Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Among the estimated 8.3 million adults in the US with gout, approximately 40% have coexistent chronic kidney disease (CKD).1,2 Further, the presence of gout in CKD appears to confer an increased risk for progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD).3 Thus, patients often proceed to dialysis with chronic gout, and some suffer from severe tophaceous gout. There has been little detailed study of the use of urate-lowering medications in the hemodialysis (HD) population. Pegloticase, a recombinant uricase conjugated to PEG, acts by converting urate to a soluble product (allantoin) that is readily excreted. Pegloticase is reserved for patients with chronic gout who are refractory to current oral urate-lowering treatments and does not require dose adjustment based on renal function. Here we present results from a Phase 1 pharmacokinetic (PK) / pharmacodynamic study of single-dose pegloticase in patients undergoing HD.
Methods: A single intravenous dose of pegloticase (8 mg) was administered over a 2-hour period to male or female (age 18-75 years) HD patients without gout (N=12), 3 hours prior to the Day 1 dialysis session; a second dialysis session was monitored on Day 4. Patients received prophylactic antihistamine and corticosteroid prior to pegloticase infusion. Blood samples were drawn predialysis and hourly over 4 hours postdialysis during the Day 1 and Day 4 sessions. The limit of detection for pegloticase was 0.6 μg/mL; all samples below this value were set to zero. Safety assessments included standard vital signs, laboratory testing, and adverse event (AE) determinations.
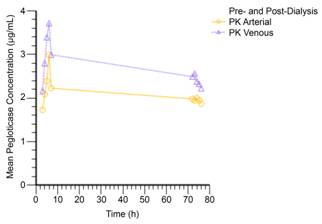
Results: Following a single dose of pegloticase started approximately 3 hours prior to HD, the mean Cmax was 3.27 μg/mL (arterial) and 4.00 μg/mL (venous). Pegloticase AUC3-7h was 9.86 h∙μg/mL (arterial) and 12.91 h∙μg/mL (venous) at the Day 1 dialysis and for the Day 4 dialysis AUC72-76h was 7.93 h∙μg/mL (arterial) and 9.70 h∙μg/mL (venous). Mean arterial and venous pegloticase concentrations during the Day 1 and Day 4 dialysis sessions are shown in the figure. Baseline mean serum uric acid in this non-gout population was 5.98 mg/dL; by 3 hours postinfusion, serum uric acid was undetectable and remained so over the 72-hour sampling period. One patient reported an AE of headache that was possibly related to study drug.
Conclusion: In a small cohort of patients with ESRD and no evidence of gout, pegloticase concentration was not affected by a first HD session and displayed stable decline during a second HD session. Serum uric acid levels in this cohort fell to nondetectable levels 3 hours postinfusion confirming that patients with ESRD can achieve urate-lowering with pegloticase. Data presented here support the use of pegloticase in patients with chronic gout undergoing HD.
References:
1. Fuldeore et al. BMC Nephrol. 2011.
2. Zhu et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2011.
3. Yu et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012.
Disclosure:
A. J. Bleyer,
None;
D. E. Wright,
Savient Pharmaceutical, Inc,
3;
A. Glicklich,
Savient Pharmaceuticals , Inc.,
3.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-pegloticase-in-patients-with-end-stage-renal-failure-receiving-hemodialysis/