Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: There is a relative scarcity of studies on the effective management of Anti-signal recognition particle (anti-SRP) myositis. Recent consensus on anti-SRP myositis shows that early rituximab (RTX) is favoured over conventional immunosuppression (cIS), but the data is derived from case series without comparative studies. This study aims to a) identify distinguishing characteristics of anti-SRP-myositis, b) explore poor prognostic features, c) assess and compare the efficacy and safety of RTX with cIS in individuals with anti-SRP myositis.
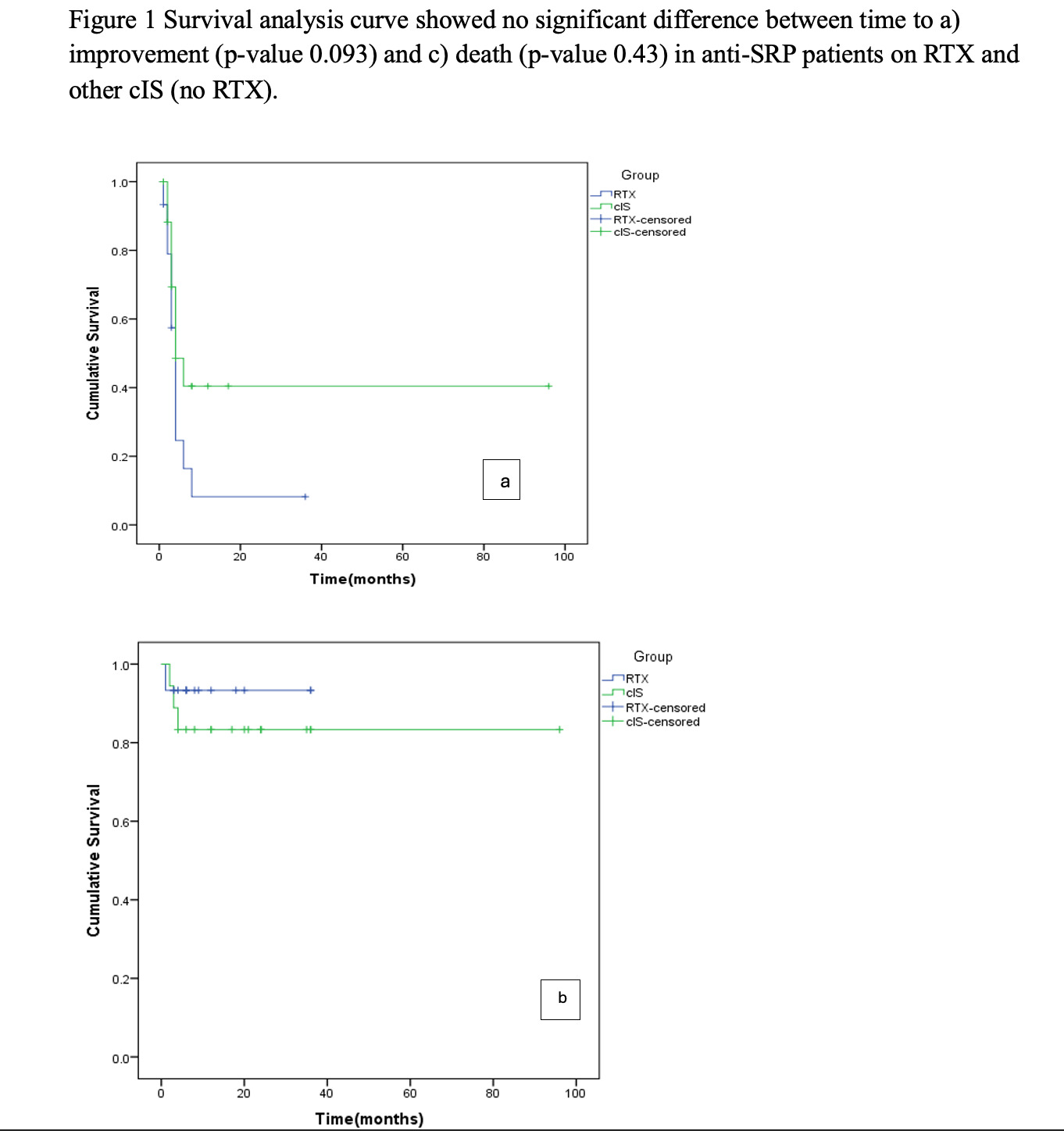
Methods: We carried out an electronic medical record (EMR) based retrospective cohort study in tertiary care centre in India. Adult patients ( > 16 years) diagnosed with myositis fulfilling either the 2017 European League Against Rheumatology (EULAR) / American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria or Peter and Bohan’s criteria were included. A total of 1033 myositis patients were screened from January 2019 to January 2024. Forty IIM patients with confirmed anti-SRP positivity fulfilling inclusion criteria with more than 4 months of follow-up were selected for the study and response analysis. Details were obtained at baseline, 4 months, and 6 months, as well as subsequent follow-up. We segregated patients into those receiving RTX and those on cIS without RTX. Treatment response was categorised as improved, worsening, or stable disease. The characteristics of patients between “RTX” and “cIS” groups were compared using a t-test for continuous data, and categorical data were compared using Chi-square/Fisher’s exact test as appropriate. Survival analysis curves were plotted for improvement and death between the two groups.
