Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoantibody mediated disease with deforming peripheral arthritis. Autoantibodies widely used are rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated peptide antibody (ACPA). 20 – 25% of patients of RA are seronegative which might hinder early diagnosis. South Asian studies on anti-Carbamylated Protein antibodies (anti-CarP) in RA were limited. In this study, we measured anti-CarP antibodies among DMARD naïve early RA patients and their correlation with standardized disease activity indices (DAI).
Methods: The primary objective was to study the correlation of anti-CarP antibodies with disease activity indices among RA patients depending on their RF and ACPA status. We evaluated the frequency of occurrence of anti-CarP and analysed the ultrasound (US) wrist and hand findings in these patients. Patients diagnosed as RA with duration less than 2years who were DMARD naïve were consented and recruited. Serum anti-CarP antibodies were measured using quantitative Human anti-CarP ELISA kit from MyBiosource. The association of anti-CarP antibodies with DAI (DAS28CRP, DAS28ESR, CDAI, SDAI) were compared depending on their RF and/or ACPA antibody profile. All patients underwent US of wrist and MCP joints of both hands, results of which were made into scoring system – 6 joint US score (1). The 6 joint US score (US6 score) includes grey scale synovial hypertrophy and Power doppler graded according to OMERACT guidelines of the bilateral wrist and bilateral 2nd and 3rd MCP joints. The composite score of US6 is being graded based on severity into 0- no activity, 1-12 – mild activity, 13-24 -moderate activity and 25-36 – severe activity. The statistical analysis was done using SPSS. The ethical clearance had been obtained from the institutional review board
Reference 1. Kawashiri et al. The power doppler ultrasonography score from 6 simplified synovial sites. Rheumatology(Oxford) vol. 50.5 (2011):962-5
