Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a large-vessel vasculitis affecting the large vessels from aorta, its proximal branches, and the extra-cranial arteries. To avoid ischemic events, e.g. irreversible visual loss, securing correct diagnosis and treatment is important. Instant confirmation or rejection of GCA is pivotal, as clinical, biochemical, imaging and histopathological signs of GCA may normalize few days after initiation of high-dose glucocorticoid. In addition, unnecessary and prolonged high-dose glucocorticoid should be avoided in those without GCA. Vascular ultrasound (US) is recommended as the first-line diagnostic tool in GCA (Dejaco C et al.: Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024;83:741-751). Our GCA Fast-Track Clinic (FTC), covering a population of approx. 900.000 in Copenhagen, Denmark, aims to see patients within one office day upon referral. Instant access for general practitioners and other hospital specialties has been a hallmark, and even persons with a low suspicion of GCA are accepted when referred.
The purpose of this retrospective study is to describe disease manifestations and diagnostic findings in patients seen in our FTC during a 12-month period in 2018-19. Further, to analyze the time required to diagnose or rule out GCA, as well as the number of malignancies found in the diagnostic process and the number of deaths occurring in the cohort.
Methods: All patients seen in the FTC during the period was included in the analysis. Patients, irrespective of clinical presentation, initially had an US of bilateral temporal-, facial-, axillary and common carotid arteries by a rheumatologist trained and experienced in vascular US. Immediately thereafter, patients were seen by a senior rheumatology consultant who was aware of the US-findings. Decisions on the need for further diagnostic tests were up to this rheumatologist.
