Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1553–1591) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a severe autoimmune disease with limited treatments. While anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy shows promise, its use is limited by cost and complexity. Blinatumomab, a bispecific T-cell engager targeting CD3 and CD19, may offer a simpler and more affordable alternative and may be effective in severe SSc. We aim to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of blinatumomab in managing severe refractory systemic sclerosis in real-world settings.
Methods: Patients with severe, refractory, Scl70-positive SSc were considered for treatment with blinatumomab following a multidisciplinary review to validate its off-label use. Informed, written consent was obtained from patients to participate in a translational study evaluating the impact of blinatumomab on their immune system. The treatment protocol included premedication with hydrocortisone (100 mg), acetaminophen (1 g), and dexchlorpheniramine (5 mg), followed by continuous intravenous infusion of blinatumomab at 9 µg/day for 7 days, then 28 µg/day for another 7 days. Patients were closely monitored in a hospital setting throughout the intravenous treatment phase and then followed ambulatorily.
Results: Five patients from three different departments were included in the study: four women (P1, P2, P3,P4) and one man (P5) of median age 64 (IQR : 61-65) years. All patients had recent (≤6 years) and progressive Scl70-positive SSc that was refractory to a median of four immunosuppressive therapies (3-8), including autologous stem cell transplantation for P2. The median modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS) was 16 (15-23). All patients had fibrosing interstitial lung disease; four had cardiac fibrosis and one had pulmonary hypertension.At the time of submission, all patients had received the complete treatment.. During infusion, 4 patients developped a grade 1 cytokine release syndrome (isolated fever) treated with acetaminophen, and one a grade 2 (fever and transient hypotension) that was treated with acetaminophen and fluids without need for tocilizumab. No Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS) was observed. All patient completed month 1 of follow-up, two