Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The study aimed to evaluate changes in enthesis areas in ankylosing spondylitis patients in remission for at least six months, using either NSAIDs or biological agents. It aimed to assess the effects of these treatments on enthesis inflammation and potential disease modification.
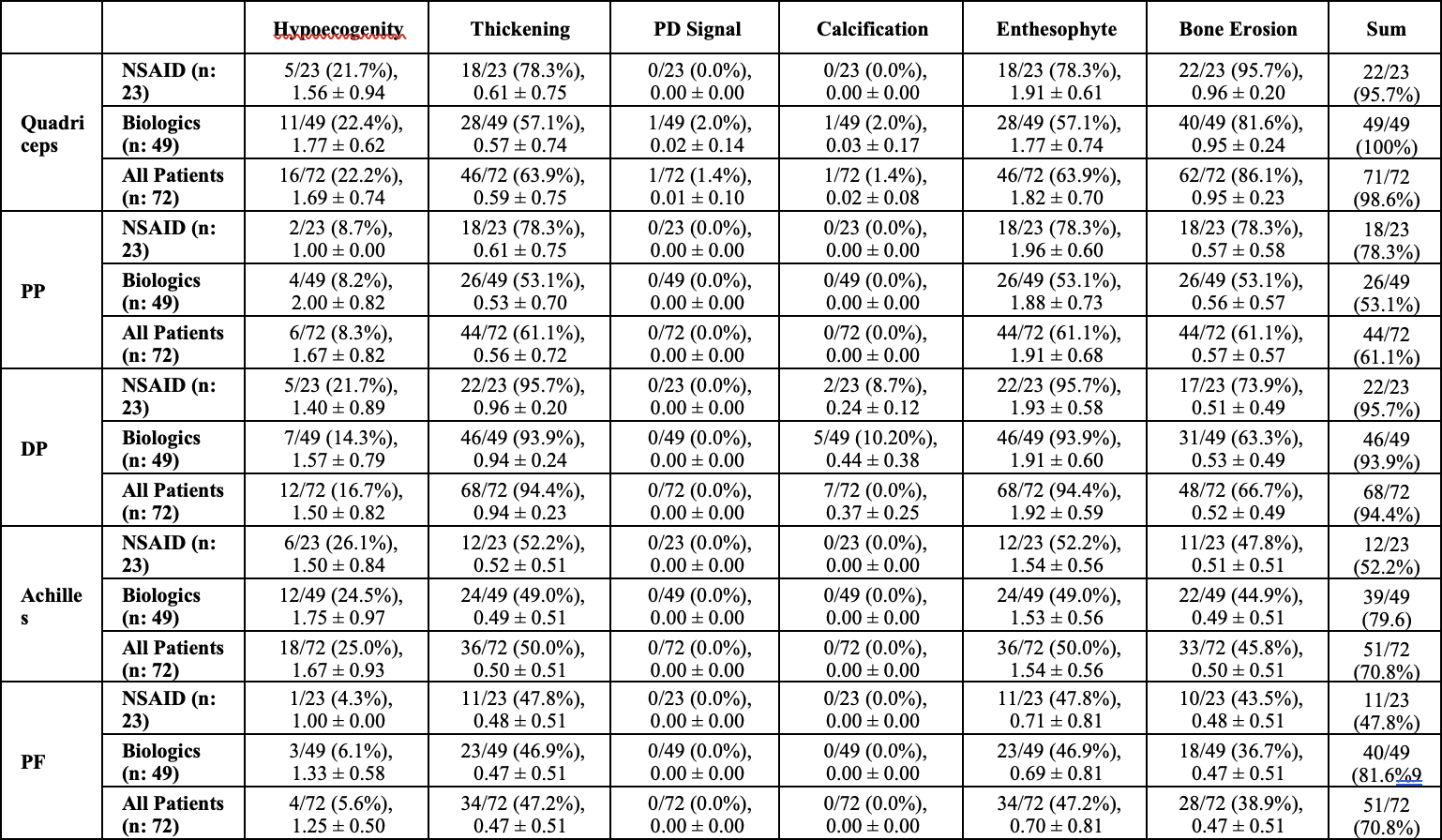
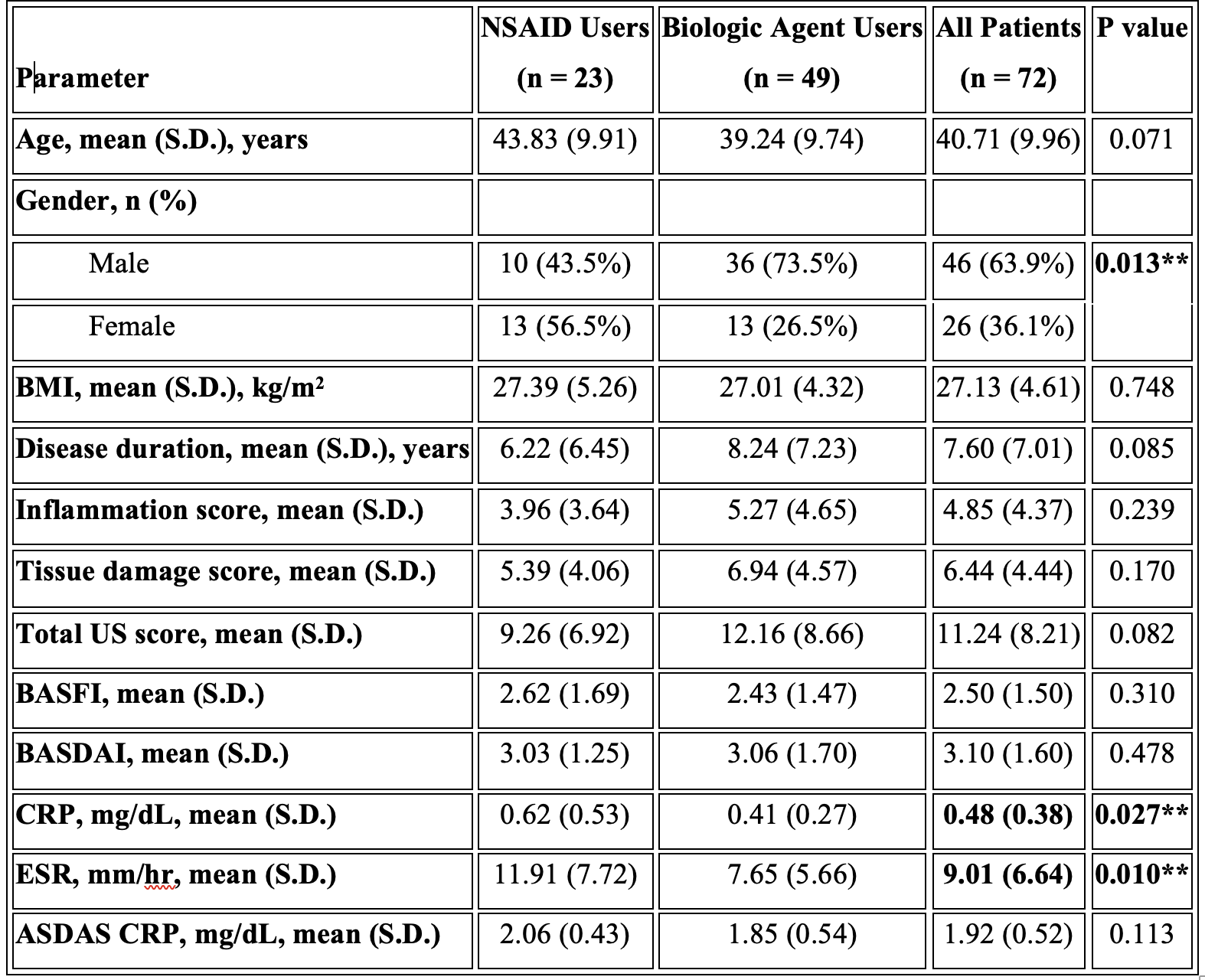
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, 72 ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients were divided into two groups: biological agent users and NSAID users. All patients underwent a clinical examination and ultrasound (US) scanning of 10 entheses by an experienced rheumatologist blinded to the physical examination findings. The US assessment evaluated the presence and severity of elementary lesions, including hypoechogenicity, thickening, power Doppler signals, erosions, enthesophytes, and calcifications. An inflammation score was calculated based on thickness increase, hypoechogenicity, and power Doppler scores, while a chronicity score was calculated from erosion, calcification, and enthesophyte scores. This study aimed to compare the US findings between the biological agent and NSAID user groups, providing insights into the structural and inflammatory changes in the entheses of AS patients receiving different treatment approaches.
