Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Ultra-high frequency ultrasound (UHFUS) has emerged as a promising tool for evaluating small superficial exocrine glands including lachrymal (LGs) and labial salivary glands (LSGs) in Sjogren’s disease (SD). The combined use of UHFUS and conventional US of major salivary glands may therefore allow to simultaneously visualize all the exocrine glands. A limited number of studies have explored the diagnostic potential of assessing multiple exocrine glands in patients with suspected SD. The aim of the study was to explore whether the assessment of the number of glands involved and of the severity of glandular involvement, as assessed by the presence of very hypoechoic areas (VHA), may improve patients’ diagnosis and phenotypic stratification.
Methods: Consecutive patients with suspected SD, undergoing LSG biopsy, were included. LSGs, LGs and MSGs were examined using 70 MHz, 48 MHz and 18 MHz probes, respectively. Patients were positioned supine with closed eyelids. Glandular inhomogeneity was evaluated with a semiquantitative score (OMERACT Score, 0-3). We specifically investigated the presence of VHA such as the typical findings of lymphoma described in literature and/or the new pattern characterized by the presence of multiple very hypoechoic areas grouping patients as follows: VHA absent in all the glands, VHA in either LSGs or LGs gland (single positive VHA) and VHA in both the glands (double positive VHA). Serum from each patient was tested for anti-Ro52, anti-Ro60, and anti-SSB/La abs, evaluating the quantitative titer of the autoantibodies with band densitometry. Descriptive statistics were performed using SPSS.
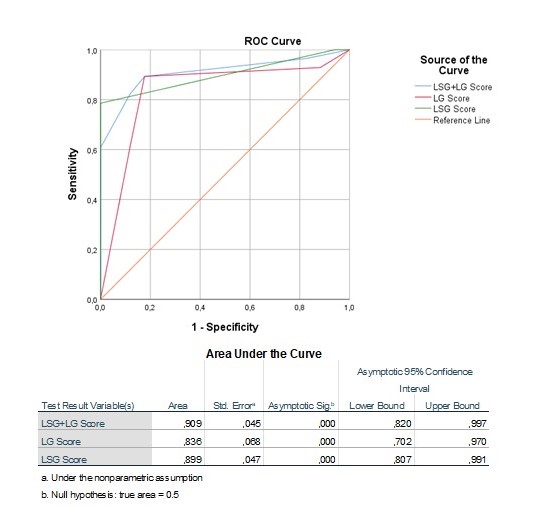
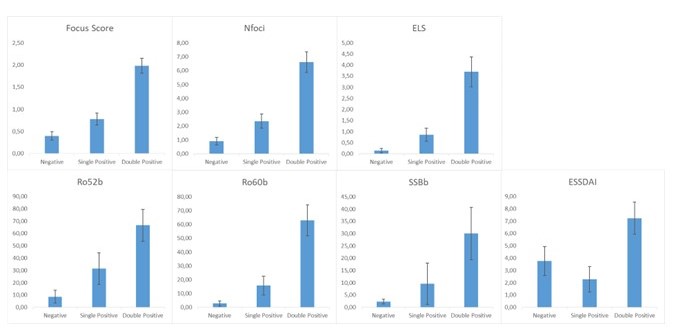
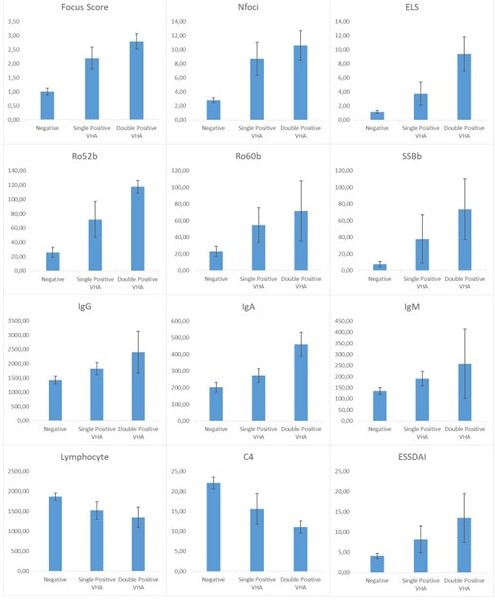
Results: A total of 71 subjects (10 males and 61 females) were evaluated. Out of them, 28 met the ACR2016 criteria for SD. The k-Cohen concordance between LGs and LSGs in gray scale was 0.600 (p< 0.001), between MSGs and LSGs was 0.553 (p=0.001) and between MSGs and LGs was 0.425 (p=0.013). ROC curve analysis indicated that LGUHFUS and LSGUHFUS, at the optimal cut-off value of 2, identified SD and sicca controls with good diagnostic accuracy (AUC=0.836, 95%CI: 0.702-0.970 and AUC=0.899, 95%CI: 0.807-0.991). The sum of the score showed an excellent accuracy (AUC=0.909, 95%CI: 0.820-0.997, Fig. 1) with all the subjects presenting a UHFUS score >2 in both LSGs and LGs receiving the diagnosis of SD. Subjects with a positive UHFUS score in all the salivary and lachrymal glands (double positive) showed higher inflammation at the tissue level, autoantibody titers, and ESSDAI activity compared to subjects with UHFUS abnormalities only in the lachrymal or salivary glands. Patients with a UHFUS < 2 in all the glands had the lowest values of tissue inflammatory biomarkers and autoantibody titers (Fig. 2). As the presence of VHA in the glands increases, histological inflammatory biomarkers, autoantibody titers, immunoglobulin levels and ESSDAI increase, whereas C4 and lymphocyte levels decrease (Fig. 3).
Conclusion: Evaluating multiple exocrine glands with UHFUS increases the diagnostic power of traditional ultrasound. Furthermore, as in joint ultrasound, an increase in the number and severity of exocrine glands is associated with higher patient activity, as measured by ESSDAI, and biohumoral activity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fulvio G, Izzetti R, Donati V, Porciani C, Fonzetti S, La Rocca G, Navarro García I, Ferro F, Baldini C, Mosca M. Quantifying Sjogren’s Disease Burden: UHFUS Evaluation of the Number and Severity of Involved Exocrine Gland [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantifying-sjogrens-disease-burden-uhfus-evaluation-of-the-number-and-severity-of-involved-exocrine-gland/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantifying-sjogrens-disease-burden-uhfus-evaluation-of-the-number-and-severity-of-involved-exocrine-gland/