Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Varying mechanisms of action are required to address the needs of rheumatoid arthritis patients with different levels of severity. Since 2010, all new FDA DMARD approvals have been Janus Kinase inhibitors (JAKi) and Interleukin-6 inhibitors (IL-6i), each utilizing a combination of different populations in efficacy studies submitted for approval. The purpose of this study was to investigate the efficacy of these recently approved DMARDs relative to the populations included in each study, to see how population in study design had an impact on efficacy endpoints.
Methods: A systematic literature review was performed on primary and secondary endpoints of all FDA-approved DMARDs since 2010 and analyzed by population. To select trials, FDA reviews for each approval were analyzed and all trials used to support efficacy for the product labels were included. Endpoints analyzed and averaged included ACR20, ACR50, ACR70, and other common measures. All data were collected from relevant publications for each trial and missing data were integrated from published data on ClinicalTrials.gov. Data were reported at 12, 14, or 24 weeks, depending on study design, and values included in this review are for marketed drug doses or placebo.
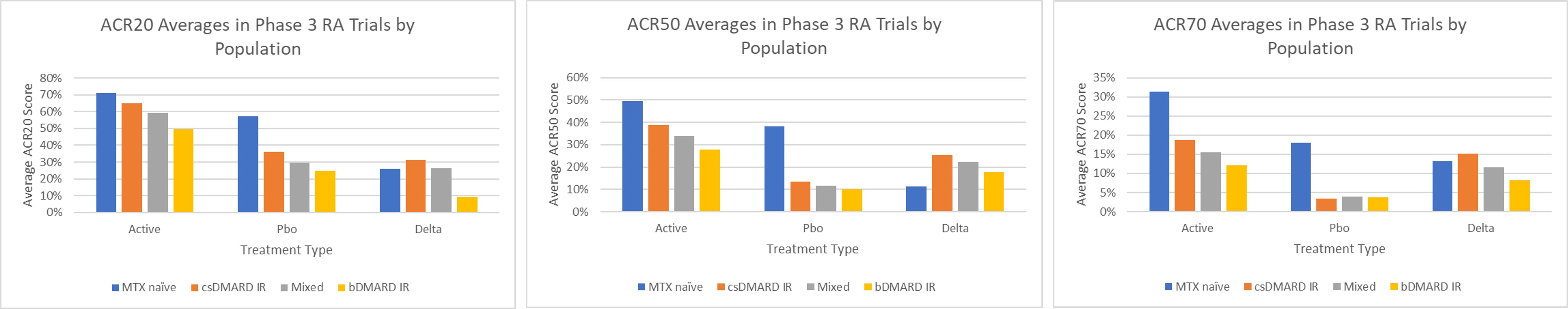
Results: Twenty-two RCTs for tocilizumab, tofacitinib, sarilumab, baricitinib, and upadacitinib with 14,096 patients were included. Populations were divided into 4 categories for this analysis: 1) methotrexate naïve (MTX naïve); 2) conventional synthetic DMARD inadequate responder (csDMARD IR); 3) mixed population of csDMARD IR, biologic DMARD IR, and biologic DMARD naïve (Mixed); and 4) biologic DMARD inadequate responder (bDMARD IR). Across ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70, the rank order of scores remained consistent in the active treatments, with responses from highest to lowest: MTX naïve, csDMARD IR, Mixed, and bDMARD IR. For ACR20, active treatment scores, respectively, were 70.9%, 65.2%, 59.2%, and 49.5%. ACR50 scores were 49.5%, 38.7%, 34.0%, and 27.8%, and ACR70 scores were 31.3%, 18.7%, 15.5%, 12.1%. In placebo treatments, the same rank order was seen for ACR20 and ACR50, excluding ACR70 where the bDMARD IR, Mixed, and csDMARD values were within 0.4% of one another. ACR20 scores were 57.3%, 36.1%, 29.7%, and 24.6% and ACR50 values were 38.3%, 13.5%, 11.7%, and 10.1%. For ACR70, the placebo values were 3.5% (csDMARD IR), 3.8% (bDMARD IR), 3.9% (Mixed), and 18.1% (MTX). The deltas between active and placebo arms overall across the populations were relatively similar, except the MTX naïve population which is explained by placebo arm being actually an active MTX arm versus compound monotherapy.
Conclusion: Clinical trial population selection can yield different efficacy outcomes across various metrics. Common primary endpoints in rheumatoid arthritis trials, particularly ACR20, 50, and 70, are consistently affected in a pattern reflecting progressively lower responses with higher treatment resistance, though the delta compared to placebo seems to be relatively preserved. Future studies should continue to evaluate varying population types to increase the breadth of their efficacy analyses.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Emanuel C, Aggarwal A. Comparison of the Efficacy of DMARDs in Phase 3 Trials of Different Populations Used in FDA Approvals for Rheumatoid Arthritis Since 2010 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-the-efficacy-of-dmards-in-phase-3-trials-of-different-populations-used-in-fda-approvals-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-since-2010/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-the-efficacy-of-dmards-in-phase-3-trials-of-different-populations-used-in-fda-approvals-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-since-2010/