Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1088–1122) Immunological Complications of Medical Therapy Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARD) treated with B-cell-depleting therapies such as rituximab (RTX) have impaired humoral immune responses, increasing their susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, including severe infections. Despite vaccination, COVID-19 remains a concern in this population. This study aimed to describe the occurrence of SARS-CoV-2 infections in RTX-treated SARD patients and to explore potential predictors of infection.
Methods: COVBIRD is an open-label, non-randomized, comparative trial evaluating humoral responses following at least three COVID-19 vaccinations in SARD patients treated with RTX. We conducted a subanalysis of participants who developed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the study period. Patients were grouped based on their infection status. Descriptive statistics and univariable logistic regressions were used to compare demographic and clinical characteristics between groups.
Results: Among the 125 RTX-treated patients, 29 (23.2%) experienced at least one SARS-CoV-2 infection, including five classified as severe. Table 1 reports on the patient demographic and diseases characteristics comparing those who developed COVID infection vs those with no infection. No significant differences were observed between groups in terms of diagnosis and treatment-related variables (see Table 1). Age was the only significantly different factor: infected individuals were younger on average (55.2 years; 95% CI, 49.7–60.8) compared to those without SARS-CoV-2 infection (61.8 years; 95% CI, 59.0–64.6); p = 0.034. We also observed a female predominance for infection, but this was not statistically significant. Table 2 summarizes the clinical presentations of the five severe cases.
Conclusion: In this cohort of immunocompromised patients treated with RTX, nearly one in four developed SARS-CoV-2 infection despite having received three to five doses of vaccines, with a subset experiencing severe disease. Baseline clinical characteristics were generally similar between infected and non-infected individuals, highlighting a broad susceptibility likely driven by both immunosuppressive therapy and underlying disease. The younger age of infected patients may reflect behavioral factors such as reduced adherence to preventive measures. These findings emphasize the elevated risk of COVID-19 in RTX-treated individuals and support the implementation of individualized, reinforced preventive strategies regardless of clinical profile.
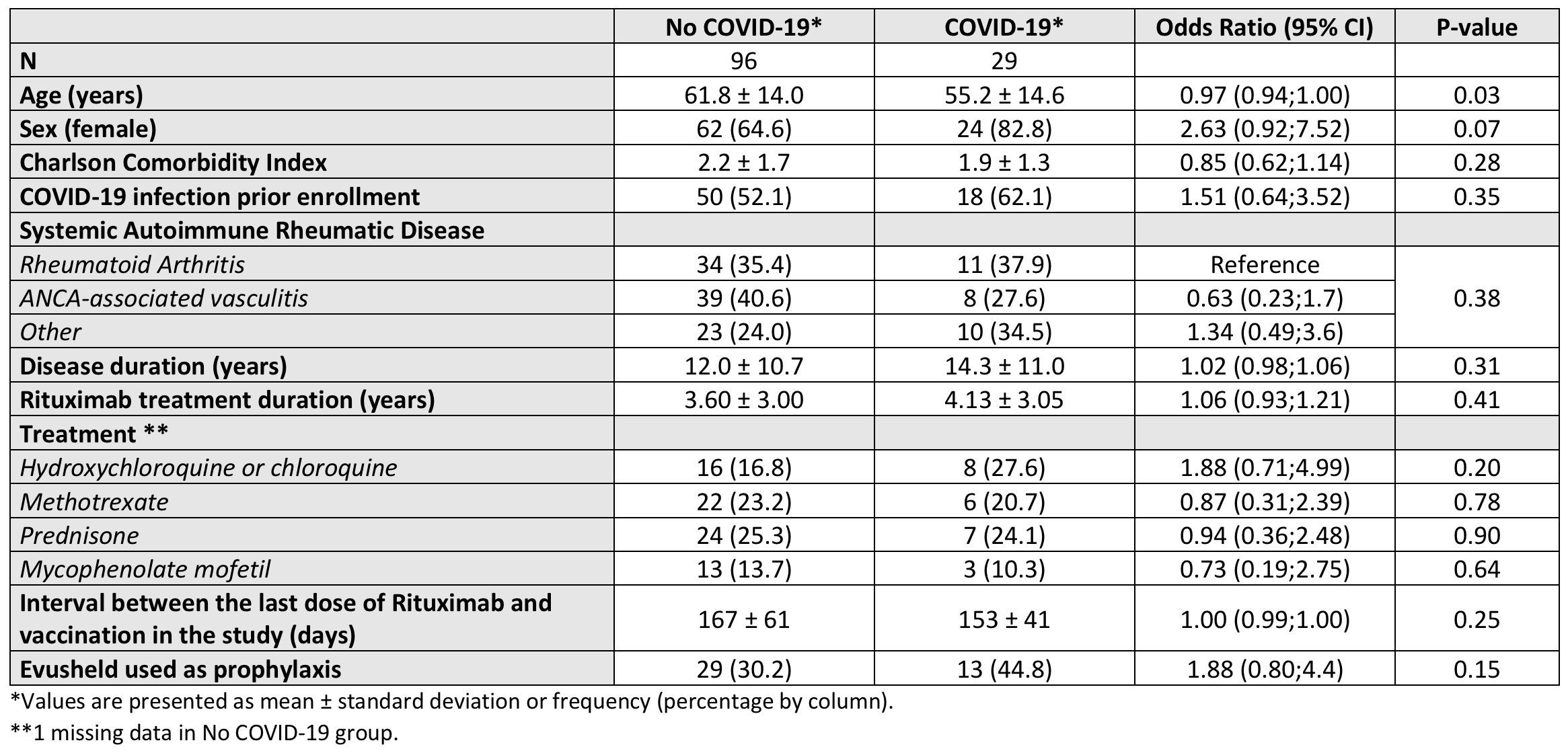 Table 1. Patient and disease characteristics with univariable logistic regression results
Table 1. Patient and disease characteristics with univariable logistic regression results
.jpg) Table 2. Severe SARS-CoV-2 infections
Table 2. Severe SARS-CoV-2 infections
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Simard L, Amiable N, Colmegna I, Julien A, Léger-Thériault S, Godbout A, Fournier L, Alfonso G, Bourre-Tessier J, Hudson M, Richard N, Makhzoum J, Mendel A, Bernatsky S, Dionne M, Libman M, De Serres G, Fortin P. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 infected Patients with Rheumatic Diseases on Rituximab: A Subanalysis of the COVID-19 Vaccine Booster in Immunocompromised Rheumatic Diseases (COVBIRD) Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-sars-cov-2-infected-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-on-rituximab-a-subanalysis-of-the-covid-19-vaccine-booster-in-immunocompromised-rheumatic-diseases-covbird-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characteristics-of-sars-cov-2-infected-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-on-rituximab-a-subanalysis-of-the-covid-19-vaccine-booster-in-immunocompromised-rheumatic-diseases-covbird-study/
