Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:30PM-3:45PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disease that affects both the skin and musculoskeletal system and is frequently associated with a heightened burden of cardiometabolic comorbidities, including hypertension (HTN), obesity, and type 2 diabetes (DM2). These conditions contribute to elevated morbidity and mortality. Despite growing awareness, management of systemic inflammation and comorbid risk factors remains suboptimal in routine care. Multi-disciplinary, integrated centers that co-locate rheumatology, dermatology, cardiology and allied specialties offer a promising approach to comprehensive, disease-targeted care. However, real-world data supporting their effectiveness in mitigating systemic burden remain limited. We aimed to evaluate whether patients with PsA seen under optimized care—the NYU Psoriatic Arthritis Center (PAC)—demonstrate improved health profiles compared to those receiving standard specialty care at the same institution.
Methods: Using the electronic medical record (EMR) system at NYU Langone Health (Epic), we identified patients with ICD-10 codes for psoriasis or PsA from 2012 to 2024. Patients with both diagnoses were classified as PsA. PsA patients were further categorized into those seen at the NYU PAC (PAC group) versus those seen exclusively outside the PAC (non-PAC group). For all groups, comorbidities were extracted using ICD-10 codes, and laboratory markers of systemic inflammation (CRP, ESR) were obtained. Comparisons of comorbidity prevalence and laboratory values were performed using Mann-Whitney U tests and mixed linear regression, adjusting for age. False discovery rate (FDR) correction was applied using the Benjamini-Hochberg method.
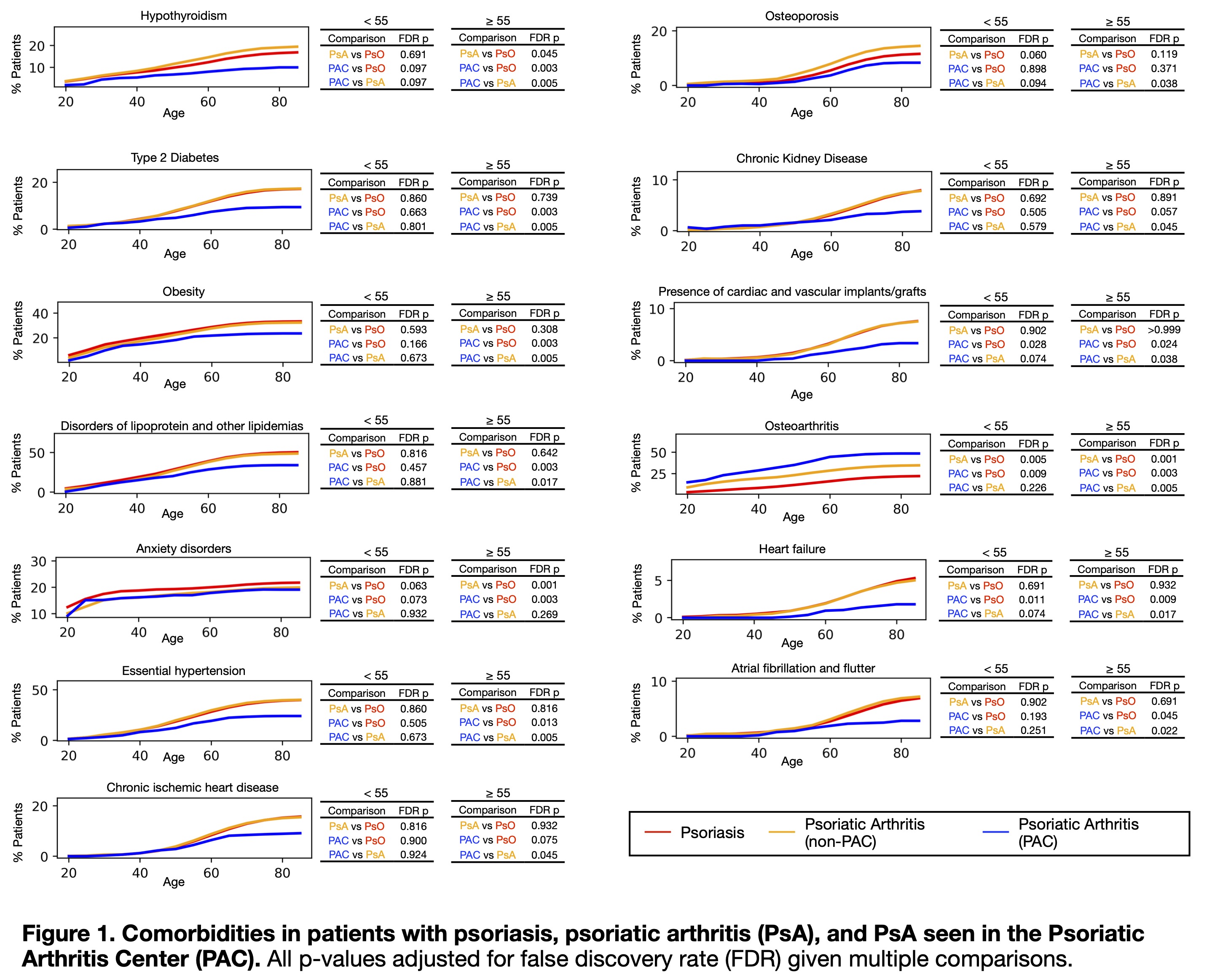
Results: 890 PAC patients, 12,079 non-PAC PsA patients, and 28,393 patients with only skin psoriasis were identified. PAC and non-PAC patients had similar rates of comorbidities prior to the age of 55 (Figure 1). Among those ≥55 years old, PAC patients had significantly lower rates of key cardiometabolic conditions compared to non-PAC PsA patients, including DM2, obesity, HTN, ischemic heart disease, atrial fibrillation, and chronic kidney disease (all FDR-adjusted p< 0.05). Inflammatory markers were also significantly lower in PAC patients (ESR p< 0.001; CRP p=0.026, Figure 2). Rates of osteoarthritis were higher in PAC patients (p=0.005), possibly reflecting more active musculoskeletal screening. Of interest, both PAC and non-PAC PsA patients had lower anxiety and systemic inflammation compared to patients with psoriasis alone or other autoimmune diseases.
Conclusion: In this large EMR-based study, patients with PsA receiving care at a dedicated, multi-disciplinary, specialized center had a significantly reduced burden of cardiometabolic comorbidities and inflammation, particularly in older adults. While validation of these observations is warranted in other combined clinics (i.e., PPACMAN dual-care facilities), our findings highlight the potential of integrated psoriatic disease care models to modify systemic disease expression, decrease the deleterious effects of metabolic and cardiovascular comorbidities and improve overall long-term outcomes in PsA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Haberman R, Coudray N, Han X, Grams M, Oermann E, Tsirigos A, Scher J. Reduced Cardiometabolic Burden and Inflammation in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Cared for in a Multi-Disciplinary, Combined Psoriasis-Psoriatic Arthritis Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reduced-cardiometabolic-burden-and-inflammation-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-cared-for-in-a-multi-disciplinary-combined-psoriasis-psoriatic-arthritis-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reduced-cardiometabolic-burden-and-inflammation-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-cared-for-in-a-multi-disciplinary-combined-psoriasis-psoriatic-arthritis-center/

.jpg)