Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 19, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases II
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: γδ T cells serve a role in immune surveillance and their capability to traffic to tissues is fundamental to their natural biology1. They are ideal for allogeneic cell therapy as their TCR recognizes MHC-independent antigens2, avoiding the risk of graft-versus-host disease without the need for gene editing. We have developed a Vδ1 γδ CAR T cell product, ADI-001, targeting CD20 for the treatment of B cell-driven diseases including autoimmune disease. ADI-001 is designed with a 2nd generation CAR incorporating a novel fully human anti-CD20 scFv, having a distinct binding epitope than that of rituxumab, and with 4-1BB and CD3ζ signaling domains. ADI-001 is also being developed in patients with B cell malignancies (NCT04735471), offering insight into aspects of clinical safety, cellular kinetics, and pharmacodynamics that may translate favorably to autoimmune indications, including extent and duration of B cell depletion in peripheral blood and active distribution into secondary lymphoid tissues.
Methods: ADI-001 is manufactured by expanding Vδ1 T cells from healthy donors and transducing them to express the engineered CAR3. ADI-001 has been phenotypically characterized and tested both clinically in patients with B cell malignancies and in preclinical in vitro and in vivo models, including evaluation against B cells derived from patients with various autoimmune indications including SLE, SS, SSc, RA, and MS.
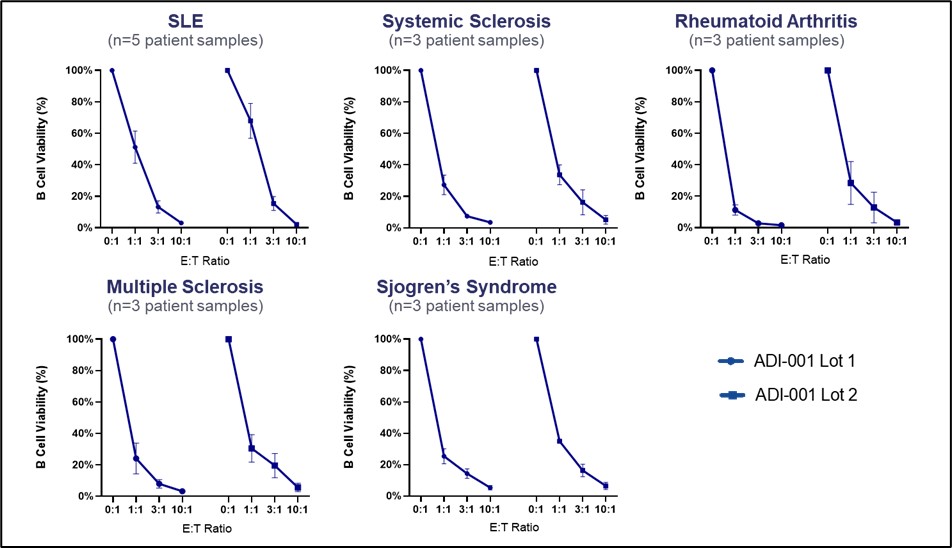
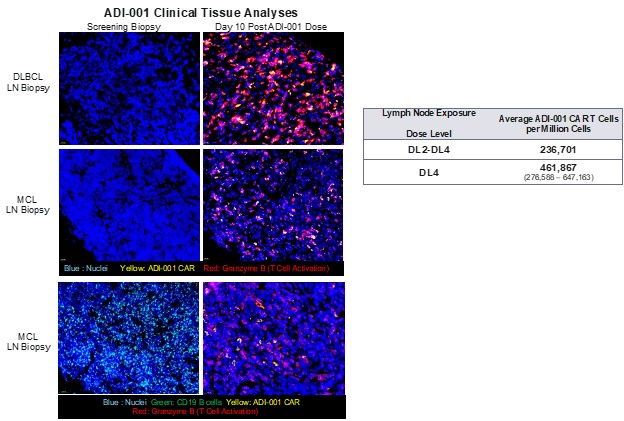
Results: ADI-001 is highly enriched for Vδ1 CAR T cells displaying a favorable differentiation phenotype associated with increased potency and persistence. When tested against transformed B cells, ADI-001 showed potent dose-dependent killing and a favorable cytokine profile with no detectable levels of IL-6 or IL-17A. Similar activity was observed against primary B cells collected from patients with a spectrum of autoimmune conditions (Figure 1). ADI-001 also inhibited growth of sub-cutaneous and disseminated transformed human B cell xenografts in NSG mice, demonstrating ability to kill B cells located in various tissues/organs. In study NCT04735471, ADI-001 showed a favorable safety profile with low incidence of CRS or ICANS, and with Cmax and AUC0-28 similar to, or exceeding, autologous CAR T products. Administration of ADI-001 with a lymphodepletion regimen was also associated with significant depletion of peripheral B cells to below detectable levels. Furthermore, analyses of post-treatment tissue biopsies confirmed robust biodistribution, CAR activation, and depletion of CD19+ B cells in secondary lymphoid tissues (Figure 2).
Conclusion: ADI-001 effectively accessed and targeted B cells in tissues/organs in preclinical and clinical settings, while also targeting primary B cells derived from patients with a spectrum of autoimmune disorders where dysfunctional B cells are implicated in disease pathogenesis. As ADI-001 demonstrated a tolerable inflammatory cytokine signature and favorable clinical safety profile, the combined features of ADI-001 represent a compelling alternative to autologous CD19-targeted CAR T cell therapies, with potential for improved efficacy against tissue-resident pathogenic B cells in autoimmune indications.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moreno M, Green S, Nishimoto K, Kennedy-Wilde J, Barca T, Au M, Costanzo S, Vosganian G, Hsu B, Galimi F, Aftab B. ADI-001: An Allogeneic CD20-targeted γδ CAR T Cell Therapy with Potential for Improved Tissue Homing in Autoimmune Indications [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adi-001-an-allogeneic-cd20-targeted-%ce%b3%ce%b4-car-t-cell-therapy-with-potential-for-improved-tissue-homing-in-autoimmune-indications/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adi-001-an-allogeneic-cd20-targeted-%ce%b3%ce%b4-car-t-cell-therapy-with-potential-for-improved-tissue-homing-in-autoimmune-indications/