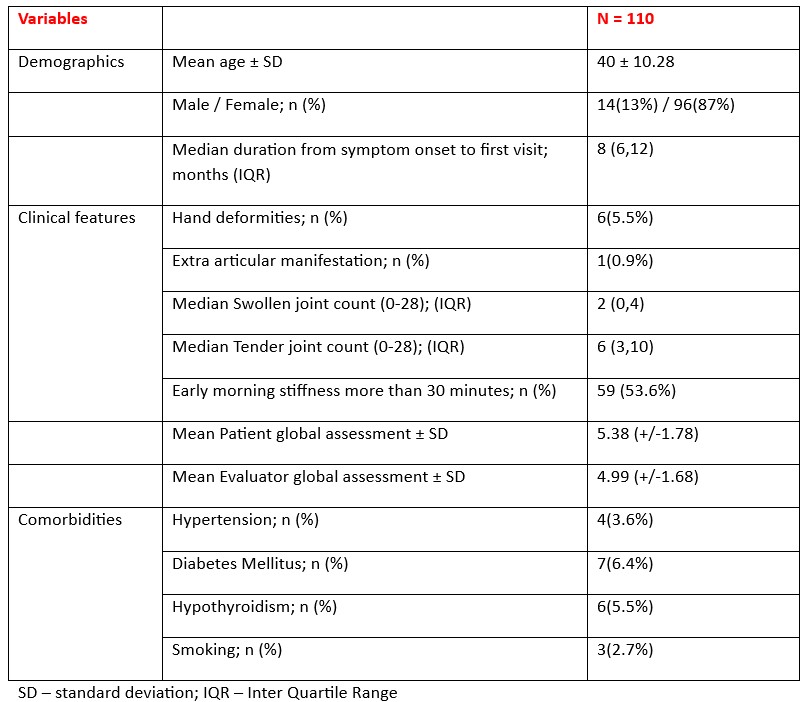
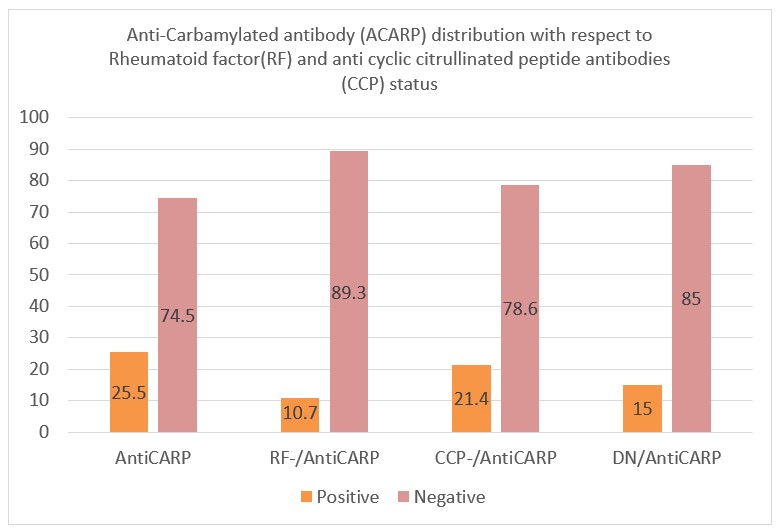
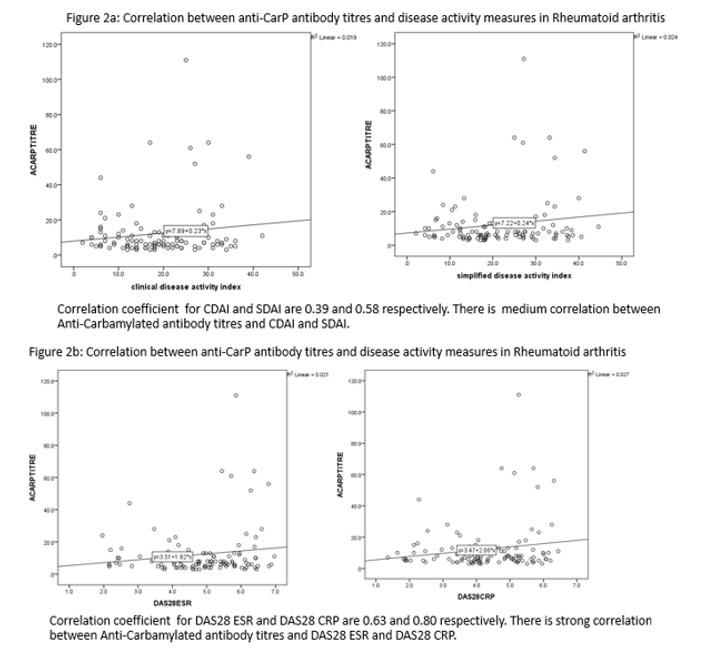
Results: 110 patients were included in the study of which 87% were females. Demographics and clinical features are shown in table1.Both RF and ACPA were positive in 81 patients (73.6%). The percentage of patients with high disease activity were 24.5% in CDAI, 45.5% in SDAI, 47.3% in DAS28 ESR, 31.8% in DAS28 CRP respectively. Anti-CarP were positive in 28 patients (25.5%). AntiCarP percentages with respect to other antibodies are shown in figure 1. There was significant correlation between anti-CarP antibody titres and all disease activity measures. Spearman coefficients of Anti-CarP with CDAI, SDAI, DAS28 ESR and DAS28 CRP were 0.039, 0.058, 0.063, 0.080 respectively (Figure 2). Median value for US6 score was 9 (IQR 4,13). Moderate activity via US6 score was seen in 16 patients (57.1%). US erosions in any of the examined joints were seen in 18 out of 28 Anti-CarP positive patients (64.3%)
Conclusion: There was significant correlation in anti-CarP antibody titres with disease activity measures in DMARD naive RA patients. US study showed moderate activity and erosions in more than half of the anti-CarP positive patients. This study showed that anti-CarP antibodies have the utility in the diagnosis and activity assessment of early RA patients
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
aS c, Joseph J, MANWATKAR A, Mathew J. Utility of Anti-Carbamylated Antibodies in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis in South Asian Population [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utility-of-anti-carbamylated-antibodies-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-south-asian-population/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utility-of-anti-carbamylated-antibodies-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-south-asian-population/