Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (1855–1876) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with interstitial lung disease associated to a connective tissue disease (CTD-ILD) are a heterogeneous population both concerning mechanisms and trajectories. In an RNA Seq approach we have previously identified differentially expressed miRNA in patients with CTD-ILD. The current study was conducted to confirm the association of 7 miRNA with CTD-ILD and with disease subgroups.
Methods: The selected miRNA were analysed with qPCR techniques. The study population comprised 110 patients (89% women) and 10 healthy controls (90% women) from the NEREA register of CTD-ILD. Demographics and process-related data were extracted from RedCap files where the register is hosted. Results are shown as mean (SEM) or n (%). Associations were assessed with cross-sectional variables and with 18 month follow-up outcomes. Functional deterioration was defined by a 10% fall in forced vital capacity (FVC). Statistics were done with t test and Spearman’s correlation. Target prediction analysis was carried out with miRPath v4.0 tools.
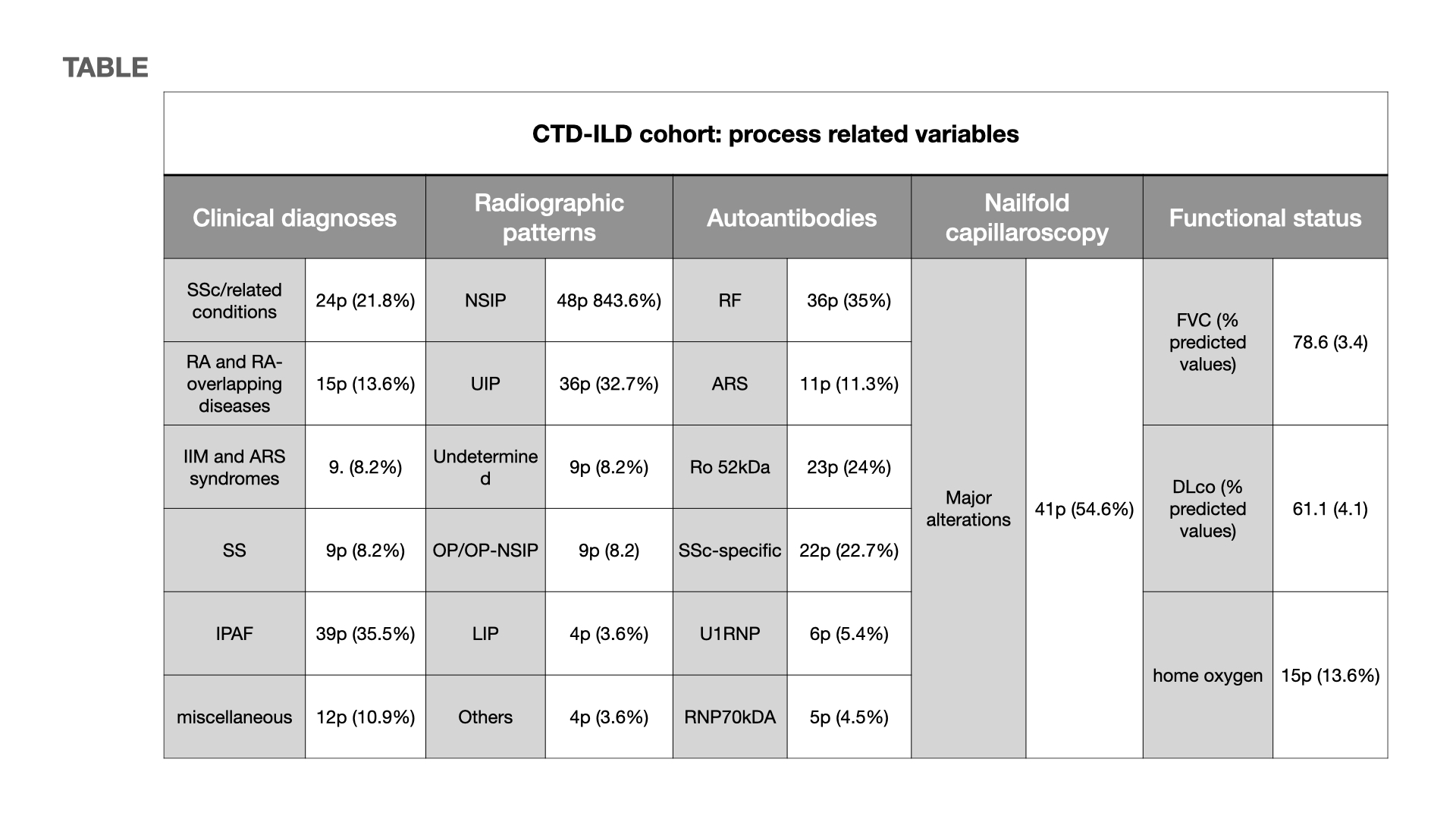
Results: Age was 64.9 (1.1) in the CTD-ILD group and 62.1 (1.2) yrs in healthy controls (ns). Process related variables are shown at the Table. At baseline, disease duration was 4.1 (0.5) yrs. Survival at endpoints was 91%, while functional decline was observed in 24%.As compared to healthy controls, patients with CTD-ILD were identified by higher Let7i-5p (p 0.001) and miR-483-5p (p 0.018), accompanied by lower miR-223-3p (p 0.025).Within the patient cohort, the presence of SSc-related antibodies associated with higher miR-142-5p (p 0.013) and lower miR185-5p (p 0.039). An increase in miR-142-5p levels was also shown in relationship with NVC alterations (p 0.04). Patients with RA had lower levels of miR-320d (p 0.03), while patients with SS had higher Let7i-5p (p 0.043), lower miR-142-5p (p 0.016) and higher miR-185-5p (p 0.025). No specific miRNA profiles differentiated between radiographic