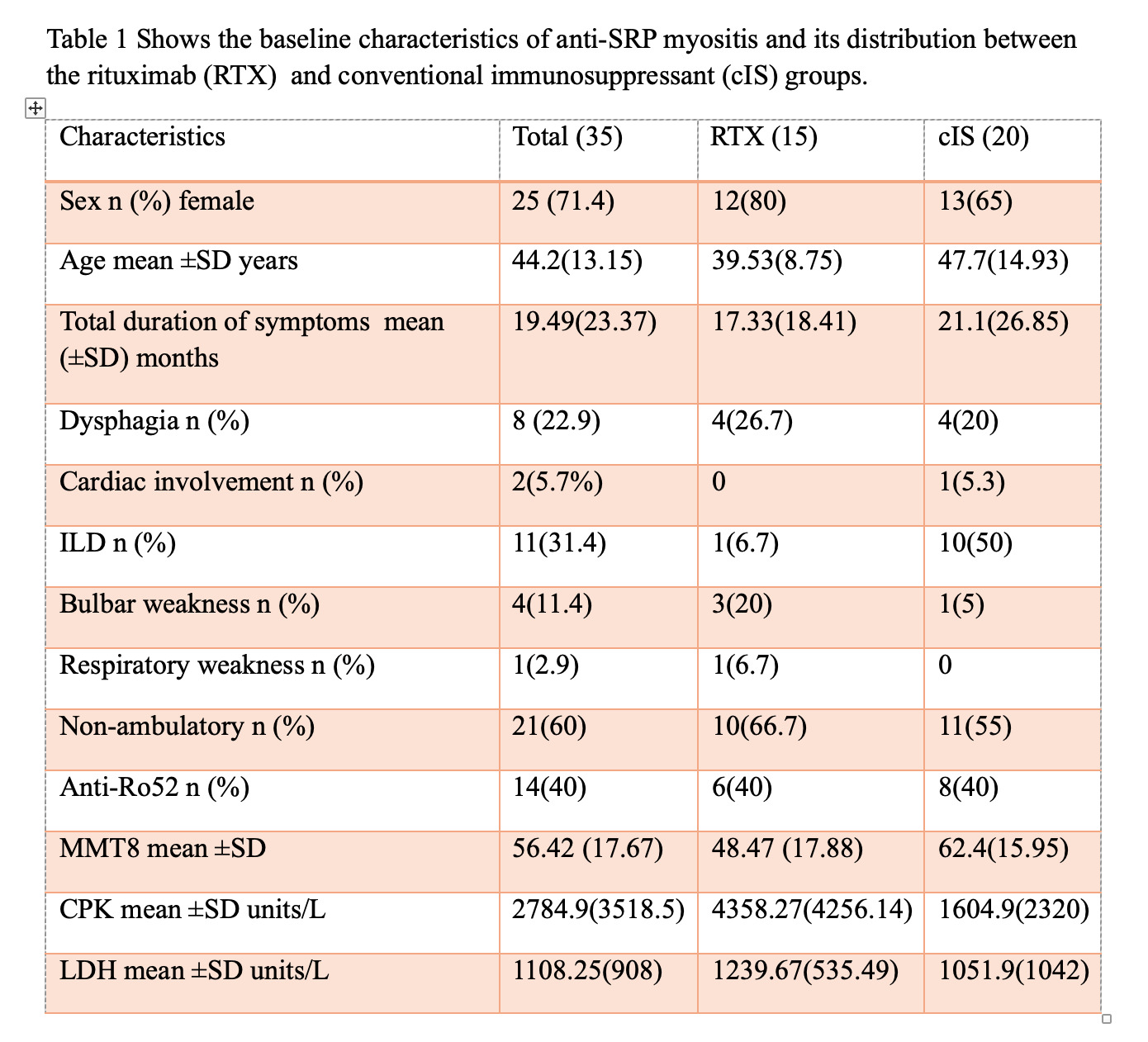
Results: The mean age of onset of anti-SRP myopathy was 44.2 (SD13.14) years; 71.4% of patients were female. Baseline characteristics are described in Table 1. No malignancies were detected in our cohort. For response analysis, we allocated 35 patients into two groups: RTX and cIS. Fifteen patients (42.85%) were given RTX (8 were treatment-naïve and 7 were refractory to cIS). While 20 received cIS (57.14%), 12/20 (60%) received mycophenolate mofetil, 8/20 (40%) received methotrexate, and 5/20 (25%) received cyclophosphamide. The median follow-up time was 12 (IQR 6-24) months. There was no significant difference in improvement between RTX and cIS groups (11/15 (73.3%) RTX group and 9/20(45%) cIS group (p-value -0.465)). Time to improvement was also not significantly different (Figure 1). However, the Mean change in MMT8 from baseline to 6 months was more in the RTX group (p-value 0.001). There was a significant decrease in mean steroid dose (prednisolone equivalent ) at 6 months post RTX with a p-value of 0.001(1600.13 mg (SD 271.53 ) in RTX versus 826.6 mg (SD 370.35) in cIS). Mortality rates stood at 1/15 (6.67 %) for RTX and 4/20 (20 %) for cIS. Unravelling predictors of mortality revealed significant associations with cardiac involvement (p value – 0.02) and severe non-ambulant muscle weakness (p value 0.03).
Conclusion: Both cIS and RTX are effective in anti-SRP myositis for muscle affection and time to response. Cardiac involvement and severe muscle weakness are associated with mortality. RTX use decreases steroid requirement.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
MANWATKAR A, Sivadasan A, Vijakrishnan a, Antony Jude Prakash J, aS c, DAS J, S N M, Ibad k i, MATHEW J. Comparing the Efficacy of Conventional Immunosuppression and Rituximab in Anti-SRP Myositis: Insights from a Tertiary Care Centre Experience [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparing-the-efficacy-of-conventional-immunosuppression-and-rituximab-in-anti-srp-myositis-insights-from-a-tertiary-care-centre-experience/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparing-the-efficacy-of-conventional-immunosuppression-and-rituximab-in-anti-srp-myositis-insights-from-a-tertiary-care-centre-experience/