Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0210–0232) Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Collection of disease activity measures (DAMs) is a key component of high-quality care for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. This study surveyed rheumatology providers at Veterans Affairs RA (VARA) registry sites to identify barriers and facilitators for collecting and documenting DAMs.
Methods: The VARA registry is multicenter, prospective cohort study of US Veterans with RA who receive care within the Veterans Health Administration. A provider survey was developed to investigate barriers and facilitators for collecting and documenting DAMs [tender joint count (TJC), swollen joint count (SJC), Physician Global Assessment (PGA), Patient Global Assessment (PtGA), pain score (PS), Multi-Dimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire (MDHAQ), Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR), C-Reactive Protein (CRP)] for RA patients at each VARA site. Survey questions were then independently evaluated and refined by 5 expert reviewers. The final 42-question survey was administered to 92 VA rheumatology providers at 16 VARA sites. Sites were designated as high- or low-performing based on whether the percentage of site notes that documented all 6 clinical DAMs (TJC, SJC, PGA, PtGA, PS, MDHAQ) for VARA participants was above or below the mean of the 16 VARA sites from 3/2024 to 3/2025. Responses were scored using 5-point Likert scales. Responses were grouped into “no difficulty or barrier” and “some difficulty or barrier” categories for DAM barrier questions and “very helpful” and “less helpful” categories for DAM facilitator questions due to clustering of responses at the low and high ends of the barrier and facilitator scales respectively. Results were reported as descriptive statistics, and provider responses from high- and lower-performing sites were compared using chi-square testing.
Results: 66 providers (71.7%) from 15 sites (93.8%) submitted survey responses. Providers at both high-and low-performing sites reported the MDHAQ, ESR, CRP, and PtGA were the most difficult DAMs to collect (Table 1). Providers at both high- and low-performing sites reported the most common DAM barriers were labs not being drawn prior to clinic visits, DAM forms not being completed, insufficient time, inconsistent DAMs assessment by fellows, and lack of research support staff (Table 2). Providers at low-performing sites cited two barriers more often than high-performing sites: lack of research support staff (77.1% vs. 51.7%; p=0.03) and failure to identify Veterans requiring DAMs assessments (65.7% vs. 37.9%; p=0.03). Among all respondents, the most common DAM facilitators were having an RA-specific clinic, using standardized DAM templates, using printed DAM forms, drawing labs before clinic visits, and having research support staff (Table 3). Providers at high-performing sites noted having an RA-specific clinic as a facilitator more often than low-performing sites (100.0% vs. 25.0%; p< 0.01).
Conclusion: Our rheumatology provider survey identified several modifiable barriers and facilitators for DAMs collection and documentation for RA patients. These results will inform future VARA registry QI efforts and may provide useful information to improve DAMs collection and documentation in other healthcare systems.