patterns, whereas fibrotic disease associated with lower miR-142-5p (p 0.004) and this miRNA levels also dropped in correlation with disease duration (p 0.047).Patients requiring oxygen therapy had lower levels of miR-483-5p (p 0.016), while functional deterioration over time was associated with lower Let7i-5p (p 0.019). Fatal outcomes were marginally associated to lower baseline levels of miR-320d (p 0.065) and of miR-483-5p (p 0.095). Principal differentially regulated molecules in each subgroup and pathways involved are shown in the Figure.
Conclusion: A 3 miRNA signature consisting of high Let7i-5p, high miR-483-5p, low miR-223- 3p defined the CTD-ILD population. According to our data, the up-regulation of Let7i-5p and miR-483-5p might drive an adaptive response to lung injury, whose loss parallels functional deterioration. On the other hand, patients with vasculopathy showed a distinc profile characterized by an increase in miR-142-5p. The latter miRNA could also have a regulatory role, since its levels descended in fibrotic disease and in advanced stages.On the whole, our results unveil both process-dependent and shared mechanisms in CTD-ILD processes of interest in the design of therapeutic strategies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sanchez Pernaute O, Rodriguez-Nieto M, Vadillo Font C, Nieto M, Cebrian L, Lopez Muñiz B, Godoy Tundidor H, Laporta R, Loarce Martos J, A Rigual J, Romero-Bueno f, Llorente Cubas I, Valenzuela C, Bonilla G, Gomez Carrera L, Garcia Vicuña R, Jaureguizar A, Morell Hita J, Abasolo Alcazar l. A miRNA signature consisting of high Let7i-5p, high miR-483-5p, low miR-223- 3p characterizes connective tissue diseases with interstitial lung disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-mirna-signature-consisting-of-high-let7i-5p-high-mir-483-5p-low-mir-223-3p-characterizes-connective-tissue-diseases-with-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-mirna-signature-consisting-of-high-let7i-5p-high-mir-483-5p-low-mir-223-3p-characterizes-connective-tissue-diseases-with-interstitial-lung-disease/

.jpg)