Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Self-efficacy is crucial for chronic disease management. Given the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, encouraging patients to actively manage their disease may be an effective strategy for decreasing morbidity and mortality, reducing healthcare costs, and enhancing quality of life (QoL). This study explores how individuals with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs) experience work, daily activities, and social interactions while managing IIM symptoms. We observed the association between s elf-efficacy and education, disease management, QoL, pain, and fatigue among IIM patients, utilizing data from Collating the Voice of People with Autoimmune Diseases (COVAD)-3 study.
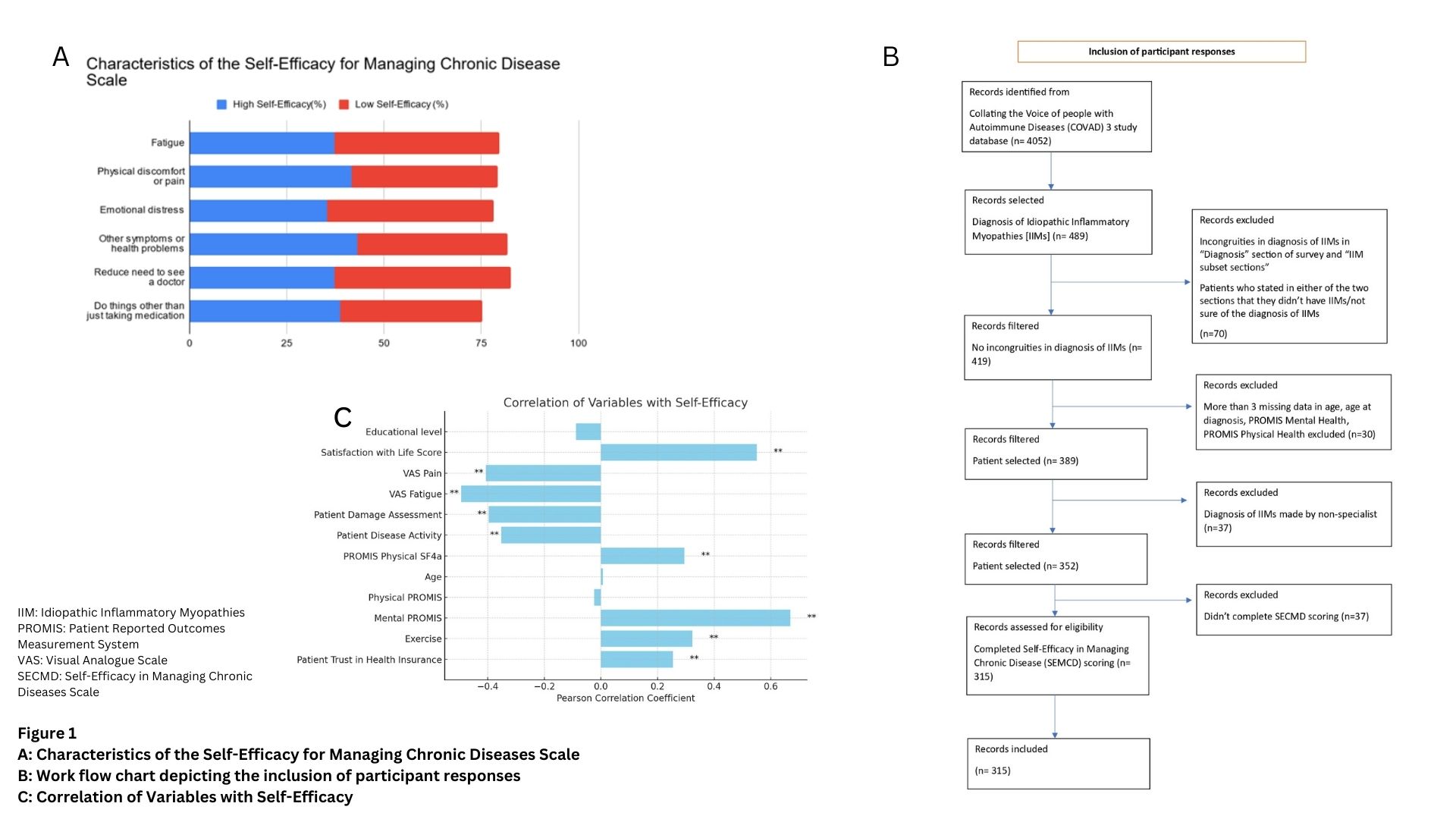
Methods: COVAD-3 is a global patient-reported survey collecting data on health outcomes using validated tools. Data was extracted in May 2024; IIM patients were assessed for self-efficacy using the Self-Efficacy in Managing Chronic Disease (SEMCD) scale. Data was categorized into two groups based on scores. Patients scoring above the 67th percentile (SEMCD 6.3) were classified as having high self-efficacy and those below the 33rd percentile (SEMCD 4.6) as low self-efficacy [Fig 1 A]. Demographic and clinical characteristics were compared between the two groups using descriptive statistics, Pearson’s correlation, and appropriate statistical tests (χ2, Mann-Whitney, or t-test).
