Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with chronic autoimmune conditions often need expensive treatments which require prior authorizations by insurance companies. However, significant delays in these processes leave patients at risk of untreated disease. Prior authorization has been needed for many years, but recently its use has massively expanded, often to cover generic investigations and treatments [1]. The aim of this study was to compare a proprietary rule engine assisted by an OpenAI-based ML model to discern if the prior authorization process could be better informed and sped up.
Methods: Data was collected on 50 patients in a rheumatology clinic who required prior authorization for either investigations or for treatments with biological medications. The patients anonymized medical report was uploaded into the AI rule engine and simultaneously also sent to the insurance companies for approvals. The rule engine would analyze the report and classify whether the patient’s diagnosis and investigations or medications ordered were a match. This information was then compared to the data from the insurance companies.
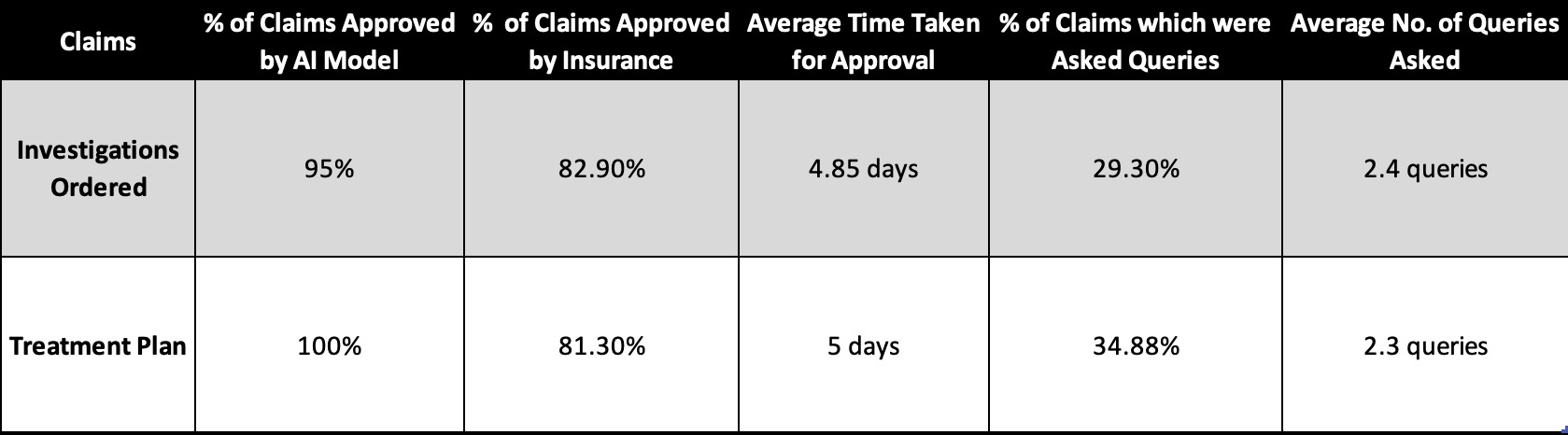
Results: Amongst the 50 patients, 41 requests were for approval of investigations and 43 were for medications. Out of the 41 approvals for investigations, the rule engine deemed, within a minute, that 95% of all investigations were appropriate for the patient’s diagnosis and symptoms. However, the data from the response of the insurance companies differs as only 82.9% of these investigations were approved with 17.1% still pending for several days and 2.4% rejected outright. Out of the 82.9% of investigations approved, 21.9% were approved within 48 hours, 46.3% took 3-6 days and 17.1% took over a week, 9% taking over 2 weeks. For 29.2% of the 41 investigations, further queries were asked, sometimes up to 5 times, with some still pending for further evaluation.
Among approvals sent for drugs, only 81.3% of the 43 requests were approved by the insurance company. However, the rule engine deemed every diagnosis and treatment plan a match. 18.6% of claims are still pending with the majority being continuously evaluated for almost a week’s time. Although 81 % of the requests were approved, 35.7% of requests are asked queries before approval, with 53.3% being asked 1-2 queries and 46.7% being asked 3-5 queries. There was an average delay of 5 days among those approved.
Conclusion: There are significant delays in prior authorizations for appropriate investigations and treatment, and these delays can have negative consequences on a patient’s health. Although most of the requests were approved by the insurance companies the process had several delays. Assistance from AI engines which include current guidelines would increase the speed at which the requests are processed. In addition, unjustified requests can be eliminated.
Reference: [1] Berg S. What doctors wish patients knew about prior authorization [Internet]. American Medical Association. 2023 [cited 2024 Jun 13]. Available from: https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/prior-authorization/what-doctors-wish-patients-knew-about-prior-authorization
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Agrawal T, Raman S, Arun J, BADSHA H. A Proprietary AI Rule Engine Assisted by an OpenAI-based ML Model Can Speed up and Better Inform the Prior Authorization Process for Rheumatology Investigations and Medications [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-proprietary-ai-rule-engine-assisted-by-an-openai-based-ml-model-can-speed-up-and-better-inform-the-prior-authorization-process-for-rheumatology-investigations-and-medications/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-proprietary-ai-rule-engine-assisted-by-an-openai-based-ml-model-can-speed-up-and-better-inform-the-prior-authorization-process-for-rheumatology-investigations-and-medications/