Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rituximab (RTX) has been shown to achieve high remission-induction and sustained maintenance rates across multiple studies and clinical trials in patients with AAV. The optimal dose and duration of rituximab for maintenance of remission in ANCA vasculitis (AAV) remains a matter of debate. In this interim analysis of an ongoing study, we aimed to compare the relapse rate, B cell depletion rate and hypogammaglobulinemia after receiving fixed protocol ultra-low dose (200mg, ULD biannually) and low dose (500mg, LD biannually) rituximab for maintenance of remission in patients with AAV.
Methods: Patients satisfying ACR / EULAR criteria for either Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) or Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA), in complete remission and receiving rituximab maintenance therapy for > 12 months, were recruited across 4 centres in India between 1st April 2023 – 1st February 2025. Based on the dose of maintenance rituximab used as per physician’s discretion, the patients were subdivided into either LD or ULD group. Details of clinical presentation, disease activity as assessed by BVASvs3 and laboratory investigations were collected prospectively at recruitment (T0), 3 monthly follow up until the last follow up visit or relapse whichever occurred earlier. Remission was defined as Birmingham Vasculitis activity score (new/worsening) (BVAS) = 0 while relapses were defined as (BVAS) ≥ 1.
Results: Among 35 patients (GPA= 30, MPA = 5) recruited, 18 and 17 patients received ULD and LD maintenance rituximab respectively. The clinical details at diagnosis and T0 visits are depicted in (Table-1). All the parameters at diagnosis except age and disease duration were similar in both groups (Table-1). During median follow-up of 12 (IQR 9-15) months (Figure 1), 1 patient given LD rituximab had major flare with renal involvement (BVAS=11) at 6 months while another 1 patient developed sepsis at 15 months follow up and died. Among patients receiving ULD rituximab, one developed exacerbation of colitis and succumbed. None of the patients in either group developed hypogammaglobulinemia during follow up. The CD19 B cell count, and IgG levels at the last visit did not differ significantly between LD and ULD group.
Conclusion: In this proof-of-concept study, frequency of relapse, mortality, B cell depletion and adverse events were comparable between both LD and ULD rituximab group.
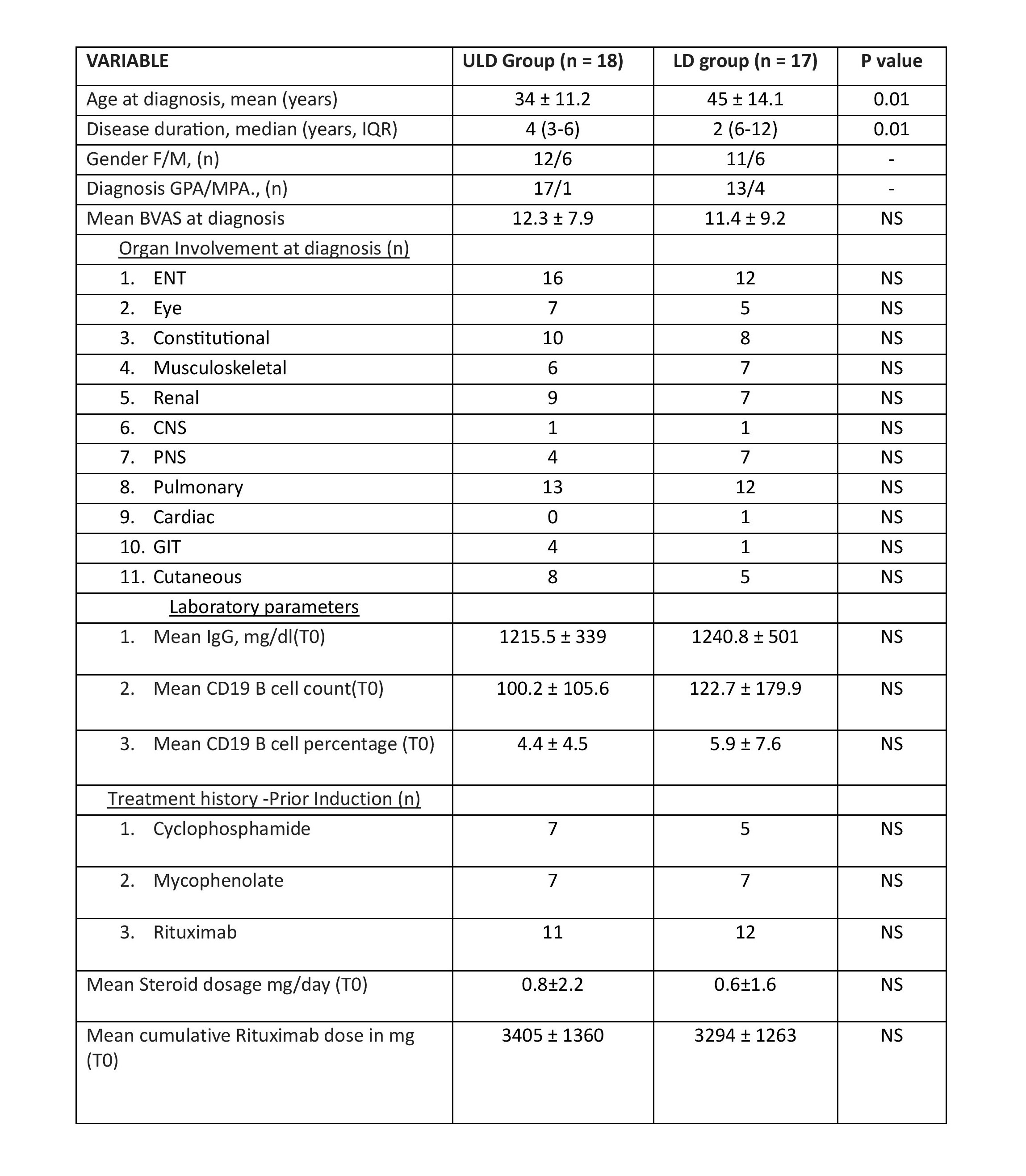 Table-1: Baseline clinical and laboratory details of the patients with AAV treated with ULD and LD maintenance rituximab, *NS-Not significant
Table-1: Baseline clinical and laboratory details of the patients with AAV treated with ULD and LD maintenance rituximab, *NS-Not significant
.jpg) Figure-1: Flow chart depicting outcomes of patients with AAV treated with ULD and LD maintenance rituximab
Figure-1: Flow chart depicting outcomes of patients with AAV treated with ULD and LD maintenance rituximab
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kumar U R, Chitrabhanu A, Janardana R, Jain A, Mathews N, Dave R, Vasantha Kumar P, mathew a, mathew j, Samuel P, Rajamurugan A, Shobha V, goel r. A Multicenter Prospective Longitudinal Observational Study To Determine Safety Of Extended Treatment With Rituximab In Maintaining Remission In Patients With ANCA Associated Vasculitis (AAV) – An Interim Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-multicenter-prospective-longitudinal-observational-study-to-determine-safety-of-extended-treatment-with-rituximab-in-maintaining-remission-in-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis-aav-an-inte/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-multicenter-prospective-longitudinal-observational-study-to-determine-safety-of-extended-treatment-with-rituximab-in-maintaining-remission-in-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis-aav-an-inte/