From electronic patient report files, we retrospectively evaluated clinical- and US-findings, results from other diagnostic tests (temporal artery biopsy and [¹⁸F]Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography computed tomography), the final diagnosis and the number of days required to establish it. The number of deaths occurring in the cohort until Dec. 31st, 2023 was recorded.
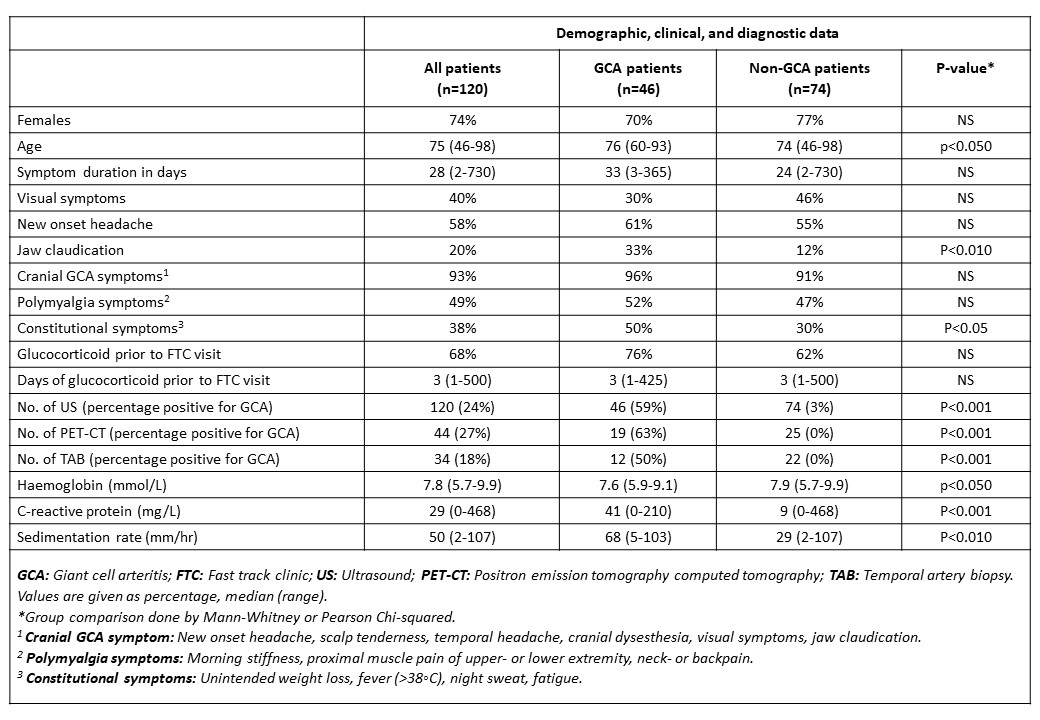
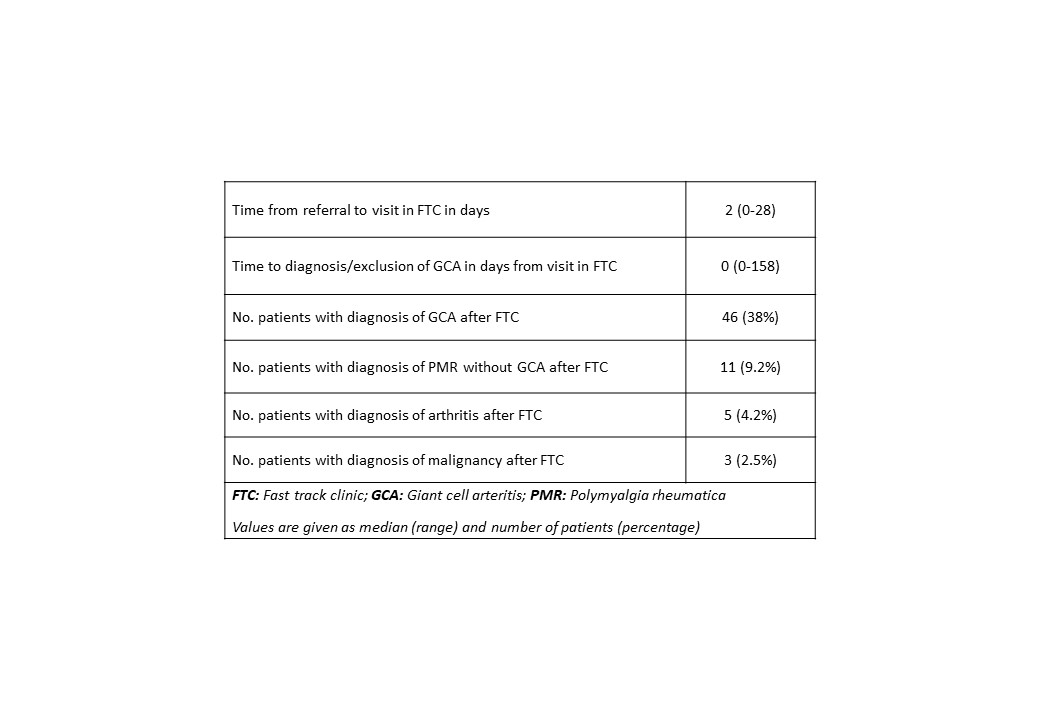
Results: In 12 months, 120 patients were seen in the FTC. Of these, 46 (38%) were finally diagnosed with GCA. See table 1 for demographic and clinical data. Diagnosis or exclusion of GCA, were obtained on the first day in the FTC in 53% of patients. When further diagnostic tests or observational time was needed, the time to diagnosis increased markedly (up to 158 days). Malignancy was found in 3 patients (lung, colon, kidney). A total of 15% of the patients had died after a median of 580 days (50-1598) during a median follow-up of 58 months (no statistical difference between GCA and non-GCA patients).
Conclusion: In our GCA FTC, an instant diagnosis was obtained in 53% of patients based on clinical findings, US and available paraclinical data, thereby limiting the need for further diagnostic tests in almost half the patients. This study also underlines vascular US as an important tool for clinical decision making in GCA. The observed occurrence of cancer in the cohort was low, but the overall mortality was surprisingly high.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moller Dohn U, Fromberg Gorlen T, Westergaard R, Fana V, Møller T, Terslev L. Disease Manifestations, Diagnostic Findings, and Mortality of 120 Consecutive Patients Suspected of Giant Cell Arteritis – Results from a Hospital GCA Fast-Track Clinic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-manifestations-diagnostic-findings-and-mortality-of-120-consecutive-patients-suspected-of-giant-cell-arteritis-results-from-a-hospital-gca-fast-track-clinic/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-manifestations-diagnostic-findings-and-mortality-of-120-consecutive-patients-suspected-of-giant-cell-arteritis-results-from-a-hospital-gca-fast-track-clinic/