Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Much of the evidence demonstrating the impact of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) on patients’ lives, functioning, and quality of life has come from observational research in which in-person physician assessments are not feasible. Instead, these studies rely on validated patient-reported measures of health, disease status, and outcomes. A validated patient-reported proxy of physician-assessed disease damage that has a moderate-high association with the SLICC Damage Index has been developed, but the only comprehensive patient-reported measure of SLE disease activity has no correlation with physician-assessed disease activity using the SLEDAI. We report on initial evaluations of a patient-reported measure of SLE disease activity intended as a proxy for the SLEDAI in observational research.
Methods: The study team, composed of lupus specialists at 2 institutions, developed questionnaire items to address 16 of the 24 SLEDAI domains. Except for proteinuria, domains based solely on laboratory measures were not included. For each domain, a positive response to primary questions triggers follow-up questions to increase specificity and exclude non-lupus etiology. The questionnaire was first reviewed by a plain language specialist. After revisions based on this initial review, one-on-one administrations were conducted with 5 lupus patients at each site, and further revisions made in response to patient comments. The SLEDAQ includes 38 primary items. Photographs illustrate several manifestations (e.g., rashes, vasculitis) to aid respondents. Scoring uses the same item weightings as the SLEDAI. For this evaluation, SLE disease activity was assessed via the SLEDAQ and concomitantly by study physicians via the SLEDAI and physician global assessment (PGA). To assess fibromyalgia symptoms, patients also completed the widespread pain index (WPI). Here we examine the correspondence of SLEDAQ scores with physician-completed SLEDAIs, SLEDAIs without labs, and PGAs.
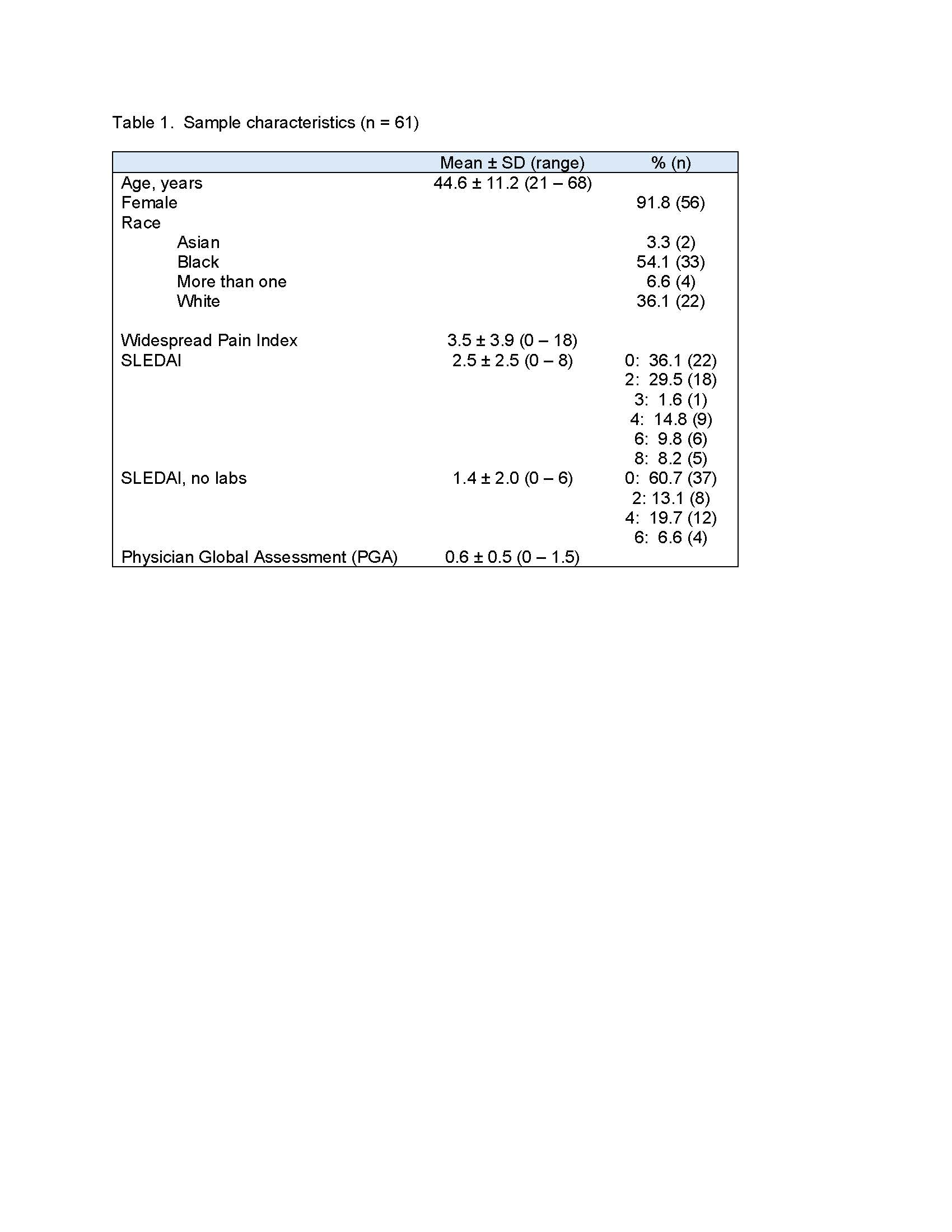
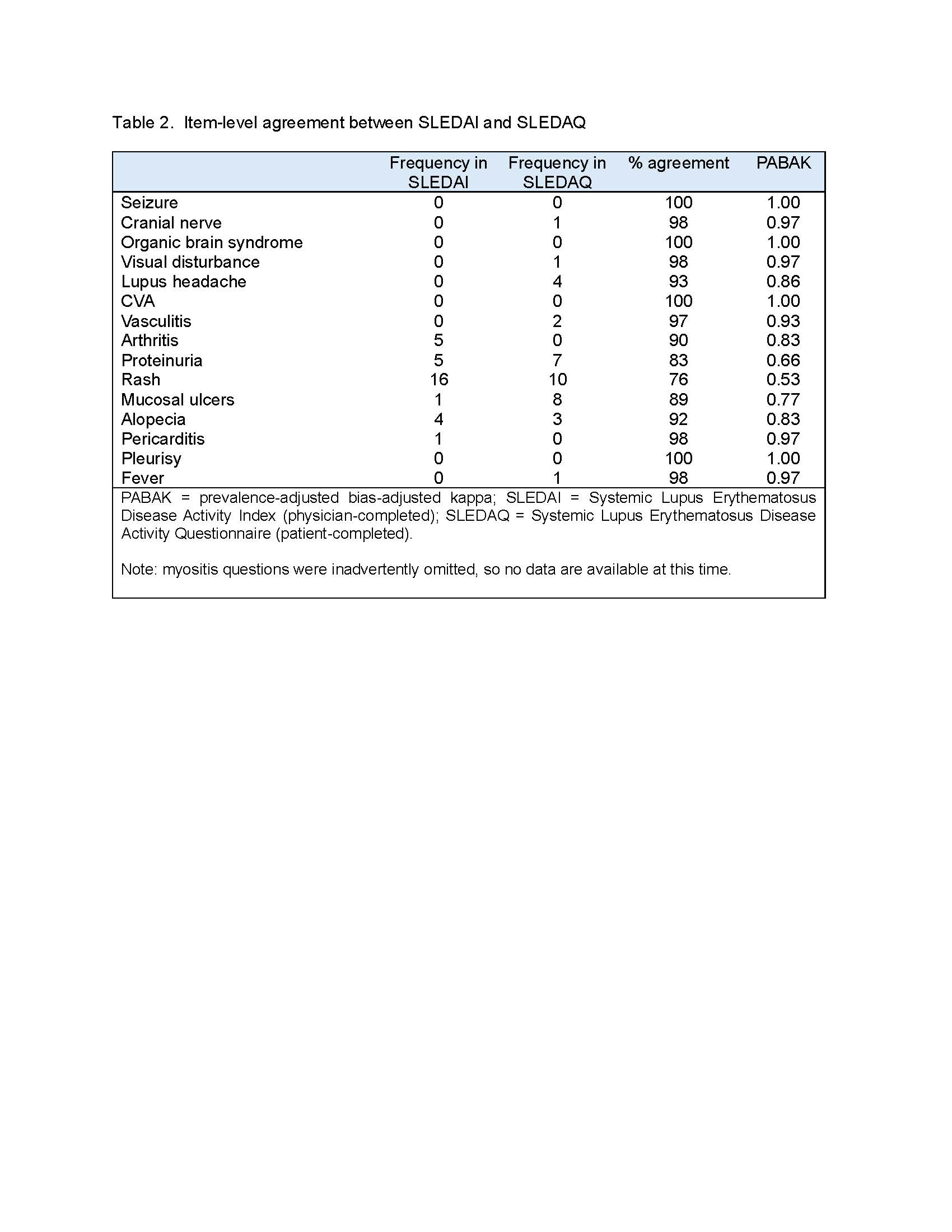
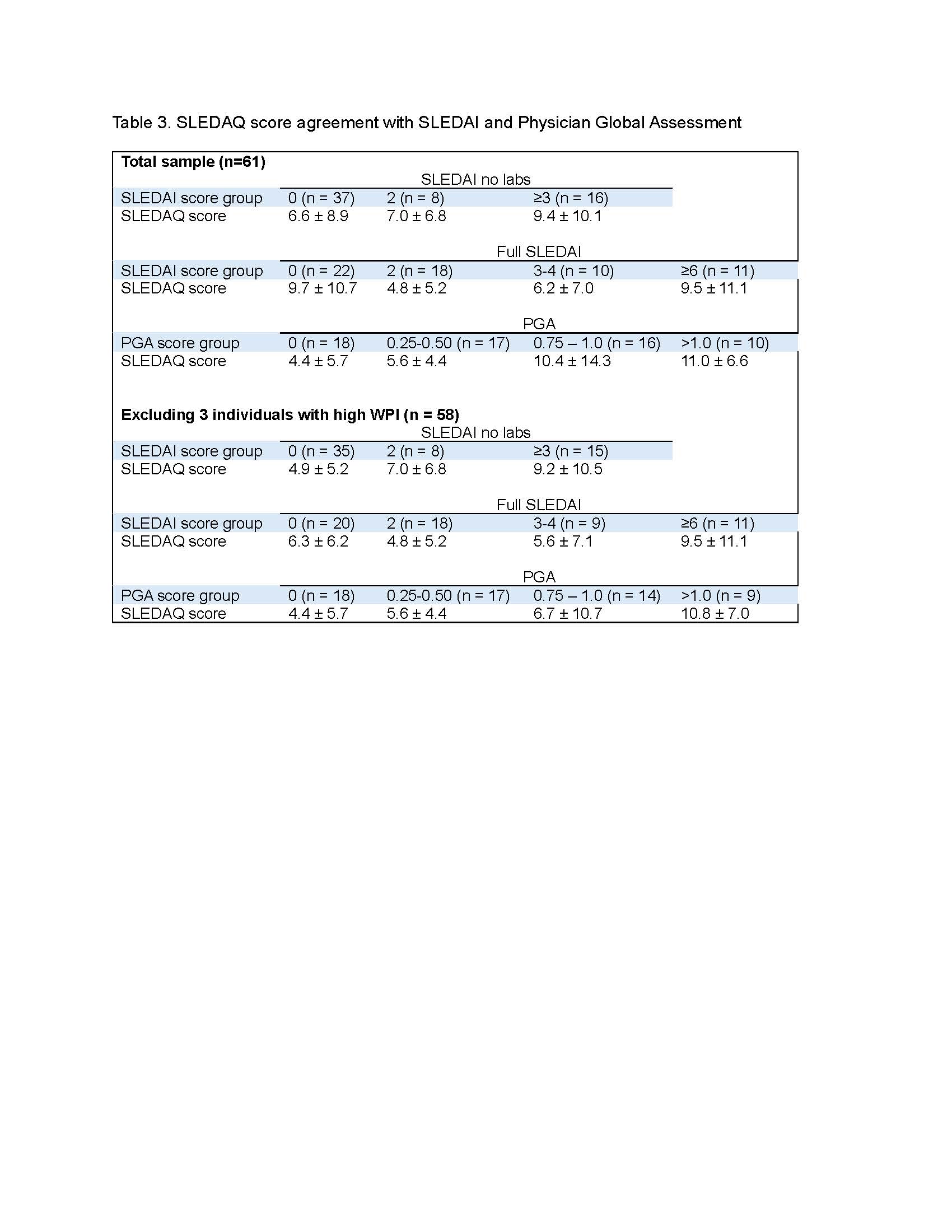
Results: To date, data from 61 patients with rheumatologist-diagnosed SLE are available. Characteristics of the sample are shown in Table 1. The majority of patients had very low SLEDAI scores (Table 1). Item-level percent agreement between SLEDAI and SLEDAQ items ranged from 75% to 100% (Table 2). All but 3 prevalence-adjusted bias-adjusted kappa values were >0.80 (Table 2). SLEDAQ scores showed reasonable correspondence with SLEDAIs without labs and PGA ratings, with scores increasing with increments of each physician-completed measure (Table 3). For full SLEDAIs, SLEDAQ showed agreement with SLEDAI scores >0; however, more than half of individuals with SLEDAI scores = 0 had SLEDAQ scores ≥6. Score correspondence improved when data from 3 individuals with very high WPIs ( >12) were removed, but SLEDAQ score for the SLEDAI=0 group remained high (Table 3).
Conclusion: The SLEDAQ shows promise as a patient-reported measure, although fibromyalgia symptoms appear to influence responses. Further work is needed to include patients with a greater range of disease activity, improve item specificity, and assess the impact of patient factors such as fibromyalgia and education on scores, other potential scoring methods, and responsiveness to change.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Katz P, Eudy A, Patterson S, Rogers J, Pisetsky D, Clowse M, Dall'Era M. Preliminary Evaluation of a Patient-Reported Version for the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI): The Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Questionnaire (SLEDAQ) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/preliminary-evaluation-of-a-patient-reported-version-for-the-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-disease-activity-index-sledai-the-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-disease-activity-questionnaire-sledaq/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/preliminary-evaluation-of-a-patient-reported-version-for-the-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-disease-activity-index-sledai-the-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-disease-activity-questionnaire-sledaq/