Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1191–1220) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: With therapeutic advances in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM), achieving remission has become an important goal. However, comprehensive data on remission, particularly across IIM subtypes, remain limited. This study assessed remission rates and identified predictors of remission in a prospective IIM registry.
Methods: We analyzed data from adult IIM patients enrolled at the University of Pittsburgh Myositis Center between January 2000 and March 2019. The “remission cohort” included 430 patients with a disease duration of ≥1 year or those who died within the first year (categorized as non-remission). We focused on four IIM subtypes: dermatomyositis (DM), antisynthetase syndrome (ASyS), immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), and polymyositis (PM), according to the physician’s judgement based on the 2017 EULAR/ACR classification criteria. ASyS was further defined by clinical symptoms and ASyS antibodies, while IMNM was further defined by clinical symptoms and either anti-HMGCR antibody, anti-SRP antibody, or consistent muscle biopsy. Overlap syndromes and inclusion body myositis were excluded. Remission was defined as the absence of disease activity based on expert clinical assessment, either while receiving stable/de-escalating therapy or off medication. Predictive factors for remission were analyzed using a Cox proportional hazard model in a subcohort of 346 patients with ≥1 year of follow-up post-enrollment.
Results: Among 430 patients (67.4% female, 88.5% white, mean age at diagnosis 50.2 ± 14.3 years), the median follow-up time was 5.1 (IQR 1.2 – 10.1) years, and the median disease duration at last visit was 7.5 (IQR 3.1 – 12.4) years. The remission rate at 12 months post-diagnosis was 3.5%, while the overall remission rate was 35.3%. IIM subtype-specific 12-month and overall remission rates were: DM (5.0%, 42.5%), ASyS (1.6%, 28.0%), IMNM (4.4%, 33.3%), and PM (0.0%, 20.5%) (Table 1 and Figure 1). The median time from diagnosis to first remission was 3.8 (IQR 2.0 – 6.3) years. Flares after remission occurred in 27.0% of patients after median 3.5 (IQR 1.6 – 7.0) years. The overall drug-free remission was achieved in 18.6% of patients, with rates by subtype: DM 23.1%, ASyS 15.2%, IMNM 17.8%, and PM 7.7%. In univariate analysis, predictors of higher remission included non-white/black race (i.e., other), DM subtype, and anti-Mi2 antibody, while predictors of lower remission included PM subtype, interstitial lung disease, pulmonary hypertension, and anti-SSA antibody. In multivariate analysis, non-white/black race (HR 9.79, P0.001) and anti-Mi2 antibody (HR 1.92, P=0.023) were independently associated with increased remission likelihood, whereas PM subtype (HR 0.37, P=0.033) and pulmonary hypertension (HR 0.37, P=0.004) were independently associated with decreased remission likelihood (Table 2).
Conclusion: Remission rates vary across IIM subtypes, with the highest rate in DM and the lowest rate in PM. Race, IIM subtype, autoantibody profile, and comorbid pulmonary hypertension significantly influence remission outcomes. These insights can inform individualized management and prognostication of IIM.
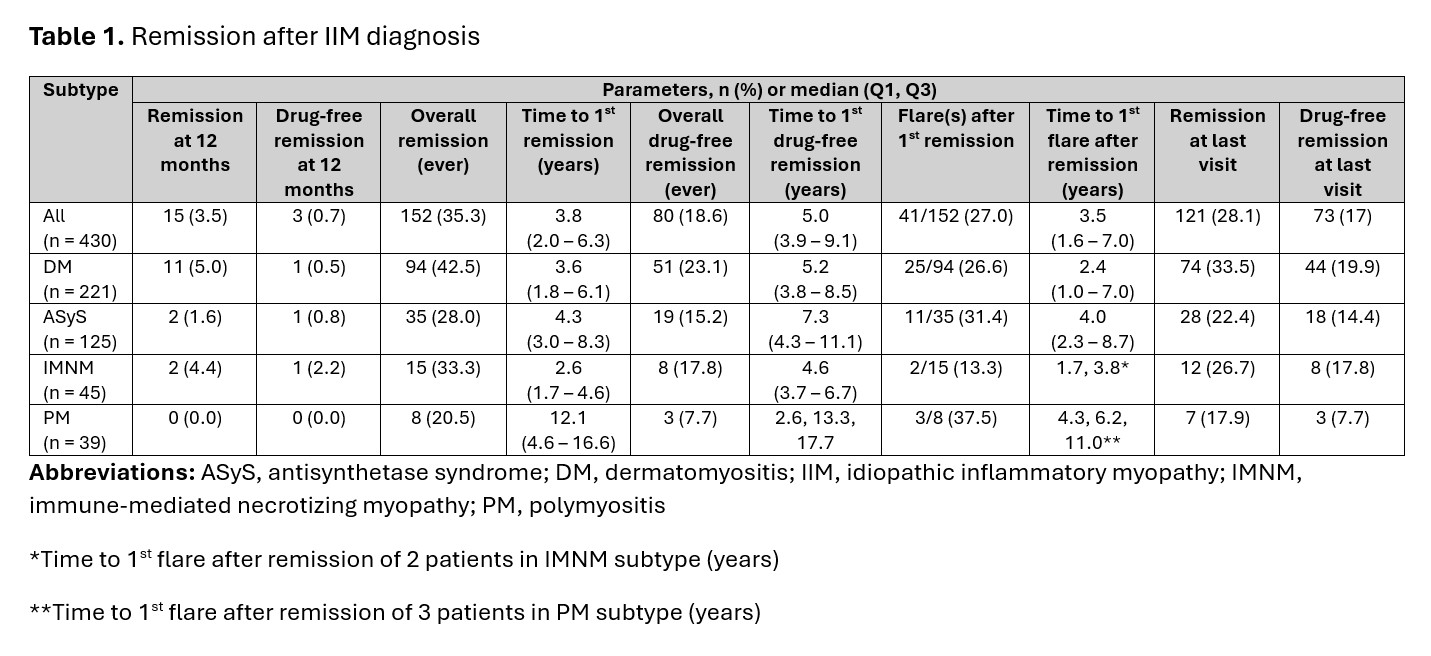 Table 1. Remission after IIM diagnosis
Table 1. Remission after IIM diagnosis
.jpg) Table 2. Cox proportional hazard model for predictive factors of first remission in 346 IIM patients followed for ≥ 1 year at the University of Pittsburgh Myositis Center
Table 2. Cox proportional hazard model for predictive factors of first remission in 346 IIM patients followed for ≥ 1 year at the University of Pittsburgh Myositis Center
.jpg) Figure 1. Cumulative first remission rate according to IIM subtype
Figure 1. Cumulative first remission rate according to IIM subtype
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pongtarakulpanit N, Tahir S, Suresh V, Kothari V, Keret S, Gkiaouraki E, Moghadam-Kia S, Liarski V, Ascherman D, Aggarwal R. Remission Rates and Predictors in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy Subtypes: Insights from a Single-Center Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/remission-rates-and-predictors-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy-subtypes-insights-from-a-single-center-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/remission-rates-and-predictors-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy-subtypes-insights-from-a-single-center-cohort/
