Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Risankizumab (RZB), an IL-23 p19 inhibitor, is well tolerated and provides long-term efficacy through 100 weeks in adults with PsA, demonstrated by the phase 3 KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2 studies (Kristensen LE, et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2024 [Epub]; Östör A, et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2024 [Epub]). Cluster analysis is a data-driven hypothesis-free unsupervised machine learning approach that can potentially inform treatment decisions. This cluster analysis classified patients into PsA phenotype clusters using baseline characteristics. The probability of response to RZB was assessed by cluster at 24, 52, and 100 weeks of treatment.
Methods: This post hoc analysis of KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2 evaluated data from bDMARD-naive adult patients with PsA. Patients in the 2 trials were required to have at least 5 tender and 5 swollen joints to be included. A finite mixture model was used to determine clusters; baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were input features. Variables with excess missing data/collinearity and patients with missing data were excluded. Optimal number of clusters and stability were assessed. Using descriptive statistics, baseline clinical and demographic characteristics were described for each cluster, as was efficacy by cluster at weeks 24, 52, and 100 for patients who received continuous RZB. Efficacy endpoints were response rates of minimal disease activity (MDA), Disease Activity in PsA low disease activity (DAPSA LDA), TJC improvement ≥ 50%, SJC improvement ≥ 50%, and clinically meaningful improvement in HAQ-Disability Index (score decrease of ≥ 0.35).
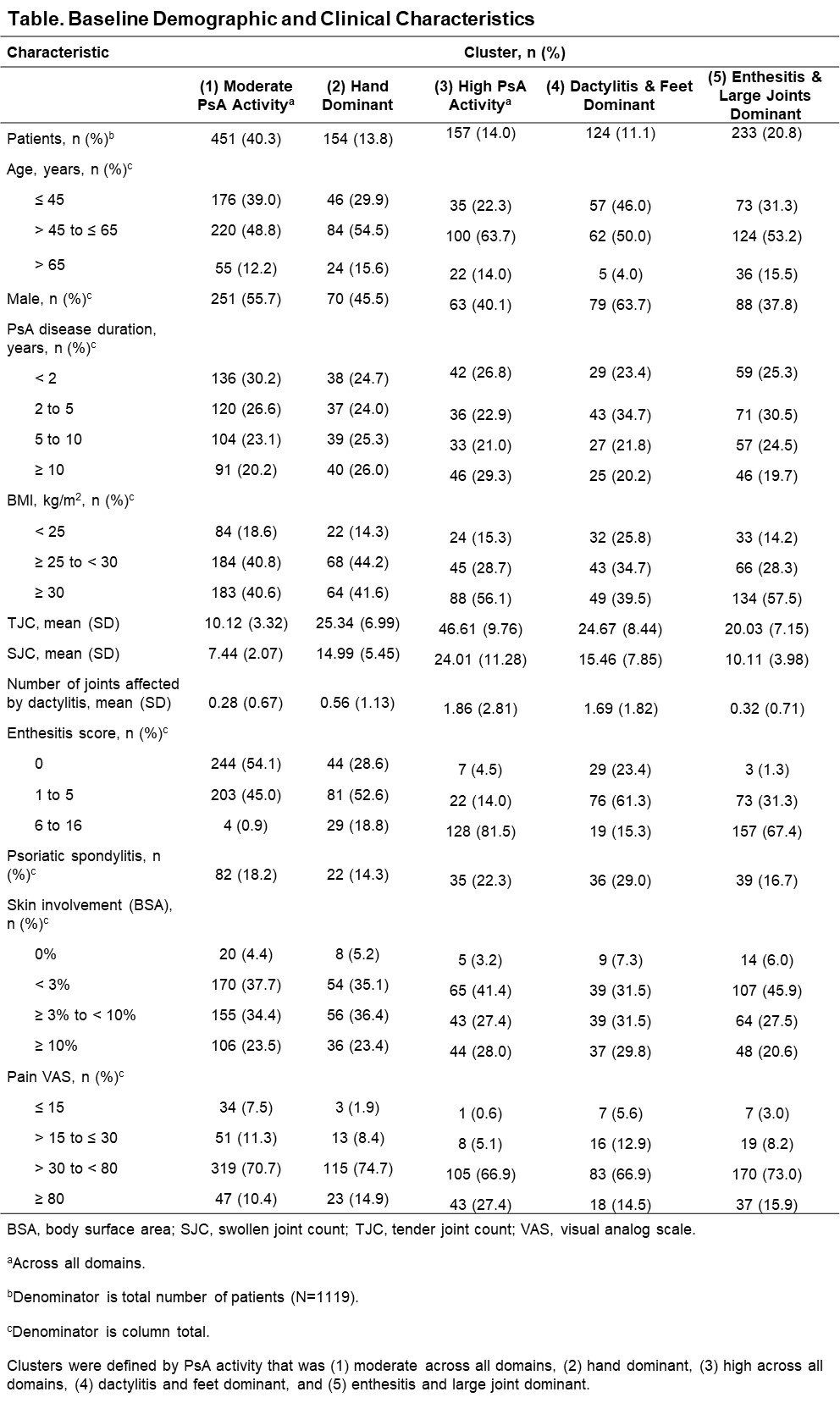
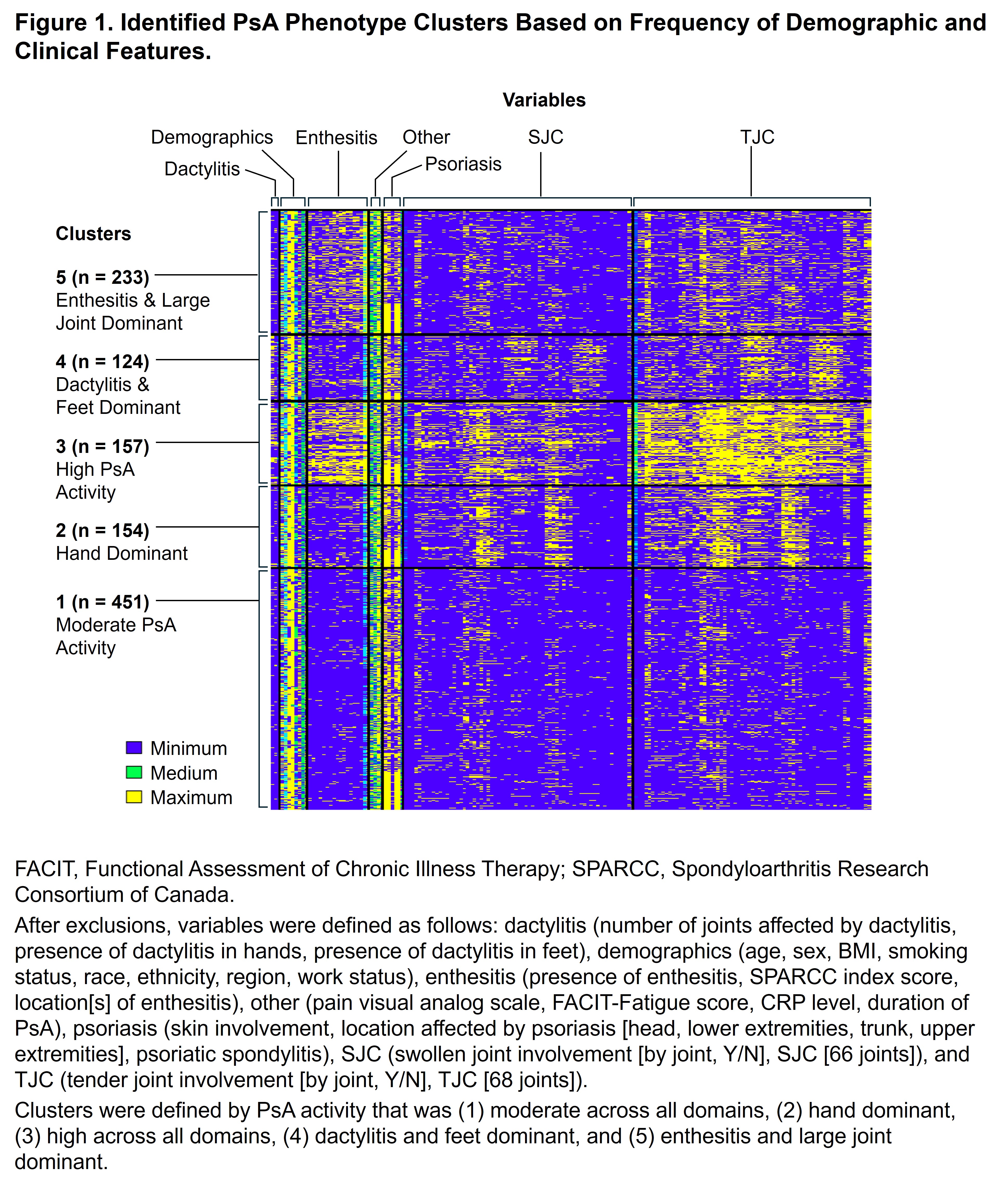
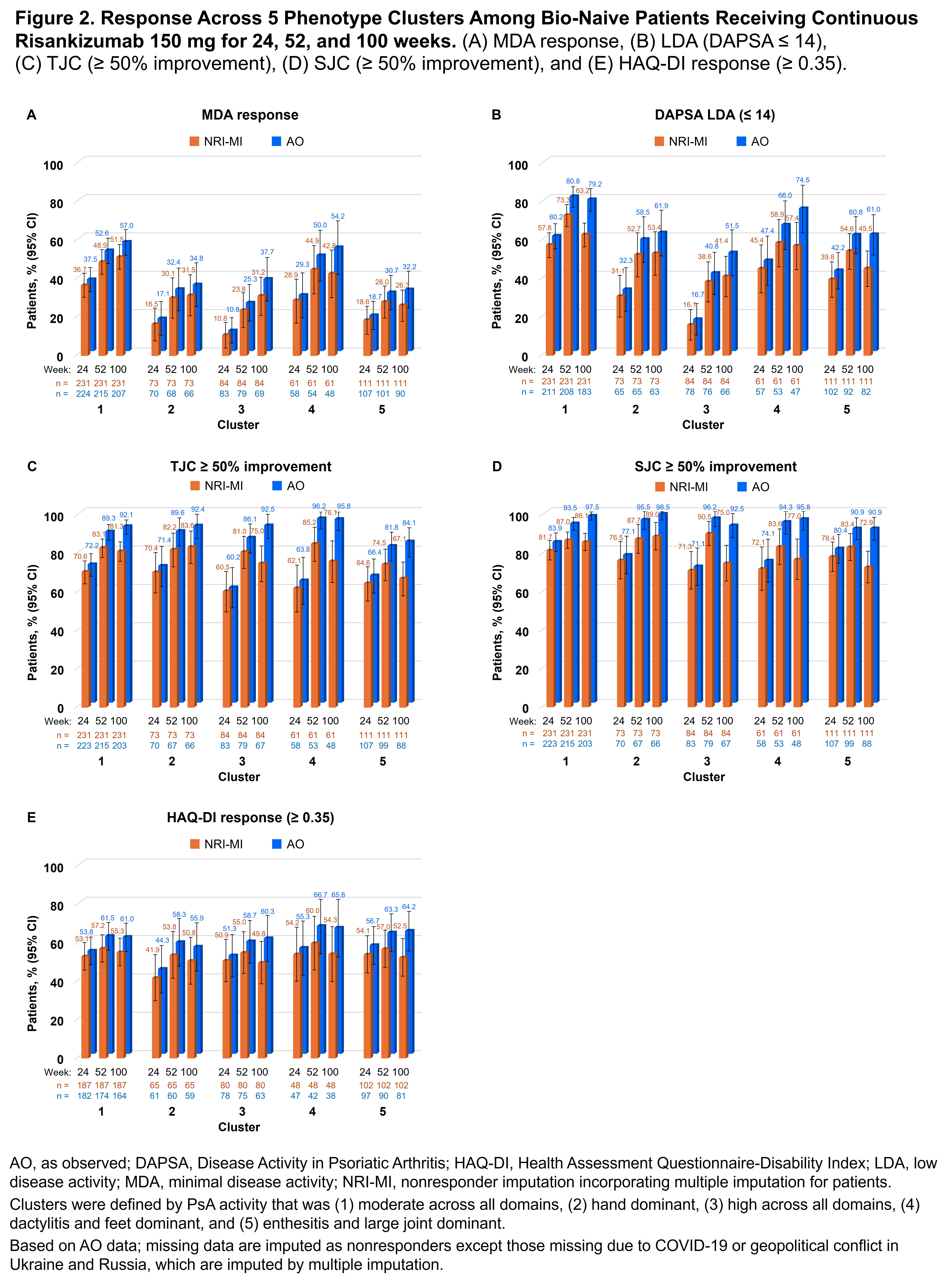
Results: Out of 1196 patients, 1119 (93.6%) were analyzed after excluding those with missing data. Five distinct phenotypic clusters were identified: patients with PsA that was (1) moderate disease activity across all domains (n [%] = 451 [40.3]), (2) hand dominant (154 [13.8]), (3) high disease activity across all domains (157 [14.0]), (4) dactylitis and feet dominant (124 [11.1]), and (5) enthesitis and large joints dominant (233 [20.8]; Figure 1). At baseline, clusters 1 and 4 were younger and had lower BMI; clusters 3 and 5 had a higher proportion of patients with BMI ≥ 30; cluster 4 had mainly male and cluster 5 had mainly female patients (Table). In patients receiving continuous RZB, the achievement of remission/low disease appeared higher in the more moderate disease activity clusters as expected, with 32.2%–57.0% of patients achieving MDA and 51.5%–79.2% DAPSA LDA at week 100; however, rates of response (change over time) appeared similar in all clusters, indicating consistent efficacy of RZB across the spectrum of PsA patients (Figure 2).
Conclusion: In this post hoc analysis, 5 distinct PsA phenotype clusters were identified based on the demographic and clinical features of PsA. RZB demonstrated efficacy across all 5 clusters through 100 weeks of treatment with notably highest achievement of remission/low disease in clusters 1 (moderate PsA activity) and 4 (dactylitis/feet dominant). These findings help to identify PsA phenotypes that may respond particularly well to RZB.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gossec L, Balanescu A, D'Agostino M, Ogdie A, Sewerin P, Deng Y, Shi L, Sugimoto Y, Zhong S, Xing Y, Lippe R, Kishimoto M. Efficacy of Risankizumab Across Distinct PsA Phenotypes Identified with Machine Learning Analytics Using Data from Biologic DMARD-Naive Patients in Two Phase 3 Clinical Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-risankizumab-across-distinct-psa-phenotypes-identified-with-machine-learning-analytics-using-data-from-biologic-dmard-naive-patients-in-two-phase-3-clinical-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-risankizumab-across-distinct-psa-phenotypes-identified-with-machine-learning-analytics-using-data-from-biologic-dmard-naive-patients-in-two-phase-3-clinical-trials/