Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1123–1146) Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: To identify novel pathogenic variants associated with chondrocalcinosis (CC), we systematically screened individuals with a family history of CPPD using an NGS panel. Among 26 index cases between 2016 and 2024, we identified a known mutation in the TNFRSF11B gene, a novel missense variant in the ANKH gene, and a novel mutation in the 5′ untranslated region (5’UTR) of the ANKH gene, which we report here.
Methods: Whole exome sequencing (WES) was performed to expand the search for pathogenic variants not detected by the targeted panel. Primary fibroblast cultures (skin biopsy) of the proband and three controls were established to assess protein levels and gene expression using Western blotting (WB), qRT-PCR, and immunocytochemistry (IC). Inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi) and ATP levels in the culture media were measured by enzymatic assay and citrate concentrations were determined by ion chromatography. Skeletal imaging of the proband was performed using a photon-counting computed tomography scanner.
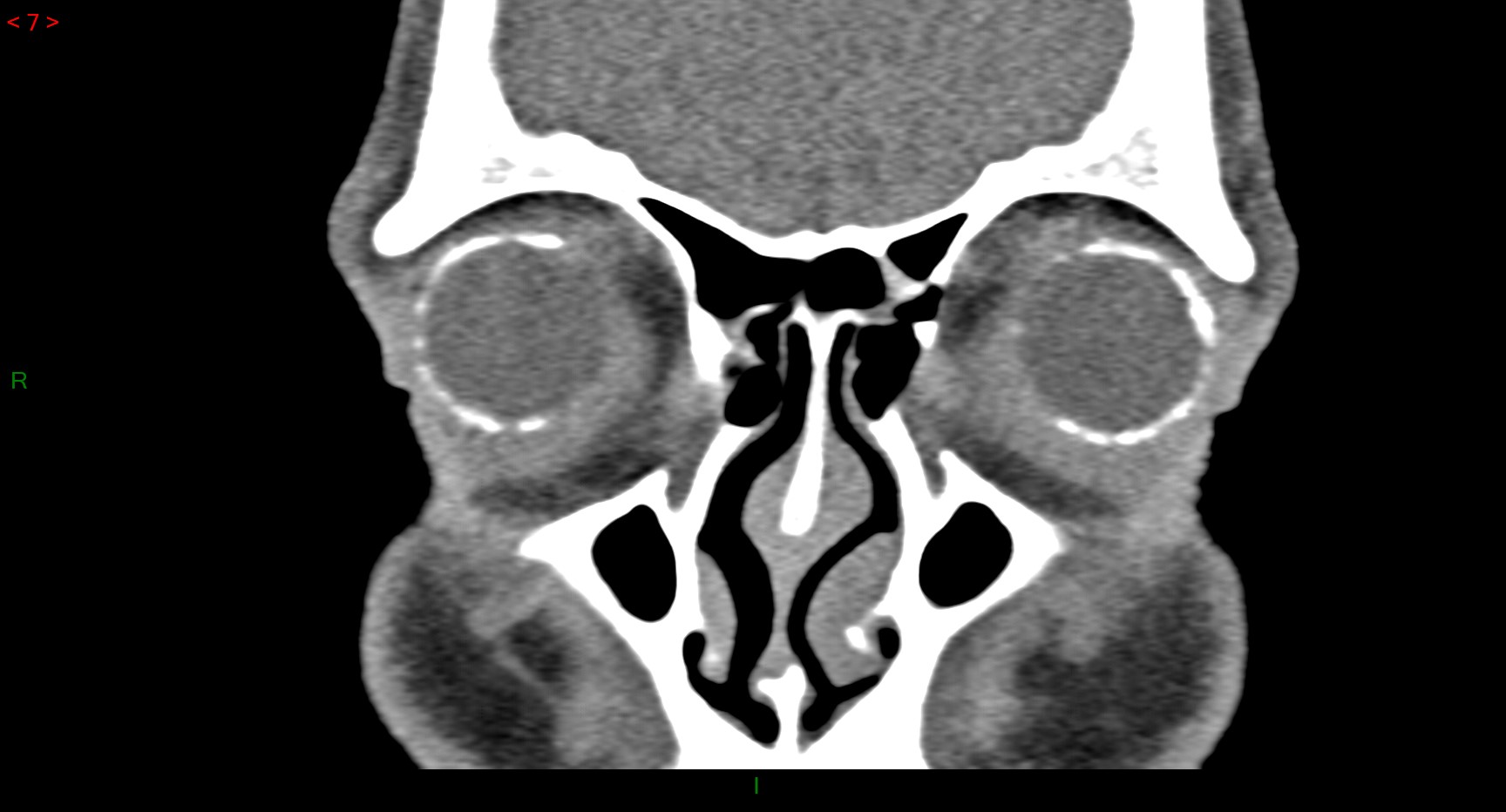
Results: The proband experienced recurrent episodes of arthritis in the wrists, knees, and ankles since the age of 23. Microscopic analysis of SF confirmed the presence of CPP crystals. CT scan showed widespread calcium deposits in almost all joints without OA changes, as well as in the choroid (Figure 1). He is a member of a multiplex family in which CPPD follows a dominant mode of inheritance. Panel NGS revealed a previously unreported heterozygous variant in the 5′ UTR (NM_054027.6: c.-113_-112delinsAT) introducing a novel ATG start codon in all affected individuals. WES confirmed that no other variant could explain this phenotype. This variant co-segregates with the CPPD phenotype and was further confirmed by Sanger sequencing. The plasma PPi level was elevated in the proband compared to the mean value measured in a control cohort (n=46): 2.40 µM vs. 1.61 ± 0.33 µM. In vitro, there were no differences in ANKH mRNA expression or protein expression (WB) between mutant and control fibroblasts. IC revealed both transmembrane and cytoplasmic localisation of the mutant protein. Notably, the levels of PPi and citrate in the fibroblast culture media (µmol/g protein) were significantly higher in the proband than in the controls: 1.45 vs. 0.77 for PPi (p < 0.0007) and 255.8 vs. 177.3 for citrate (p = 0.0024) (Figures 2-3). In contrast, no difference in extracellular ATP levels was observed. Treatment of fibroblasts with probenecid (5 mM), an ANKH inhibitor, abolished the increased citrate levels observed in the proband's fibroblast culture media. mRNA expression of IL1, IL6, MMP1, PIT1 and TNAP was unchanged in the proband's fibroblasts. In contrast, ENPP1 expression was significantly increased by approximately 8-fold (p < 0.001) - a finding that was further confirmed at the protein level by WB and IC.
Conclusion: We describe a novel 5’UTR variant in the ANKH gene that generates an ectopic start codon. Functional studies showed increased extracellular levels of PPi and citrate and overexpression of ENPP1 without alterations in ANKH mRNA or protein levels, supporting a gain-of-function mechanism
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
pascal r, Duranton c, Pinna T, Ricquebourg M, Augustin L, Bardin T, Bousson V, Ea H, Rubera I, Collet C. A Gain-of-Function 5’UTR Variant in ANKH Causes Familial CPPD with Elevated Extracellular PPi and Citrate [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-gain-of-function-5utr-variant-in-ankh-causes-familial-cppd-with-elevated-extracellular-ppi-and-citrate/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-gain-of-function-5utr-variant-in-ankh-causes-familial-cppd-with-elevated-extracellular-ppi-and-citrate/

.jpg)
.jpg)