Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is clinically present in ~10% of individuals with RA. There is recognized overlap between RA-ILD and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) with shared genetic risk, namely the MUC5B rs35705950 promoter variant. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in IPF have identified other single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) risk alleles, but GWAS in RA-ILD have been limited. We aimed to identify novel genetic risk alleles for RA-ILD in a large, multicenter RA cohort.
Methods: We utilized the Veterans Affairs Rheumatoid Arthritis (VARA) registry, a multicenter, prospective cohort of US Veterans with RA. ILD was systematically identified and validated via medical record review. All participants underwent genotyping on banked DNA via the Illumina Global Screening Array. Imputation was performed using the Trans-omics for Precision Medicine (TOPMed) imputation panel on the NHLBI TOPMed imputation server, and filtered for minor allele frequency, missingness, and Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Population stratification was accounted by ancestral principal components. GWAS was performed using SAIGE v1.3.0 (R 3.6.3) for MAF >1%. After accounting for linkage disequilibrium (r2 >0.8), variants reaching a suggestive genome-wide level of significance (p < 1x10-6) were investigated using the National Center for Biotechnology Information dbSNP database and National Human Genome Research Institute GWAS Catalog. Plots were generated using LocusZoom. A genetic risk score (GRS) for ILD was calculated using additive counts of the six significant variants weighted by the natural log of the OR compared to an additive model of the MUC5B variant alone using logistic regression.
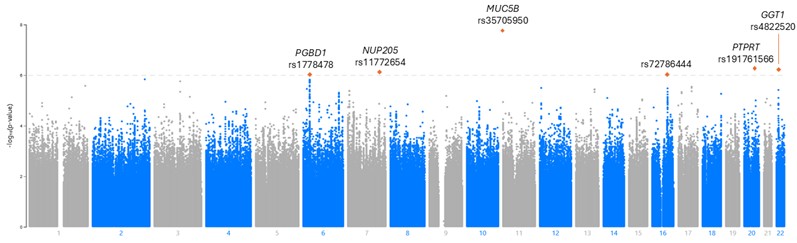
Results: We studied 3295 participants (87% male, mean age 73 years), of whom 345 had RA-ILD. A total of 28,233,561 SNPs were included. ILD signals appeared on chromosomes (chr) 6, 7, 11, 16, 20, and 22 (Figure 1). Six SNPs reached the threshold for significant associations with ILD (Table 1). As expected, MUC5B rs35705950 was the strongest risk variant for RA-ILD (Figure 2). In addition to MUC5B, we identified 5 novel SNPs. The strongest of these (rs191761566) was an uncommon variant on chr20 in the PTPRT gene, a gene implicated in the STAT3 pathway and that predicts lung cancer response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. GGT1 (chr22) is associated with IPF, NUP205 (chr7) contributes to ciliary dysfunction, PGBD1 (chr6) has been associated with RA and implicated in lung cancer, and rs72786444 (chr16) lies in a predicted enhancer region for CDH5, which is expressed in lung endothelial cells. A GRS containing the 6 variants (AUC 0.67 [0.64-0.70) significantly outperformed the MUC5B variant alone (AUC 0.57, 0.54-0.59) in discrimination of ILD in patients with RA (p< 0.001).
Conclusion: In addition to the well-established MUC5B promoter variant, this GWAS of ILD in a large RA cohort with validated ILD cases identified several other novel SNPs within genes and regions that have potential pathophysiologic connections to ILD. A GRS containing these SNPs provided significant improvement in ILD discrimination beyond MUC5B alone.
.jpg) Table 1. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease risk loci detected in genome-wide association study.
Table 1. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease risk loci detected in genome-wide association study.
Abbreviations: chromosome (chr), reference single nucleotide polymorphism (rs), minor allele frequency (MAF), odds ratio (OR)
GRCh38 position given.
.jpg) Figure 2. LocusZoom plots for top three risk loci detected by p-value.
Figure 2. LocusZoom plots for top three risk loci detected by p-value.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wheeler A, Riley T, Takei R, Baker J, Yang Y, Roul P, Wysham K, Cannon G, Kunkel G, Kerr G, Ascherman D, Monach P, Reimold A, Poole J, Mikuls T, Merriman T, England B. Genome-wide association study identifies novel genetic risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genome-wide-association-study-identifies-novel-genetic-risk-factors-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genome-wide-association-study-identifies-novel-genetic-risk-factors-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/