Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0731–0764) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interferon-gamma (IFNγ) have been identified as key drivers in the pathogenesis of giant cell arteritis (GCA), that promote disease progression. The phase 3 SELECT-GCA study showed that upadacitinib (UPA), a Janus Kinase inhibitor, was efficacious in treating GCA with a favorable benefit-risk profile compared to placebo (PBO). This study evaluated the impact of UPA on immune mediators in GCA, including IL-6 and IFNγ pathways, in the SELECT-GCA study.
Methods: Patients from SELECT-GCA were included in this analysis, termed “Biomarker Cohort”: PBO n =72/112; UPA 15 mg daily (UPA15), n =141/209. UPA15 patients underwent GC tapering over 26 weeks, while PBO patients underwent GC tapering over 52 weeks. Plasma samples were collected at baseline and weeks 2, 12, 24, and 52. A multiplexed assay platform designed for targeted detection and quantification of 45 immune related proteins was used, with significant differences identified in 30 proteins. IL-6 and IFNγ pathway proteins were assessed. A mixed model for repeated measures was used to compare biomarkers between UPA and PBO as well as to analyze treatment response and non-response. The least-square mean biomarkers between UPA and PBO were contrasted, and significant pharmacodynamic markers had a false discovery rate (FDR) ≤ 0.05.
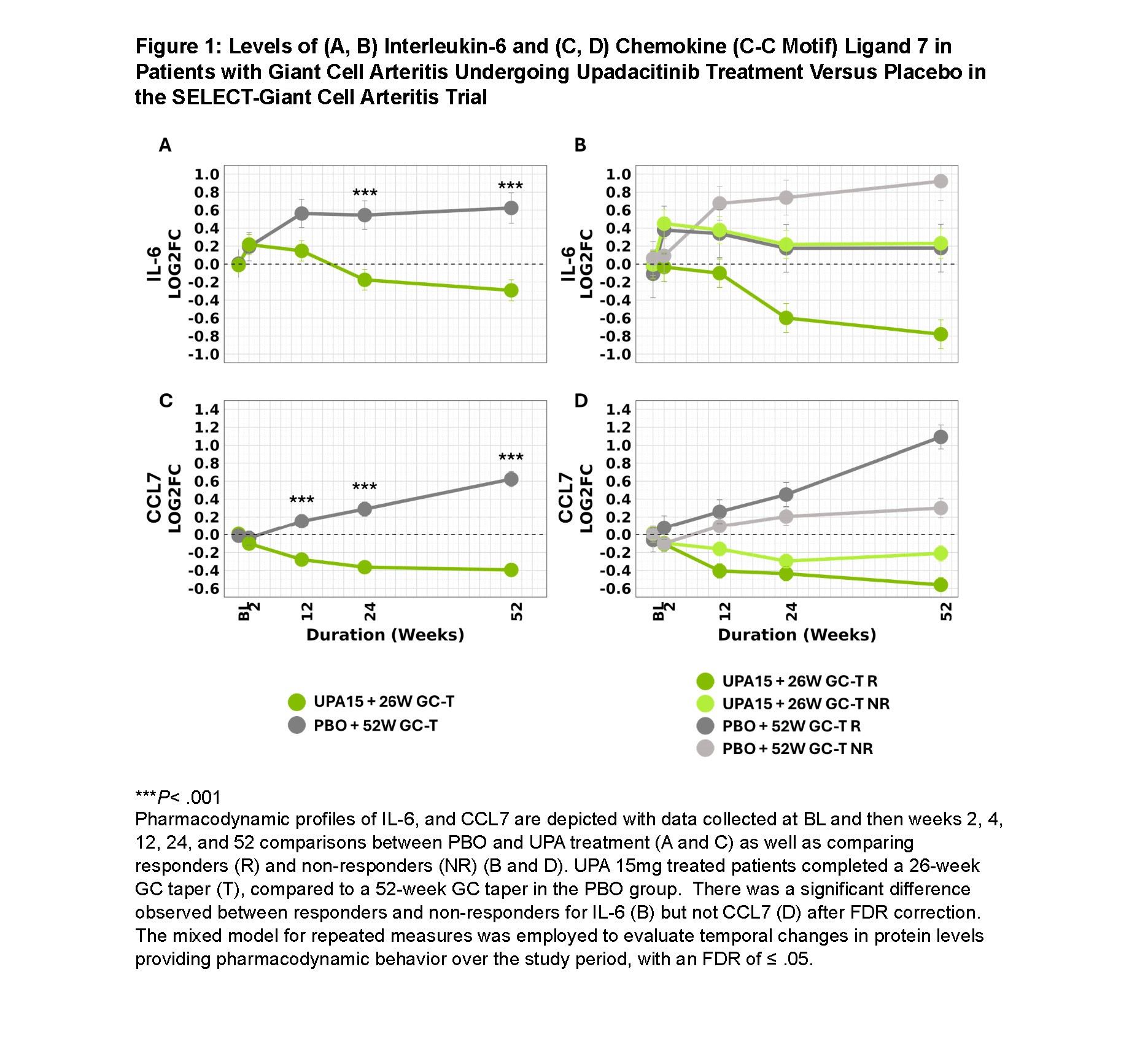
Results: This analysis focused on proteins in the IL-6 and IFNγ pathways, core pathogenic dysregulated biomarkers in GCA. UPA significantly reduced IL-6 levels compared to PBO (Figure 1). This reduction was more pronounced in responders versus non-responders in UPA. Circulating IFNγ increased with UPA; however, IFNγ-modulated chemokines CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 decreased significantly with UPA and tended to increase with PBO (Figure 2). UPA reduced IL-18, amplifying the effect of IFNγ on CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11. No significant difference was seen for these cytokines when comparing responders and non-responders to UPA. CCL7 was significantly reduced with UPA versus PBO; however, when comparing responders to non-responders with UPA, the difference was not significant by FDR. With PBO, levels of IL-6, CCL7, CXCL9, and CXCL10 progressively increased throughout the study, with no apparent reduction below baseline levels for CXCL11 and IL-18.
Conclusion: Treatment of GCA with UPA15 inhibits essential immune pathways implicated in GCA pathogenesis, including IL-6 and downstream proteins of IFNγ (CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11, IL-18). This reduction in activity of the IFNγ pathway is indicative of a decrease in T-helper 1 cytokines due to treatment with UPA. Although CCL7 is not considered a primary disease driver, its decrease with UPA treatment aligns with cytokines associated with disease activity. UPA’s molecular effect was observed as early as week 2, suggesting rapid onset of action. While the primary focus was on IL-6 and IFNγ proteins due to their roles in GCA biology, other modulated biomarkers warrant investigation to further characterize UPA’s effect. UPA’s clinical activity in GCA relates partly to its impact on IL-6, IFNγ pathway proteins, and CCL7, suggesting the efficacy of UPA for GCA is related to modulation of these cytokines.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Christ L, Taylor S, Xu Y, Sharma R, Sornasse T, Bi Y, Guay H, Setty A, Romero A, Merkel P, de Miguel E, Dejaco C, Weyand C. Impact of Treatment with Upadacitinib on Biomarkers Identified by Proteomics in Giant Cell Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-treatment-with-upadacitinib-on-biomarkers-identified-by-proteomics-in-giant-cell-arteritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-treatment-with-upadacitinib-on-biomarkers-identified-by-proteomics-in-giant-cell-arteritis/

.jpg)