Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1517–1552) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: An integrated post hoc analysis of five Phase 3 trials in adults with SLE showed greater benefit of belimumab (BEL) than placebo (PBO), plus standard therapy (ST), in attaining Definition of Remission In SLE (DORIS) and Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS).1 As these trials were conducted before glucocorticoid (GC) tapering recommendations were introduced,2 tapering was not mandated, resulting in prolonged GC courses in a large proportion of patients (pts), impacting attainability of DORIS and LLDAS.1 Assessed here was attainment of DORIS and LLDAS in these trials using definitions excluding the GC requirement (non-GC-DORIS and non-GC-LLDAS).
Methods: This post hoc analysis pooled data for adults with active SLE from five trials (BLISS-76 [GSK Study 110751; NCT00410384], BLISS-52 [110752; NCT00424476], North East Asia [113750; NCT01345253], BLISS-SC [112341; NCT01484496], EMBRACE [115471; NCT01632241]) receiving BEL (10 mg/kg/month IV or 200 mg/week [wk] subcutaneous) or PBO, plus ST. Non-GC-DORIS and non-GC-LLDAS (defined in Figure 1) attainment rates were calculated and compared between BEL and PBO using modified Poisson regression adjusted for trial variance in all pts and subgroups based on baseline/pt characteristics (SLEDAI-2K score, anti-dsDNA positivity, complement levels, GC dose, antimalarial use, race).
Results: Included were 1869 BEL and 1217 PBO pts. At Wk 52, non-GC-DORIS and non-GC-LLDAS attainment rates were higher with BEL versus PBO (Figure 1). Significance maintained to Wk 52 was reached by Wk 20 for non-GC-DORIS and Wk 24 for non-GC-LLDAS. At Wk 52, significantly greater proportions of BEL versus PBO pts were in non-GC-DORIS and non-GC-LLDAS across most subgroups (Figure 2); for baseline SLEDAI-2K score ≥10, maintained from as early as Wk 16 (non-GC-DORIS remission: risk ratio, RR [95% CI]: 1.95 [1.20, 3.16], p=0.009; non-GC-LLDAS: 1.54 [1.17, 2.02], p=0.003). At Wk 52, non-GC-DORIS and non-GC-LLDAS attainment rates were higher with BEL versus PBO for Asian (BEL n=698, PBO n=405; non-GC-DORIS: RR [95% CI]: 1.60 [1.13, 2.27], p=0.013; non-GC-LLDAS: 1.59 [1.25, 2.02], p=0.001) and White pts (n=596, n=436; 1.66 [1.23, 2.25], p=0.002; 1.76 [1.42, 2.19], p < 0.001); numerical differences were seen for pts of Black African ancestry (n=403, n=229; 1.13 [0.76, 1.69], p=0.577; 1.14 [0.86, 1.51]; p=0.438) and Indigenous American pts (n=172, n=147; 1.17 [0.80, 1.71], p=0.496; 1.35 [1.00, 1.82], p=0.117).