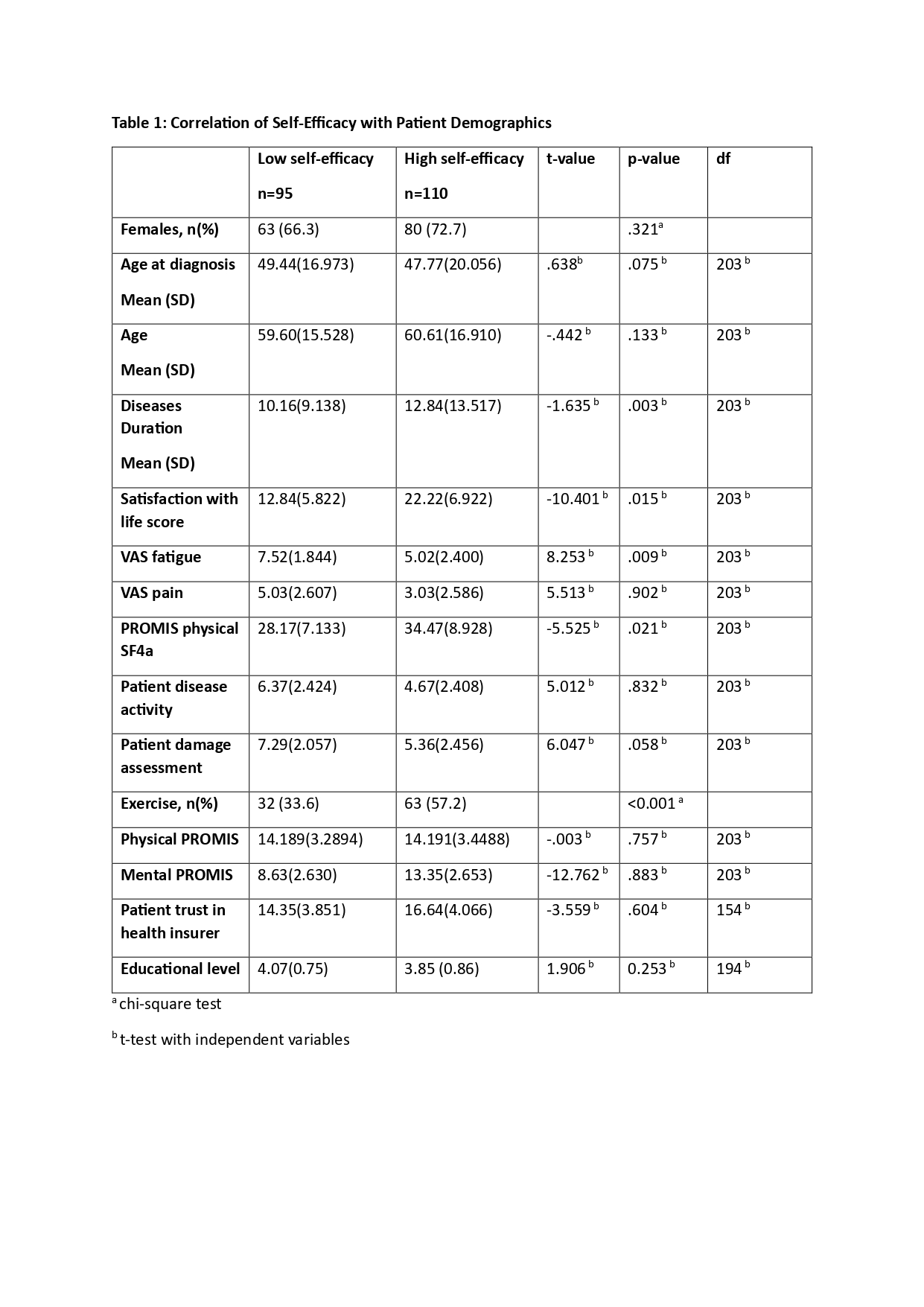
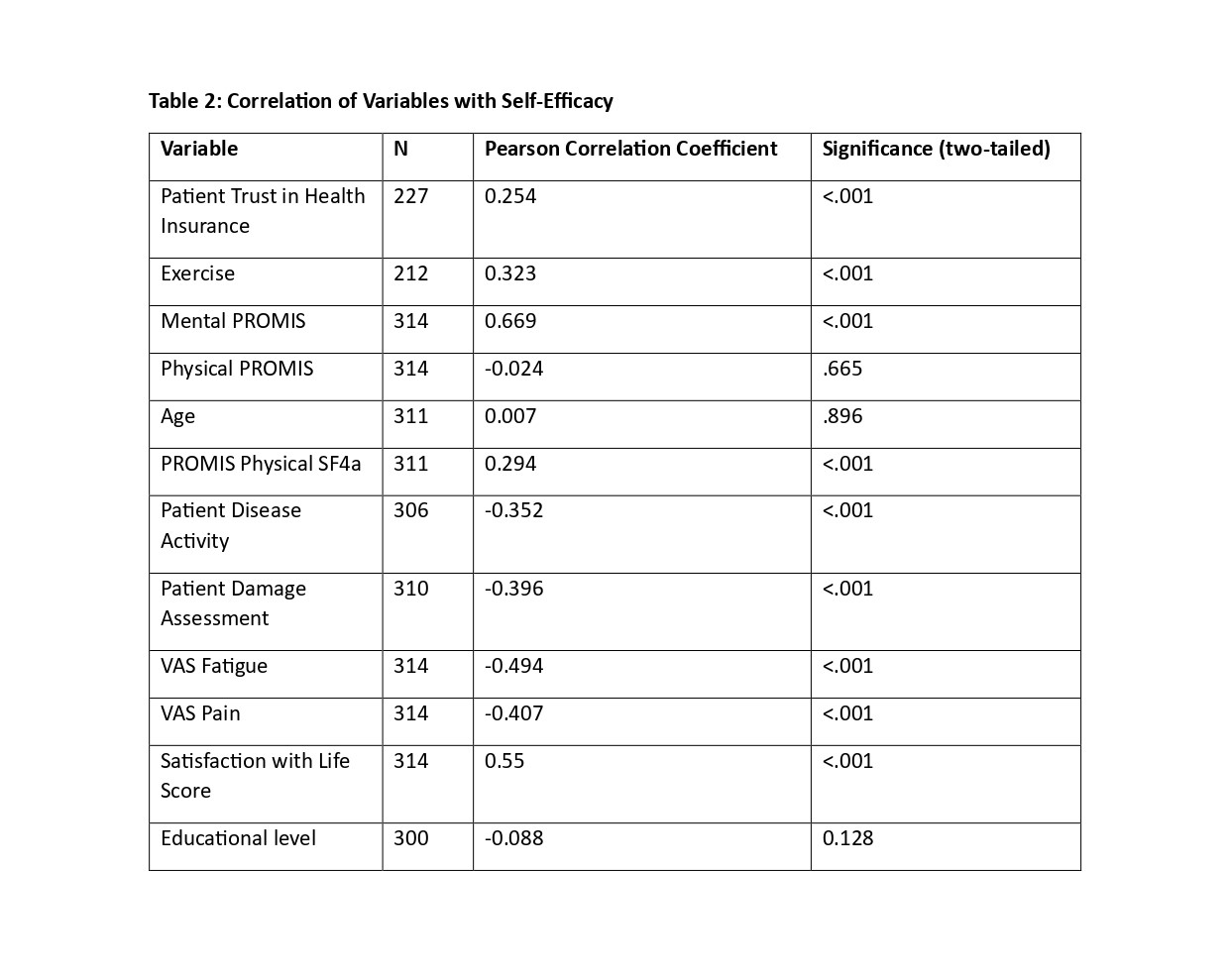
Results: Of 4,052 responses, 314 IIM patients who successfully completed SEMCD (F 228 72.6%; median SEMCD score 5.56 [range 1 -10]) were included [Fig 1B]. Based on scores, patients were stratified: 95 showed low self-efficacy scores (SEMCD < 4.3) and 110 showed high self-efficacy in managing IIMs (SEMCD >6.3). The high self-efficacy group exhibited higher satisfaction with life scores (p = 0.015), significantly longer disease duration (p = 0.003), and lower Visual Analog Scale (VAS)-fatigue scores (p = 0.009) than the low self-efficacy group. Physical function, measured by PROMIS Physical SF4a, was significantly higher in the high self-efficacy group (p = 0.021) [Fig 1C]. Furthermore, a greater proportion of individuals in the high self-efficacy group exercised regularly (p < 0.001). Interestingly, no significant difference in education level or patient trust in health provider was found with self-efficacy in IIMs [Table 1-2]. Additionally, no significant statistical difference in self-efficacy was found across IIM subgroups.
Conclusion: High self-efficacy may contribute to better physical and mental health, life satisfaction, and lower disease activity, fatigue, and pain. This underscores the importance of self-efficacy in influencing physical and psychological well-being of patients with IIMs. Healthcare providers should identify individual factors that influence self-management ability and develop strategies to facilitate communication and patient education, as this could reduce complications, healthcare costs, improve health outcomes and QoL. Thus, multidisciplinary pathways to coach patients and support group leaders can advance patient empowerment and enhance care of our patients.
A: Characteristics of the Self-Efficacy for Managing Chronic Diseases Scale
B: Work flow chart depicting the inclusion of participant responses
C: Correlation of Variables with Self-Efficacy
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
yaadav p, Pellico M, Russell A, Lanis A, Nikiphorou E, Parodis I, Saha S, Sarkar M, Parihar J, Andreoli L, Agarwal V, Gupta L. Self-Efficacy Contributes to Better Health Outcomes in Patients of Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: Insights from the COVAD 3 Dataset [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/self-efficacy-contributes-to-better-health-outcomes-in-patients-of-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-insights-from-the-covad-3-dataset/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/self-efficacy-contributes-to-better-health-outcomes-in-patients-of-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-insights-from-the-covad-3-dataset/