Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0554–0592) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Sonelokimab (SLK) is a novel IL-17A- and IL-17F-inhibiting Nanobody designed to target difficult-to-reach sites of inflammation due to its small size and albumin-binding domain. The Phase 2 ARGO trial in patients with active PsA demonstrated the efficacy of SLK on both joint and skin outcomes (McInnes et al, EULAR 2024). SLK resulted in robust multidomain clinical responses that have been associated with improved QoL. We assess the effect of SLK on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) from ARGO.
Methods: ARGO (NCT05640245) was a 24-week, global, randomized, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled trial that enrolled adults with active PsA. Patients were randomized to SLK 120mg Q4W (with induction [WI] doses at Weeks [W] 0, 2, 4, and 6), SLK 60mg Q4W WI, SLK 60mg Q4W with no induction (NI), PBO, or adalimumab 40mg Q2W (reference arm; not powered for statistical comparisons). W0–12 were PBO controlled, after which patients originally randomized to PBO switched to SLK 120mg NI; patients with < 20% improvement in SJC and TJC were reassigned treatment at W12 (except patients in the US who completed the study at W12). PROs including PsA Impact of Disease (PsAID)-12 (score range [SR] 0–10), Patient’s Assessment of Arthritis Pain (PtAAP; SR 0–100), Patient’s Global Assessment of Disease Activity (PGA; SR 0–100), and HAQ Disability Index (HAQ-DI; SR 0–3) were assessed Q4W until W24. Statistical comparisons vs. PBO were conducted at W12 using an MMRM analysis. Analyses at W24, and for patients with skin and joint responses, were observational.
Results: 207 participants were randomized. Patient-reported PsA symptom burden, as assessed by PsAID-12 score, is shown in Figure 1A (baseline median PsAID-12 total scores: 3.9–4.9). SLK resulted in significant improvements in PsAID-12 scores at W12, with mean improvements of 2.2–2.5 vs. 1.3 points with PBO (Table) and benefits across most individual domains (Figure 1B). Continued SLK treatment resulted in further improvements; most patients achieved PsAID-12 low impact (score >1.15–1.95) or remission (score ≤1.15) by W24 (median score: 1.0–1.2; Figure 1A). Improvements in PsAID-12 were pronounced (mean [SD] change from baseline [CfB] of –3.3 [1.9] points) in patients who achieved ACR50 + PASI 100, with a median score of 0.35 at W24 across pooled SLK arms. Significant improvements in pain by W12 were observed with SLK, with decreases in PtAAP scores of 30.1–30.9 vs. 18.8 points with PBO (Table). Improvements continued to W24, with mean CfB of –36.2 [–64.2%] to –40.0 [–65.6%] points with SLK. Significant improvements in patient-reported disease activity (PGA) scores by W12 were observed with SLK, with decreases of 27.8–31.9 vs. 18.7 points with PBO (Table). These improvements continued to W24, with a mean CfB ranging from –32.7 (–52.1%) to –39.7 (–35.6%) points. HAQ-DI scores improved through W24 (mean CfB at W24 of 0.47 [–47.4%] to 0.60 [–59.1%] points with SLK), although responses did not reach statistical significance vs. PBO at W12.
Conclusion: Patients treated with SLK in ARGO reported significant improvements in the symptoms and impact of PsA. Ongoing Phase 3 studies (IZAR-1: NCT06641076; IZAR-2: NCT06641089) will further assess the effect of SLK on PROs and QoL in larger patient populations.