Conclusion: When analyzing data from past trials, it is key to consider context, timing, and effects of confounding factors. GC taper was not mandated in the BEL trial protocols and was not part of the assessment of BEL benefit. In this analysis, BEL was associated with higher attainment of both DORIS and LLDAS versus PBO in all pts and most subgroups. Attainment rates were ~2-fold higher than reported with full DORIS and LLDAS definitions.1 This analysis corroborates benefits of BEL over PBO, plus ST, in inducing remission and low disease activity in pts with SLE. Funding: GSK; Parodis research group References1Parodis I et al. Lancet Rheumatol 2024;6:E751–612Bertsias G, Yazdany J. Lancet Rheumatol 2024;6:E734–5Original presentation: EULAR 2025
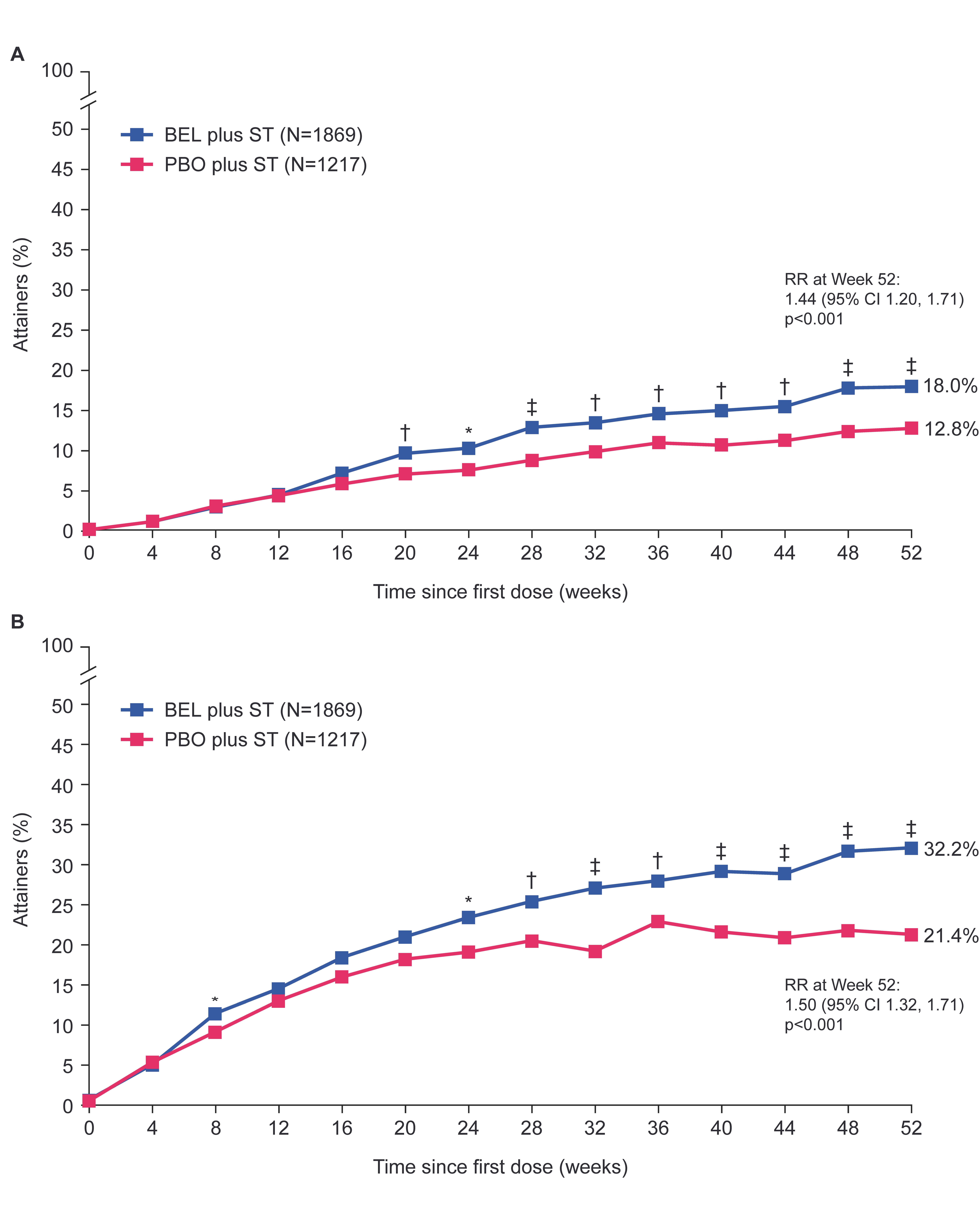 Figure 1. Attainment of (A) non-GC-DORIS and (B) non-GC-LLDAS up to Wk 52 in the overall population.
Figure 1. Attainment of (A) non-GC-DORIS and (B) non-GC-LLDAS up to Wk 52 in the overall population.
*p < 0.05; †p < 0.01; ‡p < 0.001.
Non-GC-DORIS: clinical SLEDAI=0 (irrespective of serological activity), PGA < 0.5.
Non-GC-LLDAS: SLEDAI-2K ≤4 with no activity in major organ systems (renal, central nervous system, cardiopulmonary, vasculitis, fever), no hemolytic anemia or gastrointestinal activity, and no new features of SLE disease activity (using SLEDAI-2K) compared with the previous assessment, PGA ≤1.
PGA, Physician’s Global assessment.
.jpg) Figure 2. Attainment of (A) non-GC-DORIS and (B) non-GC-LLDAS at Wk 52 in pt subgroups defined by baseline characteristics.
Figure 2. Attainment of (A) non-GC-DORIS and (B) non-GC-LLDAS at Wk 52 in pt subgroups defined by baseline characteristics.
C, complement component.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Parodis I, Lindblom J, Levy R, Tsoi A, Zen M, Nikolopoulos D, Khamashta M, Tomlinson R, Askanase A, van Vollenhoven R, Nikpour M. Achieving Remission and Low Disease Activity with Belimumab Versus Placebo in Patients with SLE Excluding the Glucocorticoid Component from Target Definitions: A Post Hoc Analysis of Five Phase 3 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achieving-remission-and-low-disease-activity-with-belimumab-versus-placebo-in-patients-with-sle-excluding-the-glucocorticoid-component-from-target-definitions-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-five-phase-3-tria/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achieving-remission-and-low-disease-activity-with-belimumab-versus-placebo-in-patients-with-sle-excluding-the-glucocorticoid-component-from-target-definitions-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-five-phase-3-tria/
