Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1612–1632) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The therapeutic landscape of giant cell arteritis (GCA) is growing rapidly but there are currently no internationally standardized criteria for assessing response to treatment in GCA. To address this issue, there is an ongoing project to develop response criteria for GCA, supported by European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) and the American College of Rheumatology (ACR). Following a systematic literature review (SLR), a Delphi exercise was conducted to determine items that might be included in the future response criteria. The goal of this Delphi exercise was to identify the most important and relevant items to consider when developing criteria to measure response to treatment in GCA.
Methods: A four-round web-based Delphi exercise was conducted. Participants from 38 countries included patients with GCA and physicians with expertise in GCA. They rated the importance (1=lowest, 9=highest) of 51 items from a prior SLR, grouped into six domains, and suggested additional items. Items obtaining a score of 7-9 by at least 70% of physicians and 70% of patients were considered critically important and to have reached consensus for inclusion. Items which scored 1-3 by 70% of physicians and patients were considered not important and excluded from subsequent rounds. In a 4th round of the Delphi (ranking round), participants selected and ranked the 10 most relevant items from those deemed most important in the previous three rounds. A task force (n=32 members) meeting followed to review the Delphi results, discuss rankings, and finalize the selection of items.
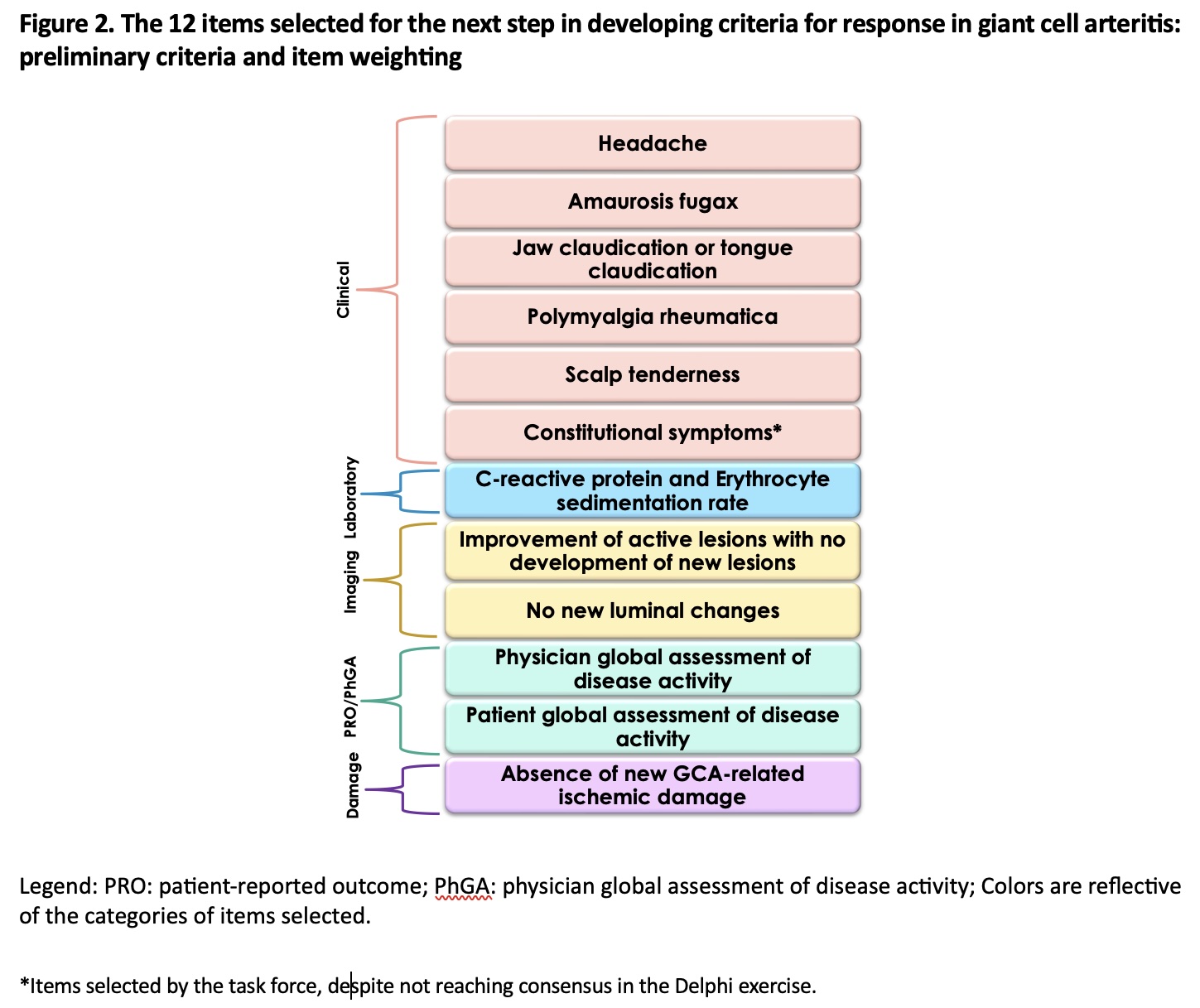
Results: A total of 187 physicians and 85 patients participated in the Delphi exercise. Thirteen new items were proposed in round 1. Twenty-four items were rated as critically important (18 in round 1, 5 in round 2, 1 in round 3) by ≥70% of patients and ≥70% of physicians (Figure 1). These items covered the six domains of the Delphi (Figure 1): 10 for clinical, 2 for laboratory, 5 for imaging, 3 for treatment, 1 for patient-reported outcomes and 3 for damage. No items were excluded during any round, and consensus was not reached for 40 items. The top three highest-rated items by both patients and physicians were headache (ranked highest by 52% of patients and physicians), amaurosis fugax (ranked highest by 10%), and jaw claudication (ranked highest by 7%).Of the task force members, 24/32 (75%) participated in the virtual task force meeting. Among the items discussed by the task force (Figure 1), glucocorticoid-related parameters were excluded as they were considered indirect indicators of response to treatment. Constitutional symptoms were added by the task force as they are important constellation of symptoms seen in GCA. The task force also decided to cluster items with similar constructs to capture the spectrum of the disease more concisely. 12 items were selected for the next phase of the project (Figure 2).
Conclusion: This Delphi exercise identified a set of 12 items within 6 domains as being relevant towards measuring response in GCA. These 12 items will be used in a subsequent group conjoint analysis to further prioritize and weigh potential items for inclusion in a draft set of criteria to measure treatment response in GCA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Soowamber M, Bond M, Sanchez Alvarez C, Langford C, Aydin S, BUTTGEREIT F, Camellino D, Cid M, Grayson P, Hellmich B, Kermani T, Khalidi N, Mackie S, Mahr A, Matteson E, Maz M, Merkel P, Monach P, Neill L, Ponte C, Salvarani C, Schmidt W, Villiger P, Warrington K, Dejaco C, Ramiro S, Touma Z. A Delphi Exercise Informing the Development of Criteria to Measure Response to Treatment in Giant Cell Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-delphi-exercise-informing-the-development-of-criteria-to-measure-response-to-treatment-in-giant-cell-arteritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-delphi-exercise-informing-the-development-of-criteria-to-measure-response-to-treatment-in-giant-cell-arteritis/

.jpg)