods-approach-incorporating-health-insurance-data-and-qualitative-interviews-with-patients-and-physicians/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-the-determinants-of-vaccine-acceptance-and-hesitancy-in-germany-a-mixed-methods-approach-incorporating-health-insurance-data-and-qualitative-interviews-with-patients-and-physicians/
