Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0357–0386) Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Polymyositis (PM) is a subtype of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) characterized by muscle inflammation and muscle weakness. Extra muscular manifestations like interstitial lung disease (ILD), joint pain or skin rashes may also be experienced. This study aimed to evaluate the content validity of patient-reported outcome (PRO) measures used in PM (encompassing ASyS, OM, Others, IMNM), i.e., whether the content of these measures 1) captures symptoms or impacts that are important to adults with PM and 2) is comprehensible to respondents.
Methods: Adult (≥18 years) patients in the US with a clinical diagnosis of PM were recruited by a clinical site to take part in individual, semi-structured, 90-minute online interviews conducted from September 2023 to June 2024. Osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, neurological disorders, cardiac conditions, and lung conditions unrelated to IIM were excluded. The IRB-approved interview guide included open-ended questions to explore the content validity (i.e., relevance, comprehensiveness, and comprehensibility) of 8 PRO measures which assess physical functioning, fatigue and disease activity (Table 1). Participants were also asked about their perceptions of meaningful changes in scores. Purposive sampling with recruitment targets were used to recruit a diverse sample in terms of age, sex, race, ethnicity, and education level. Interviews were audio-recorded, transcribed, anonymized and analyzed using qualitative framework analysis in Atlas.ti v9.
Results: Participants were mostly female (n=21/34, 62%) and/or white (n=30/34, 88%) with a mean age of 58 years (range 32 – 77 years). Most participants had a graduate/postgraduate (n=14/34, 41%) or bachelor’s degree (n=10/34, 29%). Due to time constraints, not all measures were debriefed by all participants.An overview of findings is presented in Table 1. The instructions and item wording were interpreted as intended by the majority of participants for all PRO measures debriefed. The measures were conceptually relevant to the majority of the sample. Most participants interpreted the recall periods correctly. The response options/scales were correctly interpreted by participants. Participant feedback indicated that none of the suggested changes were critical for understanding.Meaningful change was assessed at the item level for multi-item PRO measures. For the HAQ-DI and the PROMIS-PF items, participants considered an improvement of 1- or 2-points as meaningful. A 2-point improvement on FACIT-Fatigue item(s) was considered meaningful to most participants.A 2-point improvement on the single-item PGA-NRS and PGIC-PA, or 1-point worsening on the PGA-NRS was considered by most participants to be meaningful. A 1-point improvement or worsening on the PGA-VRS and PGIS-PA was considered meaningful.
Conclusion: All 8 PRO measures demonstrated content validity for use in research with adults with PM. For multi-item and single-item PROs, a 1- to 2-point item-level change was considered meaningful, demonstrating the value of small improvements for individuals with this debilitating condition. These insights are valuable for interpreting quantitative within-patient changes when evaluating treatments for PM.
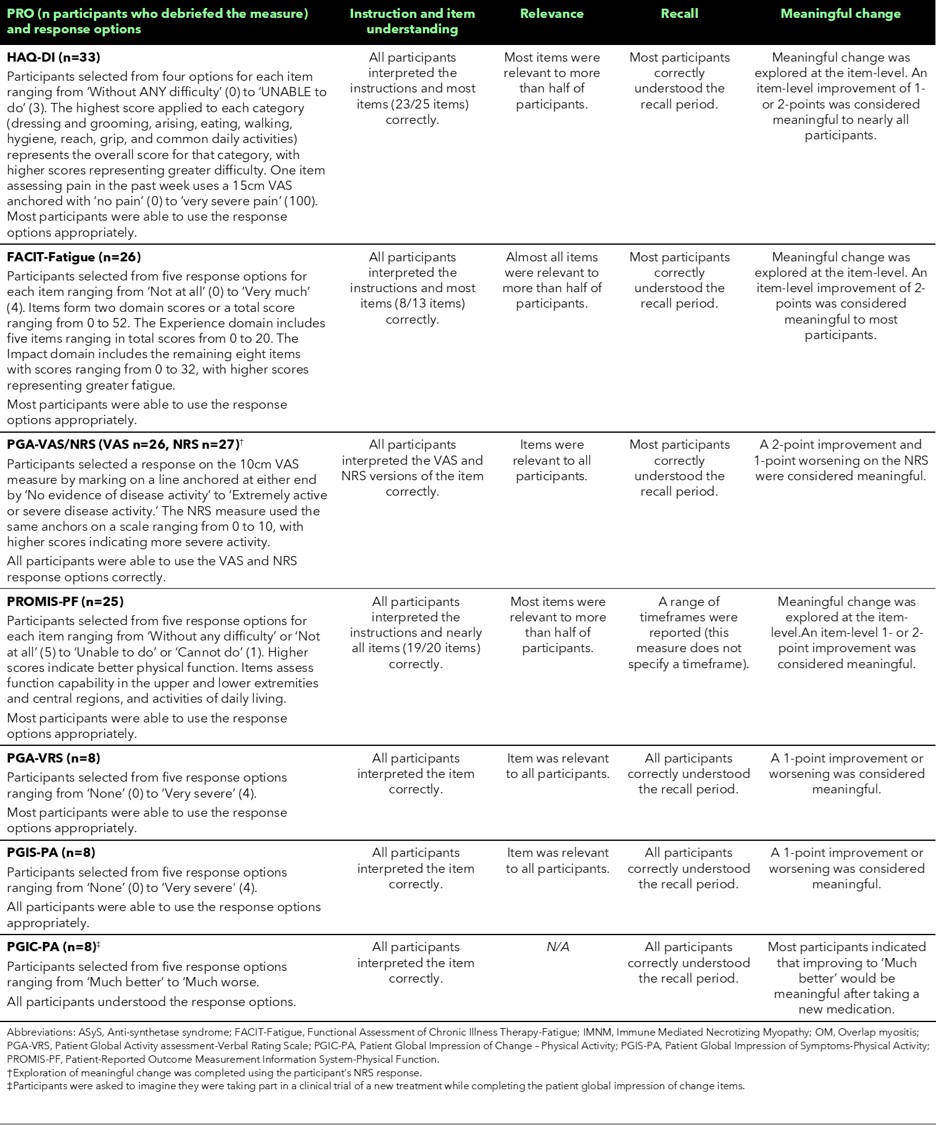 Table 1. Overeview of findings from cognitive debriefing interviews
Table 1. Overeview of findings from cognitive debriefing interviews
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Xenakis J, Yi E, Mazar I, Knight S, Makin H, Wratten S, Aggarwal R, McKee S. Content validation of patient-reported outcome (PRO) measures for fatigue, physical function and disease activity in Polymyositis (PM) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/content-validation-of-patient-reported-outcome-pro-measures-for-fatigue-physical-function-and-disease-activity-in-polymyositis-pm/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/content-validation-of-patient-reported-outcome-pro-measures-for-fatigue-physical-function-and-disease-activity-in-polymyositis-pm/
