Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1434–1466) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Bimekizumab (BKZ) is a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17F in addition to IL-17A. BKZ has shown sustained efficacy to Week (Wk) 52 in patients (pts) with non-radiographic/radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-/r-axSpA) in the BE MOBILE 1 and 2 studies.1,2 Studies have shown male and female pts with axSpA can experience different disease manifestations, clinical burden and treatment efficacy.Here, we assess efficacy of BKZ treatment to Wk52 in pts across the full axSpA disease spectrum, focusing on potential sex-based differences.
Methods: BE MOBILE 1 (NCT03928704) and 2 (NCT03928743) both comprised a 16-wk double-blind and 36-wk maintenance period. Pts were randomized to receive subcutaneous BKZ 160 mg every 4 wks (Q4W) or placebo (PBO); from Wk16, all received BKZ 160 mg Q4W.Outcomes reported to Wk52, stratified by sex, include ASAS40, ASDAS < 2.1, BASDAI, Ankylosing Spondylitis Quality of Life Questionnaire (ASQoL) and objective signs of inflammation (OSI; MRI SPARCC SIJ, MRI Berlin spine and hs-CRP).
Results: 254 pts (M=138, F=116) were randomized in BE MOBILE 1 and 332 pts (M=240, F=92) were randomized in BE MOBILE 2; of these, 220/254 and 298/332 completed to Wk52. Baseline (BL) differences between males and females included longer mean symptom duration (years) in females (nr-axSpA: 7.2 vs 11.1; r-axSpA: 12.9 vs 15.0) and lower HLA-B27 positivity (%) in females (nr-axSpA: 84.8 vs 69.0; r-axSpA: 88.3 vs 78.3). Across BKZ and PBO-randomized pts at BL, males had lower mean ASQoL scores vs females (nr-axSpA: BKZ: 8.5 vs 10.8, PBO: 8.6 vs 10.2; r-axSpA: BKZ: 8.3 vs 11.1, PBO: 8.4 vs 9.0), and generally had higher mean OSI values. Across ASAS40, ASDAS < 2.1 and BASDAI change from BL (CfB), a pattern of higher BKZ vs PBO treatment effect in males vs females at Wk16 was reflected in the relative odds ratios (rORs) and relative differences (RDs) at this timepoint (Figure 1). At Wk52, response rates were higher/comparable in males vs females with nr-axSpA/r-axSpA respectively. Full results of ASAS40, ASDAS < 2.1 and BASDAI can be seen in Figure 1.For ASQoL, males and females showed improvements with BKZ at Wk16 (nr-axSpA: −5.5 vs −4.8; r-axSpA: −4.8 vs −5.5) compared with PBO (nr-axSpA: −2.1 vs −2.9; r-axSpA: −3.1 vs −3.7). Improvements continued to Wk52 with BKZ (nr-axSpA: BKZ: −5.7 vs −6.2, PBO/BKZ: −5.5 vs −5.1; r-axSpA: BKZ: −5.4 vs −6.5, PBO/BKZ: −5.5 vs −5.8). For CfB in OSI outcomes, RDs generally indicated a higher BKZ vs PBO treatment effect in males vs females at Wk16 (Figure 2). However, absolute OSI values in males and females were generally comparable at Wk16, with values maintained or improved to Wk52 (Figure 2).
Conclusion: The treatment effect of BKZ vs PBO at Wk16 tended to be higher among male vs female pts with axSpA. However, at Wk52 female pts showed marked improvement and comparable efficacy to male pts following longer-term treatment with BKZ. Overall, efficacy of BKZ in clinical, patient-reported, and OSI outcomes was demonstrated in both pt populations across the full axSpA disease spectrum. References: 1. van der Heijde D. Ann Rheum Dis 2023;82(4):515–26; 2. Baraliakos X. Ann Rheum Dis 2024;83(2):199–213.
