Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0233–0279) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: A new subcutaneous formulation of infliximab (CT-P13) has recently become available for the treatment of inflammatory rheumatic diseases (IRDs), psoriasis and inflammatory bowel diseases. To date there are no real-life data on the use of this product nor is any real-world effectiveness evidence available in rheumatological settings. This study aims to provide a snapshot of subcutaneous infliximab (scIFX) use in IRDs evaluating treatment persistence and any factor able to influence drug retention rate (DDR).
Methods: We conducted a multicentric observational retrospective study enrolling consecutive adult patients with immune-mediated diseases treated with scIFX for at least 6 months. Disease status was assessed with standard activity indexes according to diagnosis (i.e. DAS28 for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), DAPSA for Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA), ASDAS-CRP for Axial Spondyloarthritis and clinician’s evaluation for the other conditions). Treatment persistence was assessed using the DRR at 6, 12, and 18 months. Factors influencing DRR were identified using the Log-Rank test.
Results: A total of 201 patients were included [134 women (66.7%), mean±SD age 49.9±13.8 years (range 18-82)]. Sixty-six (32.8%) patients had a diagnosis of AxSpA, 68 (33.8%) of PsA, 18 (9%) of RA, 18 (9%) of Behçet’s disease (BD), 10 (5%) of Takayasu arteritis (TA), 16 (8%) of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) (16; 8%) and 5 (2.5%) of other IRDs. Patients were treated with scIFX for a median duration of 14.0 months (IQR 13). Among them, 71 (35.3%) were treated with IFX as first-line biologic, 75 (37.3%) as second-line biologic and 55 subjects were treated as third or more line of treatment. Ninety-five (47.3%) patients were treated with intravenous (iv)IFX before switching to scIFX. Figure 1 shows our cohort disease status variations after scIFX start at the different timepoints. While starting scIFX, an induction regimen was used in 74 patients (78.3%), while 32 patients started scIFX every other week without any loading dose. The DRR for scIFX (Figure 2) was 88.5% at 6 months, 76.9% at 12 months, and 68.3% at 18 months (Figure 2). DRR was significantly higher in patients switching from ivIFX than directly stating with scIFX (p=0.038). Patients starting scIFX without loading dose had a significant lower DRR (p=0.033) than those who underwent a loading dose both subcutaneously or intravenously (Figure 3A). Patients starting scIFX (no previous ivIFX) had a similar DRR regardless of the line of biologic treatment (p=0.066). Similarly, there were no differences in DRR among BMI classes in the whole cohort (p=0.445) (Figure 3B). Forty-seven subject (23.4%) discontinued scIFX during the observation time. Concerning safety, 21 patients (10.4 %) experienced adverse events.
Conclusion: The study results suggest that scIFX provides sustained effectiveness over time for the treatment of IRDs. While factors such as line of treatment or BMI class do not affect DRR, the use of an induction dose appears to predict better treatment persistence.
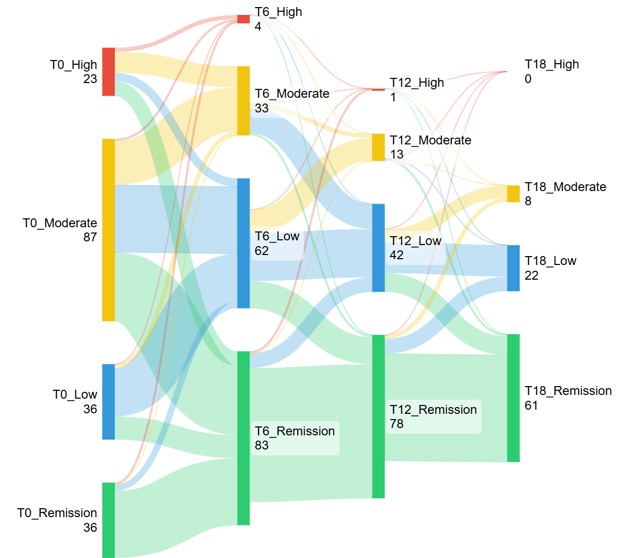 Disease status variation during the observation period.
Disease status variation during the observation period.
.jpg) scIFX drug retention rate of the whole cohort
scIFX drug retention rate of the whole cohort
.jpg) A: Drug Retention rate according to scIFX initiation (switchers from ivIFX vs new scIFX treatments) and according to the performance of a loading dose (LD vs no-LD) at the start of treatment. B: Drug retention rate according to BMI classes.
A: Drug Retention rate according to scIFX initiation (switchers from ivIFX vs new scIFX treatments) and according to the performance of a loading dose (LD vs no-LD) at the start of treatment. B: Drug retention rate according to BMI classes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gentileschi S, Gaggiano C, Placido F, Terribili R, Cometi L, Lopalco G, Dipetrangelo G, Cozzi G, Padoan R, Bixio R, Parisi S, Ditto M, Lepri G, Fabiani C, Cantarini L, Iannone F, Ramonda R, Frediani B, Guiducci S. A snapshot of subcutaneous infliximab use in inflammatory rheumatic diseases: a multicenter Italian study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-snapshot-of-subcutaneous-infliximab-use-in-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-a-multicenter-italian-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-snapshot-of-subcutaneous-infliximab-use-in-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-a-multicenter-italian-study/
