Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) and giant cell arteritis (GCA) are systemic inflammatory conditions which predominantly affect individuals over the age of 50 years. The conditions share overlapping clinical features1,2 and can significantly impact patients’ quality of life. The main symptoms of PMR include pain and stiffness in the shoulder, neck, and hips1; whereas patients with GCA present with headache, scalp tenderness, fever, jaw claudication, as well as aortic aneurysm, aortitis and visual disturbances2,3. Both conditions are associated with significant disease burden, including cardiovascular, cerebrovascular and malignancies for PMR and detrimental effects on vision for GCA1,2. This real-world cohort study aims to understand the clinical profile and healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) of patients with PMR and GCA in the US.
Methods: Adult patients with a first diagnosis (index date) of PMR or GCA aged ≥50 years during Jan 2017- May 2023 and with at least 1 year of database continuous enrolment pre- and post-index were identified from Optum® Clinformatics Data Mart (CDM) claims. To increase the specificity of the diagnosis, at least two ICD-10 CM codes (PMR: M35.3 – GCA: M31.6) recorded 7-30 days apart were required. Patients were also required to have ≥2 outpatient prescriptions of oral glucocorticoids within six months post-index. The total number of patients, and the distribution by age, sex, comorbidities, as well as HCRU during follow-up were reported. Patients were followed from index to earliest of death, end of insurance or study period (5/31/2024).
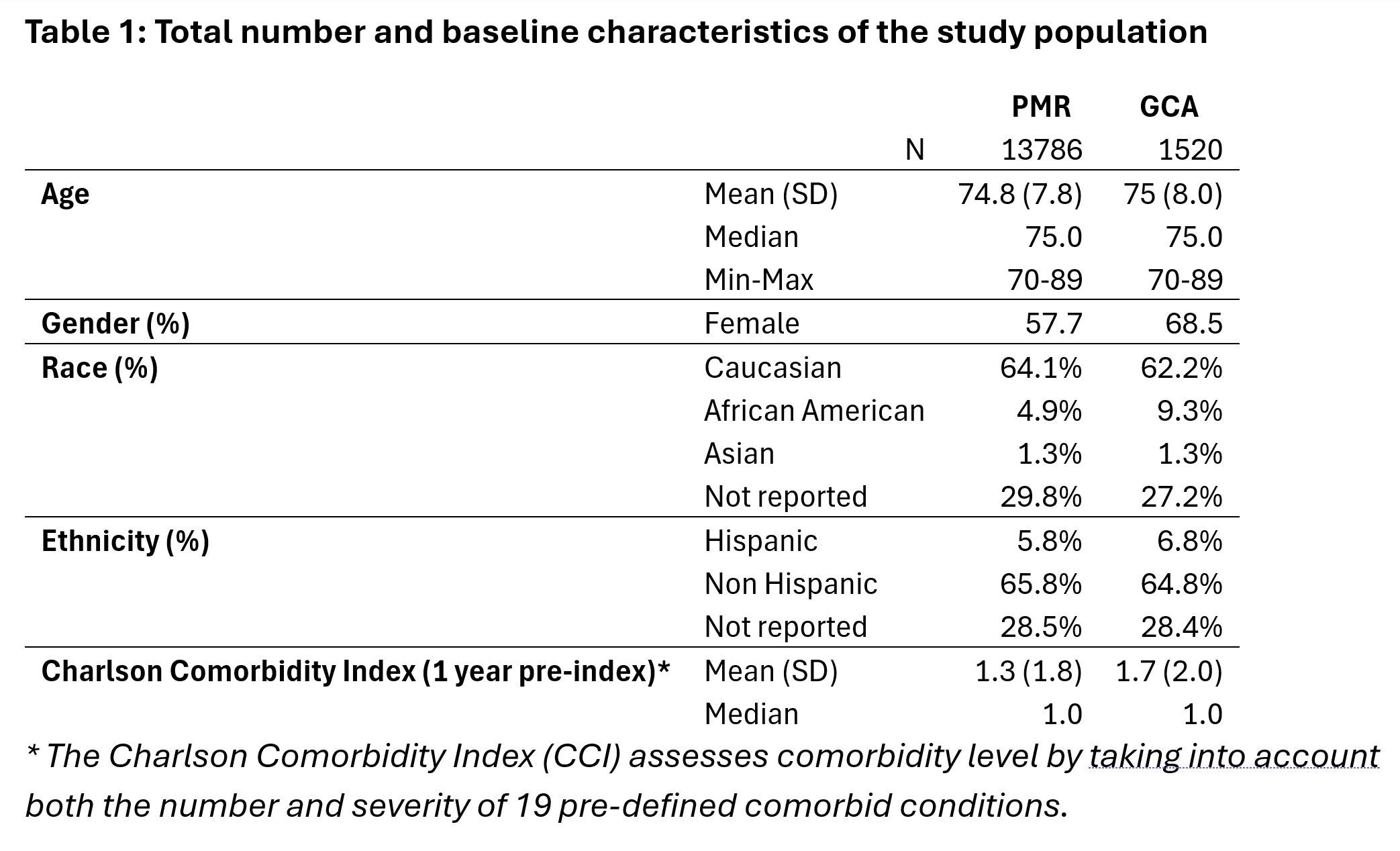
Results: A total of 13,786 patients newly diagnosed with PMR and 1,520 patients with GCA were included in the study population (Table 1). Mean age (SD) was 74.8 (7.8) years for PMR and 75.0 (8.0) years for GCA. Women represented 57.7% and 68.5% of the PMR and GCA patients, respectively. The mean Charlson Comorbidity Index was slightly higher for GCA (1.7) vs. PMR (1.3). Prevalence of the top 10 comorbidities at baseline ranged from 22 to 68% (Figure 1). On average, patients with PMR and GCA were followed 3.5 (1.7) and 3.3 (1.7) years, respectively. Inpatient and ER visits were reported for 44.0% and 64.3% of patients with PMR. Higher proportions were observed for GCA patients with 66.3% and 80.1% for inpatient and ER visits, respectively.