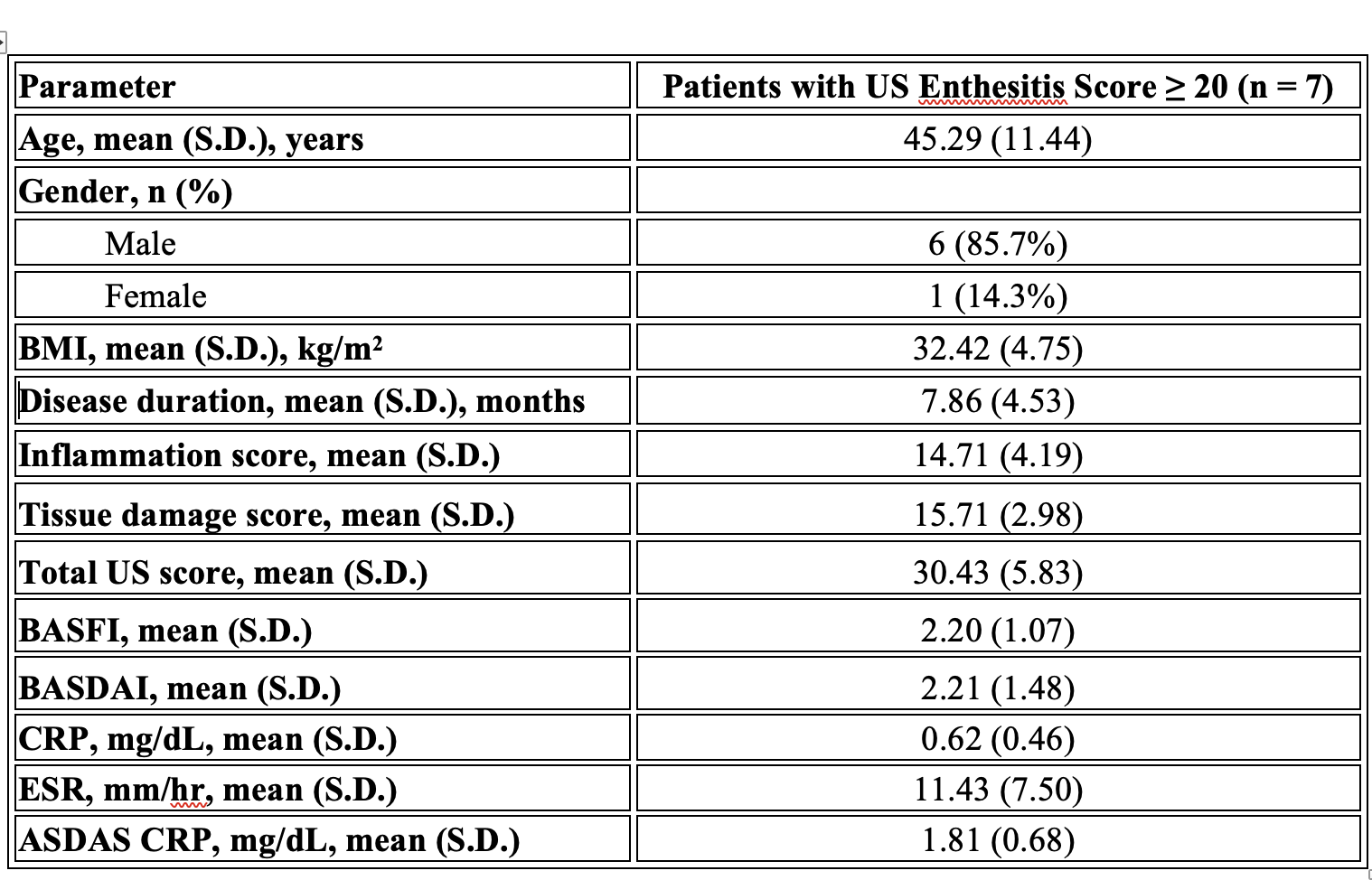
Results: In our study, 98.6% of the quadriceps tendon, 61.1% of the proximal patellar tendon, 94.4% of the distal patellar tendon, 70.8% of the Achilles tendon and 70.8% of the plantar fascia had at least one of the six parameters. The most common pathologies seen in all patients were hypoechogenicity, thickening, enthesopathy, and bone erosion (Table 1). In our study’s ASDAS assessment using CRP, the mean score of NSAID users was 2.06 ± 0.43, while the mean score of biological agent users was 1.85 ± 0.54. However, this difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.113). The mean inflammation score was 4.85, the mean tissue damage score was 6.44, and the total US enthesitis score was 11.24 in all patients (Table 2). Seven patients had a total enthesopathy score of > 20 points. The mean inflammation score was 14.71, the mean tissue damage score was 15.71, and the mean total enthesopathy score was 30.43 (Table 3). Treatment changes were made in five of the seven patients, taking into account their conditions and preferences. The mean inflammation score, tissue damage score, and total US enthesopathy scores improved by an average of five points in five patients within one month.
Conclusion: Our study can indicate that even more objective evaluations, such as ASDAS CRP, may be incomplete in assessing low disease activity or remission. In addition, similar US enthesopathy scores were measured in patients in remission using both NSAIDs and biological agents. ASDAS CRP < 2.1 and BASDAI < 4 in all patients receiving effective treatment. However, is the treatment adequate? Our US evaluation detected at least one finding in 98.6% of patients in the quadriceps tendon and 70.8% in the Achilles tendon. These results suggested that an objective assessment such as the US should be integrated into the total assessment. The favourable treatment modification results in five patients emphasised the importance of US findings and the necessity of combination therapies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Koç E, Okyar B, Bakırcı S, Badak s, Demir A, Uçar İ, Sargın G, Yüce S, Ersözlü E. Is the Remission Achieved with Asdas, Basdaı a Real Remission? Should Ultrasound Be Added to the Parameters? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/is-the-remission-achieved-with-asdas-basdai-a-real-remission-should-ultrasound-be-added-to-the-parameters/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/is-the-remission-achieved-with-asdas-basdai-a-real-remission-should-ultrasound-be-added-to-the-parameters/