Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of tofacitnib, a JAK inhibitor, in a multicentric cohort of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA).
Methods: Patients with JIA attending a pediatric rheumatology clinic who were treated with tofacitnib at some point of their follow-up were retrospectively included. Data collection: at Baseline, sociodemographics, JIA features and subtype and immunology status, JIA disease course of treatments and time on tofacitinib and number of previous therapies, JIA disease status variables and ongoing treatment/discontinuation were collected at 3 and 12 months of follow-up (Wallace criteria); and overall time on tofacitinib (drug survival). Descriptive and comparative statistical analysis comparing baseline and 3- and 12- months variables (JAMOVI (R)) were performed.
Results: Nf23 (60% female), mean age 16.5 years (SD 5.02), age at diagnosis 7 years (SD 5.02), mean disease duration 114 months (SD 71.1), age at tofacitinib onset 13.8 years old (SD 4.61). JIA subtypes: RF- poly 26%, ERA 21%, persistent oligo 17%, RF+ polyarthritis 13%, soJIA 13% and psoriatic 4%; 65% ANA positive. Previous failure to biologicals (BT): 48%, 2; 26%, 1; 22%, 3; 4%, 5. Mean time on last therapy: 21.1 months (SD 18.8), 95% innefficacy.Concomitant therapy: at baseline, 65% DMARD, 43% oral steroids; at 3 months, 58% DMARD, 30% oral steroids; at 12 months, 54% DMARD, 15% oral steroids.At 12 months, 56% were still receiving tofacitinib, 58% fulfilled inactivity criteria, 58% clinical remission on treatment, 8% clinical remission off treatment. No adverse event were recorded.Drug survival (from onset to current date): median of 13 months (range: 2-96).No differences were found among all variables, except for the significant reduction on oral steroids intake from baseline to 12-months follow-up (p=0.040).
Conclusion: Our results show that very refractory JIA patients who received tofacitinib after biological therapy failure (75% failed to ≥2 biologicals), either combined (DMARD) or in monotherapy, showed clinical statistical significant benefit in all JIA assessments (TJC, SJC, PGA, JADAS-71), both at 3 and 12 months of follow-up. Drug retention was 13 months (2-96). Safety profile was very positive with no adverse events recorded, specially with the higher rates of combined therapy (tocilizumab and canakinumab). Both an 11% and 28% of patients were allowed to discharge DMARD and oral steroids through follow-up, respectively. No particular subsets of patients were found to predict tofacitinib response. Further studies with larger cohorts are recommended to confirm our data. Abbreviations: RF, rheumatoid factor; ANA, anti-nuclear antibodies; CCP, anti-citrulline antibodies; B27, HLA B27 positive; TJC, tender joint count; SJC, swollen joint count;PGA, physician global assessment; ESR, erythrocite sedimentation rate; CPR, C reactive protein.
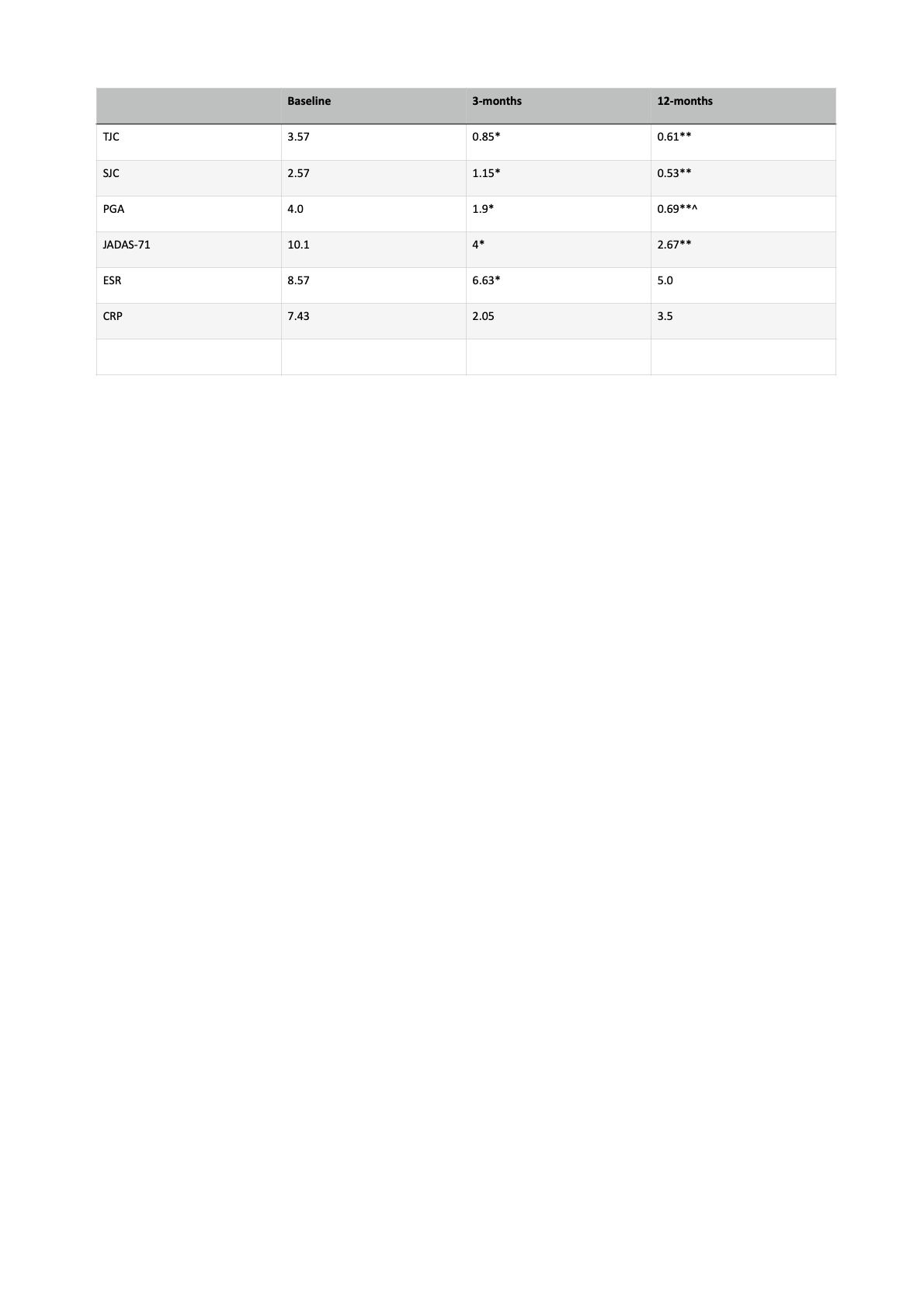 Table 1. JIA activity status at baseline, 3 and 12 months.
Table 1. JIA activity status at baseline, 3 and 12 months.
*p < 0.005 (Baseline vs 3-months)
**p < 0.005 (Baseline vs 12-months)
^p < 0.005 (3-months vs 12-months)
.jpg) 1st-year Survival tofacitinib rate.
1st-year Survival tofacitinib rate.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Torrente-Segarra V, Zacarias A, Rojas C, Antón-López J, Sanchez J, Salles Lizarzaburu M. Tofacitinib in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: efficacy and safety in a clinical practice setting. [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-in-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-efficacy-and-safety-in-a-clinical-practice-setting/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tofacitinib-in-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-efficacy-and-safety-in-a-clinical-practice-setting/