Conclusion: In the US, both PMR and GCA predominantly affect elderly female patients. The clinical profile of these patients indicates a considerable burden related to highly prevalent comorbidities including cardiovascular, endocrine and musculoskeletal disorders. This impacts HRCU substantially, highlighting the need for better management strategies to reduce clinical and economic burden among patients with GCA and PMR. 1 Gazitt T, Zisman D, Gardner G. Polymyalgia Rheumatica: a Common Disease in Seniors. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2020;22(8):40. doi:10.1007/s11926-020-00919-22 Mohammad AJ, Englund M, Turesson C, Tomasson G, Merkel PA. Rate of Comorbidities in Giant Cell Arteritis: A Population based Study. J Rheumatol. 2017;44(1):84-90. doi:10.3899/jrheum.1602493 Mahr A, Hachulla E, de Boysson H, et al. Presentation and Real World Management of Giant Cell Arteritis. Front Med. 2021;8. doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.732934
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mouchet J, Nguyen T, Jordan M. V, Ramakrishna G, Grinnell-Merrick L, Heaney A, Mitra Das A, Shah P, Zhuleku E. Clinical profile and healthcare resource utilization of patients diagnosed with giant cell arteritis or polymyalgia rheumatica in the US: a real-world cohort study using a large database of administrative health claims [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-profile-and-healthcare-resource-utilization-of-patients-diagnosed-with-giant-cell-arteritis-or-polymyalgia-rheumatica-in-the-us-a-real-world-cohort-study-using-a-large-database-of-administra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-profile-and-healthcare-resource-utilization-of-patients-diagnosed-with-giant-cell-arteritis-or-polymyalgia-rheumatica-in-the-us-a-real-world-cohort-study-using-a-large-database-of-administra/

.jpg)