Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0430–0469) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: In India, Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is often diagnosed late. Artificial Intelligence (AI) driven Large Language models (LLMs) can be deployed via widely available mobile phone devices, offering a potential screening solution. Here, we attempted to explore various AI agentic frameworks to identify the most effective model SARA (Screening Agent for RA), and also to validate how these models arrive at a diagnosis of RA.
Methods: We had developed the PreRAID (Pre-Screening Rheumatoid Arthritis Information Database) from consenting patients with joint pain, classifying patients into RA or not RA as per treating physician diagnosis. The dataset was split into 280 cases for the knowledge base (KB) and 70 for testing. A Neo4j vector database enabled embedding-based retrieval.Six LLMs were evaluated—four closed-source (OpenAI o1, OpenAI o3 mini, Gemini 2.5 Pro, Gemini 2.0 Flash) and two open-source (QwQ, Deepseek R1 70B). Each model was tested under three agentic configurations: (1) a single agent without knowledge base (KB) access; (2) a single agent with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG); and (3) a dual-agent setup, where the first agent generated a diagnosis and reasoning, validated by a second agent. [Figure 1]Each model-configuration pair was evaluated on 50 new cases. The models were also asked to explain the reasons behind each diagnosis, which was independently assessed by two fellows and one consultant rheumatologist using a four-point Likert scale.
Results: The PreRAID dataset included 84% RA-confirmed cases and 16% controls. Deepseek R1 showed the highest accuracy (82%) in the single-agent with KB setting, followed by o1 and o3 mini (80% each). Accuracy dropped in the two-agent setup, most notably in Gemini 2.5 Pro (37%) and Gemini 2.0 Flash (40%) [Figure 2].Despite moderate to high accuracy, Gemini models underperformed in reasoning when agentic complexity increased. Reasoning quality was suboptimal across all models. Gemini 2.0 Flash (36/50) and Deepseek R1 (28/50) had the most correct justifications, while QwQ and Gemini 2.5 Pro scored the lowest (6 and 10, respectively). Many outputs showed minor or major reasoning flaws, indicating a disconnect between diagnostic accuracy and reasoning integrity.
Conclusion: Deepseek R1 achieved the highest diagnostic accuracy (82%) in the single-agent with KB configuration. However, reasoning quality across all models was suboptimal, with many correct diagnoses attributed to flawed reasons. The dual-agent setup, intended to enhance reasoning, led to decreased diagnostic performance. Though we built a robust system (SARA) for screening, the lack of proper reasoning by the LLMs preclude the use as a diagnostic tool. Future directions should prioritize explainable AI approaches so that clinicians can trust the tool.
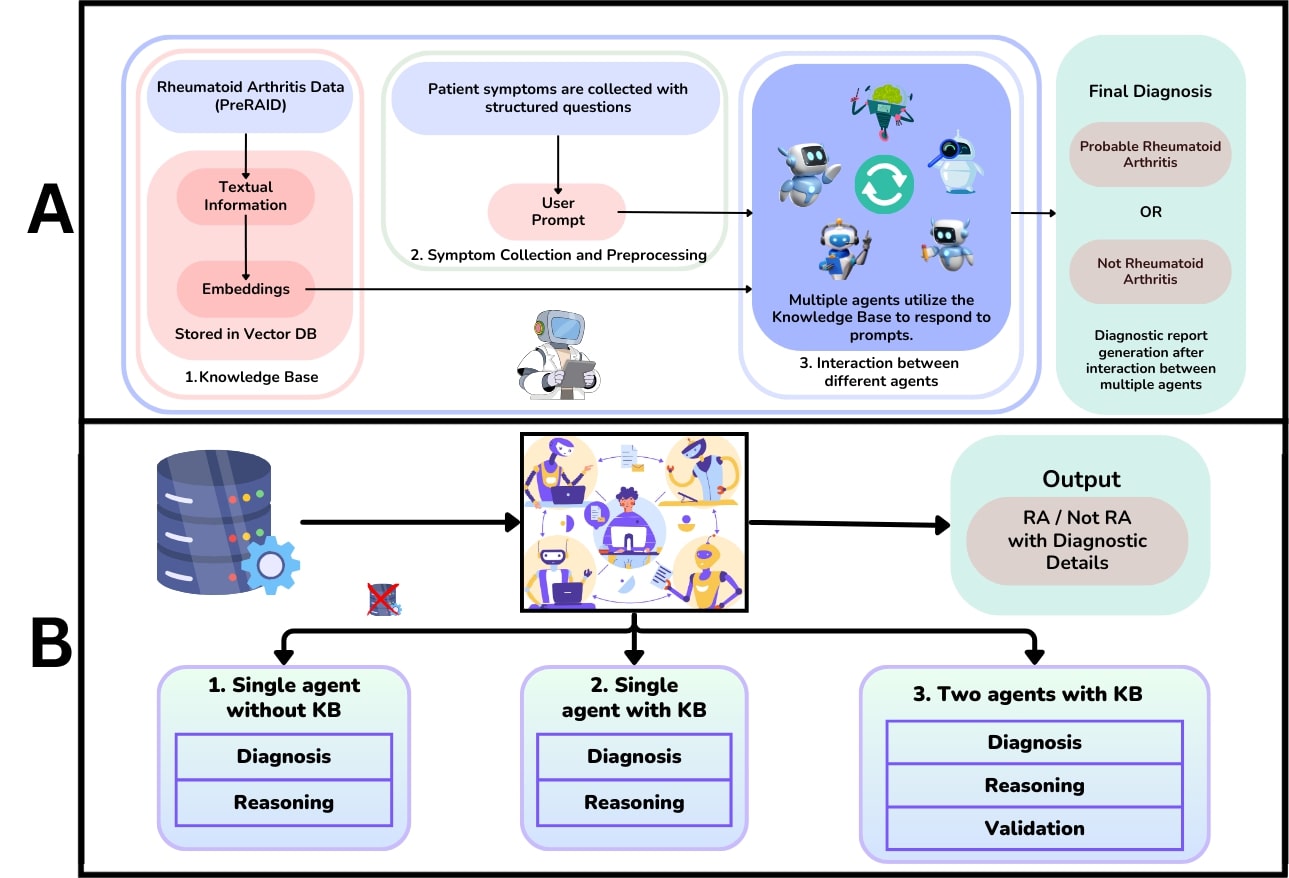 Figure 1: Agentic framework. (A) Workflow of the SARA framework and (B) Illustration of the sequential steps involved in diagnosing RA with single agent without knowledge base (KB), single agent with KB and Two agents with KB
Figure 1: Agentic framework. (A) Workflow of the SARA framework and (B) Illustration of the sequential steps involved in diagnosing RA with single agent without knowledge base (KB), single agent with KB and Two agents with KB
.jpg) Figure 2: Validation of the different models. (A) Accuracies of different LLM models under different agentic configurations and (B) Accuracies of reasonings provided by different models as validated by clinicians
Figure 2: Validation of the different models. (A) Accuracies of different LLM models under different agentic configurations and (B) Accuracies of reasonings provided by different models as validated by clinicians
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Verma S, Agarwal A, Maharana U, Mandal M, Padhan P, Mruthyanjaya P, Ahmed S. Right Diagnoses For the Wrong Reasons: Limitations of Current Large-Language Model based Agentic Frameworks for Screening of Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/right-diagnoses-for-the-wrong-reasons-limitations-of-current-large-language-model-based-agentic-frameworks-for-screening-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/right-diagnoses-for-the-wrong-reasons-limitations-of-current-large-language-model-based-agentic-frameworks-for-screening-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/