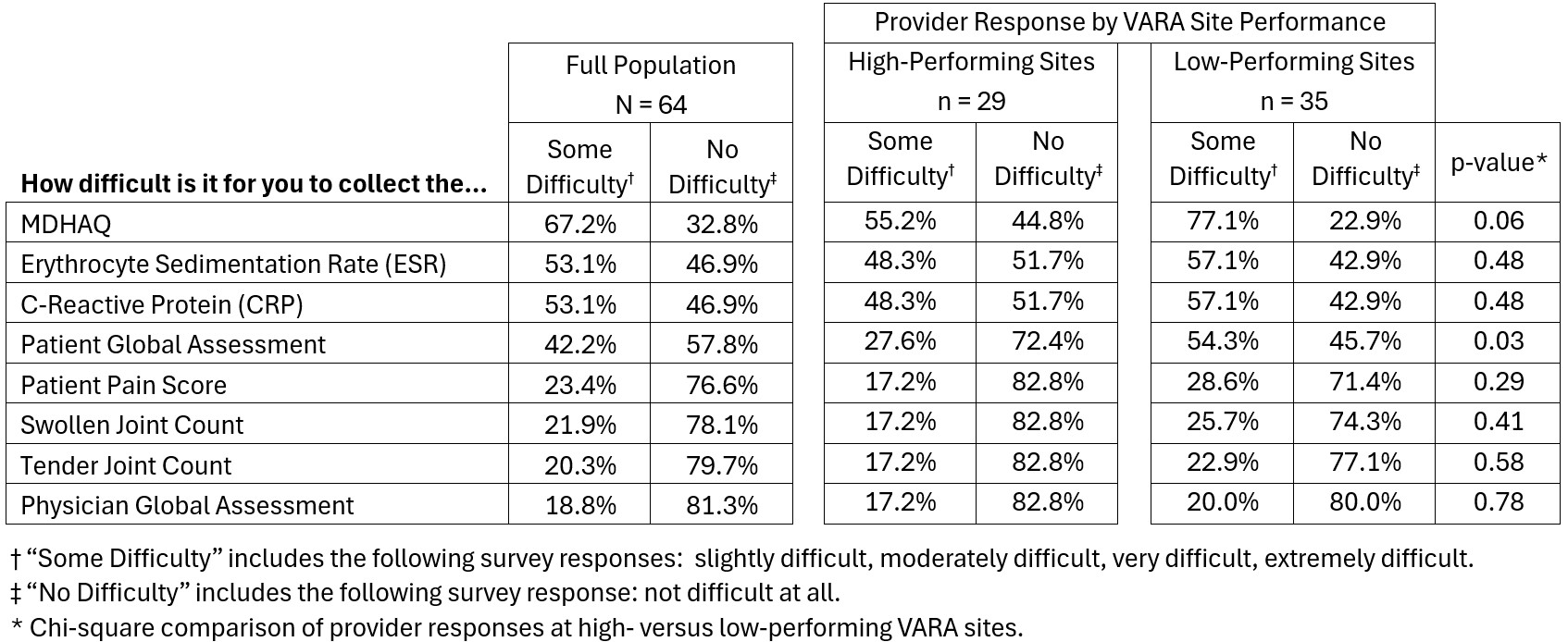 Table 1. Disease Activity Measurement Components Ranked by Difficulty of Collection based on Rheumatology Provider Responses. CRP, C-Reactive Protein; ESR, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate; MDHAQ, Multi-Dimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire; VARA, Veterans Affairs Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry
Table 1. Disease Activity Measurement Components Ranked by Difficulty of Collection based on Rheumatology Provider Responses. CRP, C-Reactive Protein; ESR, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate; MDHAQ, Multi-Dimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire; VARA, Veterans Affairs Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry
.jpg) Table 2. Barriers to Collecting Disease Activity Measures Ranked by Provider Response Frequency. CPRS, Computerized Patient Record System; CRP, C-Reactive Protein; DAMs, Disease Activity Measures; ESR, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate; VARA, Veterans Affairs Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry.
Table 2. Barriers to Collecting Disease Activity Measures Ranked by Provider Response Frequency. CPRS, Computerized Patient Record System; CRP, C-Reactive Protein; DAMs, Disease Activity Measures; ESR, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate; VARA, Veterans Affairs Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry.
.jpg) Table 3. Facilitators of Collecting Disease Activity Measure Ranked by Provider Response Frequency. Note: the “N” and “n” of the full population and high- and low-performing sites excludes providers who responded, “not currently available at my site.” CPRS, Computerized Patient Record System; CRP, C-Reactive Protein; DAMs, Disease Activity Measures; ESR, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate; VARA, Veterans Affairs Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry.
Table 3. Facilitators of Collecting Disease Activity Measure Ranked by Provider Response Frequency. Note: the “N” and “n” of the full population and high- and low-performing sites excludes providers who responded, “not currently available at my site.” CPRS, Computerized Patient Record System; CRP, C-Reactive Protein; DAMs, Disease Activity Measures; ESR, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate; VARA, Veterans Affairs Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Smith I, Tovar L, Battistone M, Barker A, England B, Shah A, Baker J, Wysham K, Wallace B, Mikuls T, Lazaro D, Schwab P, Monach P, Kerr G, Reimold A, Kunkel G, Caplan L, Richards J, Lenert A, Jones A, Danila M, Sauer B, Rojas J, Cannon G. Evaluating the Barriers and Facilitators for Collecting and Documenting Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity Measures Using a Rheumatology Provider Survey [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-the-barriers-and-facilitators-for-collecting-and-documenting-rheumatoid-arthritis-disease-activity-measures-using-a-rheumatology-provider-survey/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-the-barriers-and-facilitators-for-collecting-and-documenting-rheumatoid-arthritis-disease-activity-measures-using-a-rheumatology-provider-survey/
