Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0098–0114) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is a chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disease with strong genetic predisposition, driven by HLA-B27 and over 100 additional loci identified by genome-wide association studies (GWAS). As most risk variants lie in non-coding regions, pinpointing causal variants and their functional roles remains a major post-GWAS challenge. CARD9 encodes an adaptor protein critical for innate and adaptive immune responses, promoting NF-κB and MAP kinase activation, proinflammatory cytokine production, and Th17 differentiation—key processes in axSpA. Although the CARD9 locus is associated with axSpA, the causal variant(s) and their functional impact are still unknown. The aim of this study was to identify the functional basis for the genetic association of CARD9 variants with axSpA and its consequences on proinflammatory cytokines production.
Methods: Bayesian fine mapping on the CARD9 locus was conducted using the British subset of the IGAS Immunochip GWAS (Cortes A et al. doi: 10.1038/ng.2667). To assess regulatory effects of candidate causal variants, expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) and chromatin accessibility quantitative trait loci (caQTL) mappings were performed using RNA-seq and ATAC-seq from CD14+ monocytes, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells of 45 individuals (20 axSpA, 35 healthy controls (HC)) (Brown AC et al. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100306). Transcription factor binding disruption was evaluated via ATAC-seq footprinting with Tobias (Bentsen M et al. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18035-1) in public CD14+ ATAC-seq data from 41 controls (Stevens NE et al. doi: 10.1172/JCI171742).Finally, TNFα, IL-6 and IL-23 production was measured by flow cytometry in monocytes from 59 axSpA patients before and after stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or Candida albicans (C.alb) , and associations with candidate variant genotypes were tested using linear regression adjusting for age, sex, cell mortality, stimulation, and biologics use.
Results: Fine mapping in 4,101 axSpA patients and 9,700 HC prioritized one variant -denoted “SNVCARD9”- with >95% posterior probability of causality. This variant lies in a monocyte-specific open chromatin region upstream of the CARD9 promoter. The axSpA-risk G allele was associated with increased CARD9 mRNA expression and with enhanced chromatin accessibility in its surrounding region (figure 1). ATAC-seq footprinting predicted an allele-specific binding of the transcription factor ZBTB24. Functionally, the G allele was associated with a dose-dependent increase in IL-6 (p-value < 0.001) and IL-23 (p-value < 0.05), production but not with TNFα production (Figure 2).
Conclusion: These findings identify “SNVCARD9” as a likely causal variant at the CARD9 locus in axSpA, linking increased CARD9 expression and IL-6/IL-23 production to disease risk. This supports the functional role of CARD9 in axSpA pathogenesis and its potential as a therapeutic target in risk allele carriers.
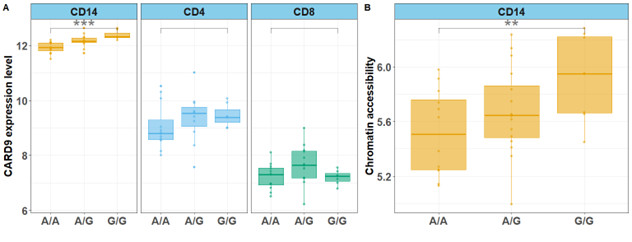 Figure 1. CARD9 mRNA expression levels in CD14+ monocytes, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (panel A) and chromatin accessibility of CD14+ monocyte-specific regulatory region upstream of CARD9 promoter (panel B) according to genotype of SNVCARD9 (axSpA-susceptibility allele : G); ** : p-value < 0.01; *** pvalue < 0.001.
Figure 1. CARD9 mRNA expression levels in CD14+ monocytes, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (panel A) and chromatin accessibility of CD14+ monocyte-specific regulatory region upstream of CARD9 promoter (panel B) according to genotype of SNVCARD9 (axSpA-susceptibility allele : G); ** : p-value < 0.01; *** pvalue < 0.001.
.jpg) Figure 2. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of IL-6 (panel A), IL-23 (panel B), and TNF alpha (panel C) in monocytes of 59 axSpA patients according to SNVCARD9 genotype in monocytes left unstimulated (“NS”) or after stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or Candida albicans (C.alb). ns: not significant * : p-value < 0.05; *** pvalue < 0.001
Figure 2. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of IL-6 (panel A), IL-23 (panel B), and TNF alpha (panel C) in monocytes of 59 axSpA patients according to SNVCARD9 genotype in monocytes left unstimulated (“NS”) or after stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or Candida albicans (C.alb). ns: not significant * : p-value < 0.05; *** pvalue < 0.001
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Costantino F, Frison E, Brown A, Cohen C, Jacoutot M, Migliorini G, Said-Nahal r, Scozzafava G, Bowness P, Wordsworth P, Garchon H, Glatigny S, Breban M, Knight J. Dissecting the Genetic and Functional Association of CARD9 with Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dissecting-the-genetic-and-functional-association-of-card9-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dissecting-the-genetic-and-functional-association-of-card9-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/