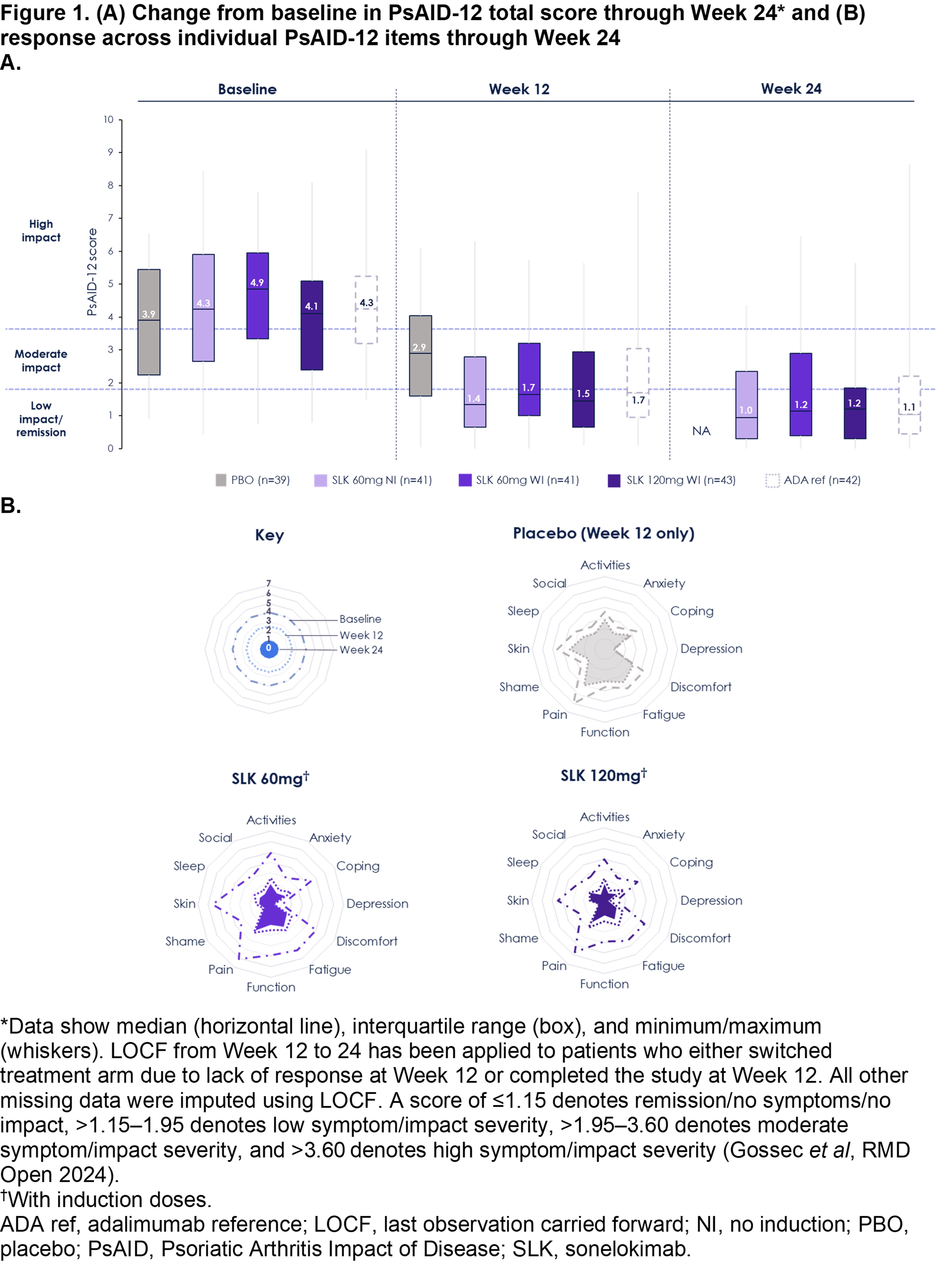 Figure 1. (A) Change from baseline in PsAID-12 total score through Week 24* and (B) response across individual PsAID-12 items through Week 24
Figure 1. (A) Change from baseline in PsAID-12 total score through Week 24* and (B) response across individual PsAID-12 items through Week 24
.jpg) Table. PsAID-12, PtAAP, and PGA outcomes at Week 12
Table. PsAID-12, PtAAP, and PGA outcomes at Week 12
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Merola J, Ogdie A, Gottlieb A, Proft F, Brennan N, Godwood A, Thomas M, Cullen E, Reich K, Coates L, Gossec L. Effects of Sonelokimab, an IL-17A- and IL-17F-Inhibiting Nanobody, on Patient-Reported Symptoms and Quality of Life in Psoriatic Arthritis: Results From the Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 ARGO Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-sonelokimab-an-il-17a-and-il-17f-inhibiting-nanobody-on-patient-reported-symptoms-and-quality-of-life-in-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-the-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlle/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-sonelokimab-an-il-17a-and-il-17f-inhibiting-nanobody-on-patient-reported-symptoms-and-quality-of-life-in-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-the-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlle/