completed month 3 and one month 6. Peripheral B-cell depletion was complete by day 3, persisted until day 14, and B cell repopulation was seen at month 1 (Fig. 1A). Despite a small decrease in total IgG, all patients remained above the lower limit (Fig. 1B). There was no impact on post-vaccination serologies, and no severe infections during follow-up was identified.Clinically, a notable decrease in mRSS was observed in the two patients who completed the 3-month follow-up (Fig. 2A). While antinuclear and anti-Scl70 antibodies remained unchanged post-treatment, there was a marked reduction in the type I interferon signature. Pulmonary function, as indicated by lung volumes (e.g., forced vital capacity), showed significant improvement after treatment (Fig. 2B). B-cell receptor (BCR) sequencing is currently underway.
Conclusion: This real-world study indicates that blinatumomab is safe for use in systemic sclerosis and may lead to clinically significant improvements, including benefits for skin and lung manifestations.
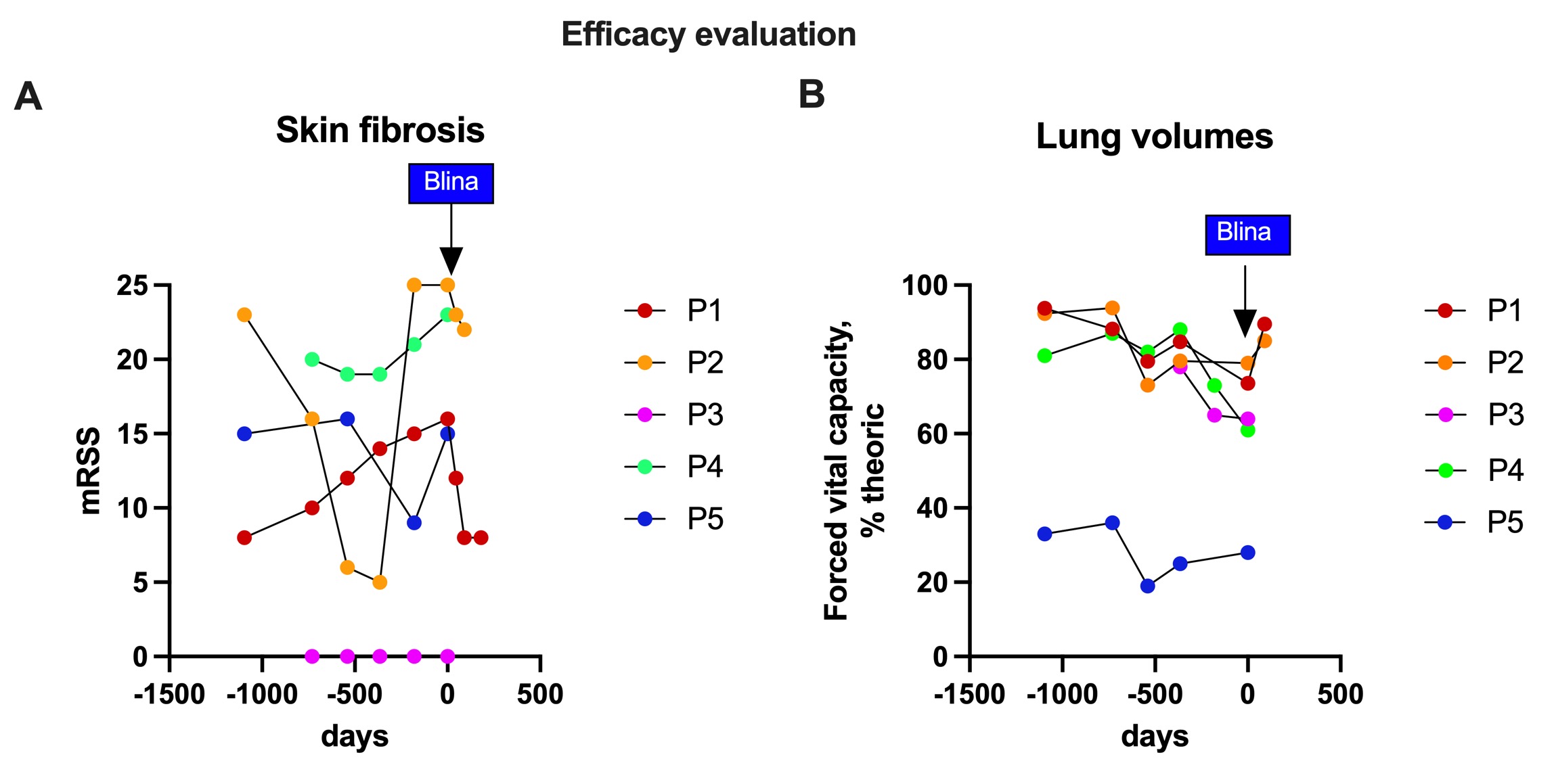 Figure 1: Safety evaluation after blinatumomab treatment. (A) Peripheral CD19+ B cells, (B) total immunoglobulin levels.
Figure 1: Safety evaluation after blinatumomab treatment. (A) Peripheral CD19+ B cells, (B) total immunoglobulin levels.
.jpg) Figure 2: Efficacy evaluation blinatumomab treatment. (A) modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS), and (B) forced Vital capacity (FVC) expressed in % of the theoric value.
Figure 2: Efficacy evaluation blinatumomab treatment. (A) modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS), and (B) forced Vital capacity (FVC) expressed in % of the theoric value.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Scherlinger M, dieudonne Y, Molto A, Chatelus E, Guffroy a, Martin T, GOTTENBERG J, Simand C, El Aatmani A, Decroocq J, Sebbag E, Sibilia J, AVOUAC J. Use of the CD19/CD3 T cell engager blinatumomab in refractory diffuse systemic sclerosis : a case series [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/use-of-the-cd19-cd3-t-cell-engager-blinatumomab-in-refractory-diffuse-systemic-sclerosis-a-case-series/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/use-of-the-cd19-cd3-t-cell-engager-blinatumomab-in-refractory-diffuse-systemic-sclerosis-a-case-series/