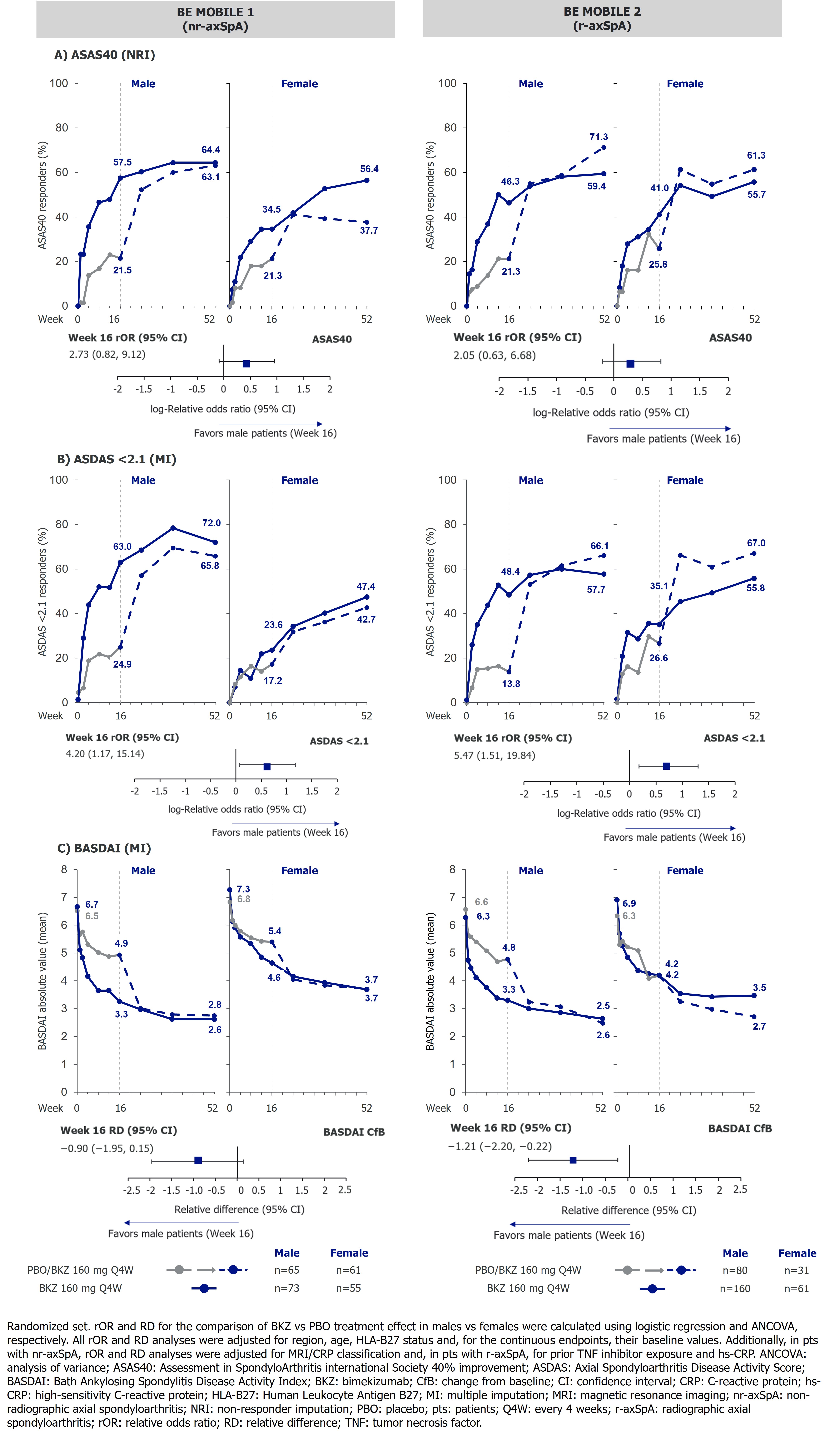 Figure 1. ASAS40, ASDAS < 2.1 and BASDAI to Week 52 and relative odds ratios and relative differences at Week 16, stratified by sex
Figure 1. ASAS40, ASDAS < 2.1 and BASDAI to Week 52 and relative odds ratios and relative differences at Week 16, stratified by sex
.jpg) Figure 2. MRI SPARCC SIJ, MRI Berlin spine score and hs-CRP absolute values to Week 52 and relative differences at Week 16, stratified by sex (OC)
Figure 2. MRI SPARCC SIJ, MRI Berlin spine score and hs-CRP absolute values to Week 52 and relative differences at Week 16, stratified by sex (OC)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gensler L, Ramiro S, Poddubnyy D, Magrey M, van der Horst-Bruinsma I, Deodhar A, Taieb V, Voiniciuc D, de Peyrecave N, Rudwaleit M. Bimekizumab Demonstrated Comparable One-Year Efficacy in Male and Female Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: Results from Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-demonstrated-comparable-one-year-efficacy-in-male-and-female-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-demonstrated-comparable-one-year-efficacy-in-male-and-female-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/
