Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1191–1220) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Treatment of anti-synthetase syndrome (ASyS) presents clinical challenges: myositis can lead to permanent disability and severe organ involvement is life-threatening.
Methods: We treated three patients with multidrug-resistant severe anti-Jo-1 positive ASyS with blinatumomab 143µg and added rituximab (RTX) 1000mg for maintenance therapy. Patient 1, 67-year-old female, had reoccurring myositis and new interstitial lung disease (ILD). Patient 2, 36-year-old male, suffered from progressive ILD and myocarditis. Patient 3, 47-year-old male, had debilitating myositis. All patients were unresponsive to at least three immunosuppressants including rituximab.
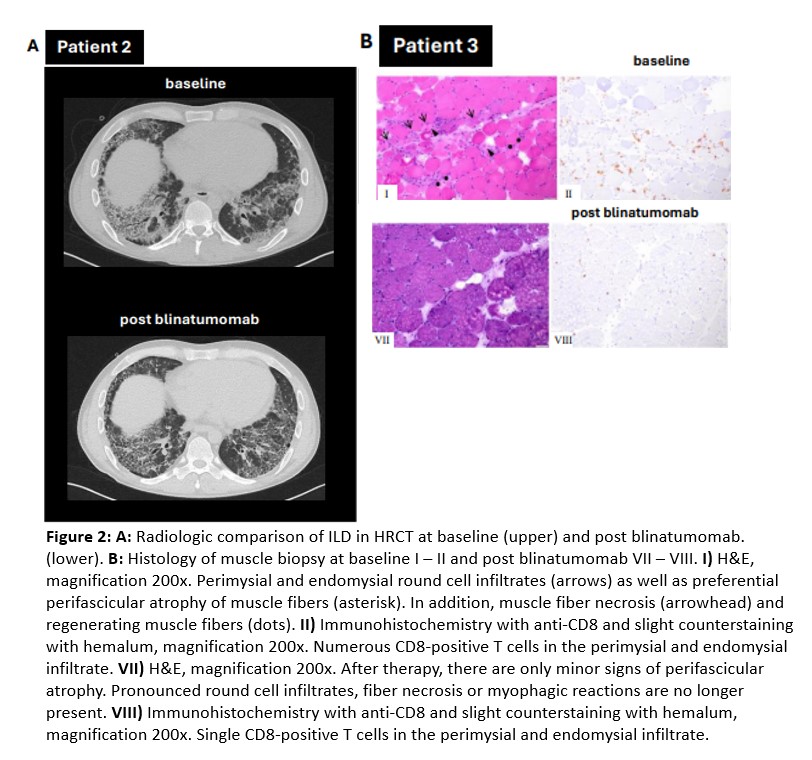
Results: Blinatumomab induced complete depletion of CD19+ B cells in circulation and muscle tissue (Figure 2) and profound decreases in anti-Jo-1 titers. Blinatumomab induced glucocorticoid-free remission with normalization of muscle enzymes, improvement of muscle strength (Figure 1) in all patients. Patient 1 showed an increase in CD19+ B cells and recurrence of myositis 4 months after blinatumomab. We re-started blinatumomab plus RTX and reinduced clinical remission followed by maintenance therapy with RTX (follow-up six months). Patient 2 showed ongoing remission of myositis and improvement of ILD for six months after blinatumomab and repeated RTX. Patient 3 demonstrated ongoing remission for 6 months after blinatumomab and RTX.Adverse events: cytokine release syndrome (CRS) grade 3 (same day recovery) and respiratory infection in patient 3. No neurotoxicity occurred.
Conclusion: This is the first report on treating patients with severe, treatment-refractory ASyS with blinatumomab. When followed by RTX, glucocorticoid-free remission remained stable for up to 10 months follow-up. Combining blinatumomab with RTX may offer potential in treatment-refractory ASyS patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Duesing C, Stuetz A, Györfi A, Lahu L, Deicher F, Chehab G, Richter J, van Saan M, Tümerdem B, Matei A, Buehring B, Grieshaber-Bouyer R, Hagen M, Schett G, Merkt W, Distler J. Induction of stable, GC-free remission in patients with severe, therapy-refractory anti-synthetase syndrome after using the bispecific CD19xCD3 T cell engager blinatumomab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/induction-of-stable-gc-free-remission-in-patients-with-severe-therapy-refractory-anti-synthetase-syndrome-after-using-the-bispecific-cd19xcd3-t-cell-engager-blinatumomab/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/induction-of-stable-gc-free-remission-in-patients-with-severe-therapy-refractory-anti-synthetase-syndrome-after-using-the-bispecific-cd19xcd3-t-cell-engager-blinatumomab/

.jpg)