Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Sex determinants may play a role in the immunological sexual dimorphism of childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (cSLE). This study aimed to investigate the impact of sex determinants on immune transcriptomic changes and their association with cSLE.
Methods: We performed PBMC RNAseq analysis on post-pubertal cis-female adolescents with cSLE (n=74) and healthy controls (HCs, n=20), as well as transgender adolescents (trans-male, XX TM; trans-female, XY TF, n=32 samples) undergoing gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) across 3 timepoints; pre-treatment, on gonadotrophin-releasing hormone agonist (GnRHa, puberty blocker) and on GAHT, TM on testosterone (T) and TF on oestradiol (E). Rstudio was used to identify the significantly differentially expressed genes (DEGs, DEseq2). Pathway enrichment analysis (PEA), clustering and normalised gene count analysis were conducted with compatible software.
Results: We identified 40 DEGs (fold change >1.5, P < 0.05) in the cis-female cSLE cohort vs. HCs (defining a post-pubertal cSLE signature) that overlapped with the transgender cohort (on GAHT) (Figure 1A). Specifically, in the XY TF group (on E vs. GnRHa), there were 24 upregulated/1 downregulated DEGs, including TLR2 (upregulated, p= 0.0077), and IL1R2 (upregulated, p=0.018), which overlapped with the cSLE signature. Similarly, in the XX TM group (on T vs. GnRHa), there were 6 upregulated/4 downregulated overlapping DEGs, including IL15 (upregulated, p= 0.019). PEA revealed DEGs linked to the inflammatory response processes, cell migration/activation and lipid regulation (Figure 1B). Additionally, we discovered 63 X-linked DEGs (P < 0.05) in the GAHT vs. GnRHa groups across both XX and XY backgrounds, however, these did not overlap with the cSLE signature, suggesting a lesser impact of sex hormones on X-linked transcripts related to cSLE susceptibility. However, the X-linked non-coding RNA X-inactive specific transcript (XIST) and the XIST antisense non-coding RNA TSIX, were both significantly increased in cSLE vs. HCs (p=0.018 and 0.0007). XIST correlated negatively with cSLE interferon scores (P=0.0010, r=-0.38) and X-linked TLR7 expression (P=0.0004, r=-0.40), but TSIX did not, supporting a role for X chromosome inactivation in controlling the pathogenic mechanisms associated with cSLE in females.
Conclusion: This analysis demonstrated unique inflammatory transcriptomic changes (DEGs) induced by GAHT in transgender adolescents, which overlapped with cis-female cSLE adolescents, as well as sex hormone-independent associations between XIST expression and inflammatory cSLE pathogenic mechanisms. To our knowledge, this is the first exploration of the impact of sex hormones disaggregated from their corresponding sex chromosomal background in driving transcriptomic changes potentially relevant for understanding female cSLE pathogenesis.
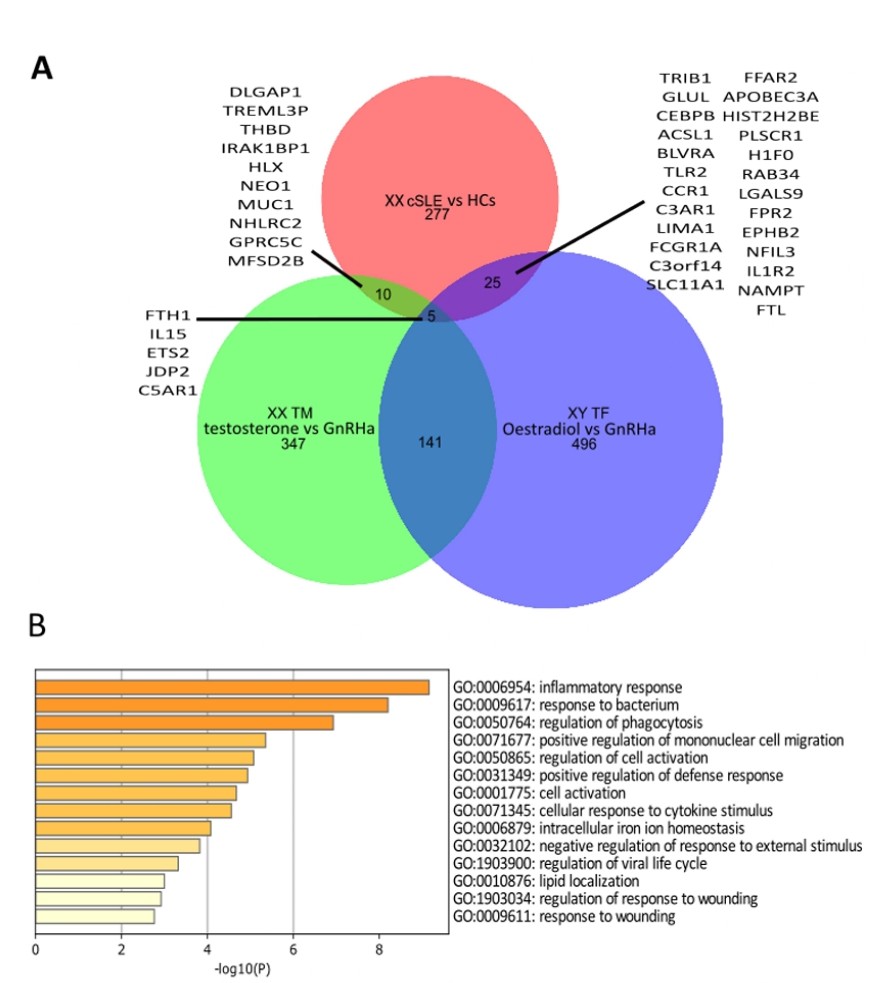 Figure 1. A. Venn diagram showing DEGs shared between cSLE cohort vs. age matched healthy controls (HCs) and transgender cohort for each distinct sex chromosomal background, comparing the effect of GAHT (XX TM receiving testosterone vs. VY TF receiving estrogen) vs. GnRHa (P < 0.05). B. Pathway enriching analysis of the overlapping 40 DEGs between the cSLE cohort vs. HCs vs. transgender cohort, indicating the inflammatory response as being the most enriched.
Figure 1. A. Venn diagram showing DEGs shared between cSLE cohort vs. age matched healthy controls (HCs) and transgender cohort for each distinct sex chromosomal background, comparing the effect of GAHT (XX TM receiving testosterone vs. VY TF receiving estrogen) vs. GnRHa (P < 0.05). B. Pathway enriching analysis of the overlapping 40 DEGs between the cSLE cohort vs. HCs vs. transgender cohort, indicating the inflammatory response as being the most enriched.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cross H, Peckham H, Butler G, Rosser E, C Jury E, Robinson G, Ciurtin C. Sex-specific mechanisms associated with female childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus revealed by transcriptomic analysis of transgender adolescents undergoing gender-affirming sex hormone therapy. [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sex-specific-mechanisms-associated-with-female-childhood-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-revealed-by-transcriptomic-analysis-of-transgender-adolescents-undergoing-gender-affirming-sex-hormone-thera/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sex-specific-mechanisms-associated-with-female-childhood-onset-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-revealed-by-transcriptomic-analysis-of-transgender-adolescents-undergoing-gender-affirming-sex-hormone-thera/
