Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
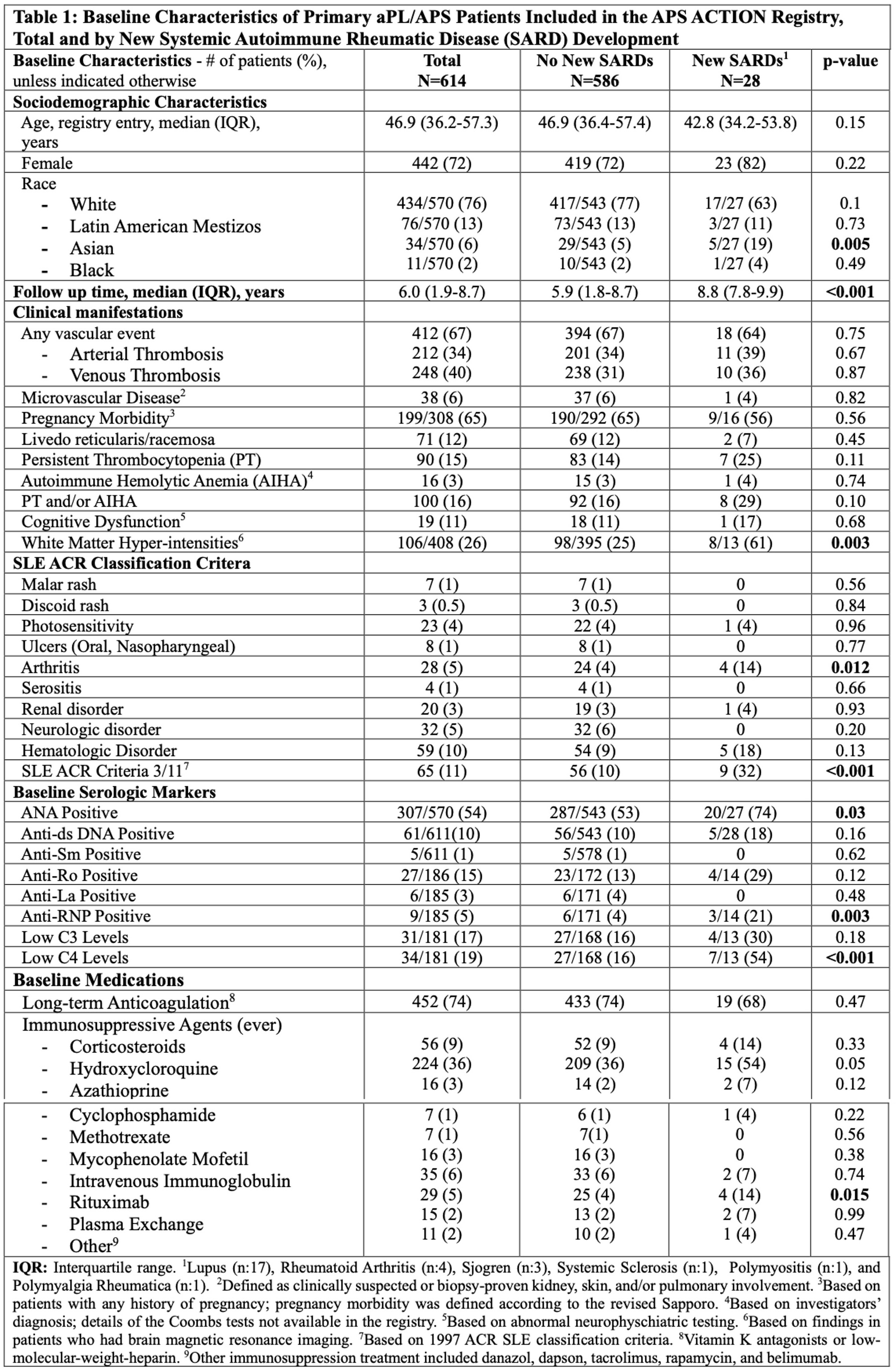
Background/Purpose: APS ACTION “Registry” was created to study the natural course of disease in persistently antiphospholipid antibody (aPL)-positive patients with/without other systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs). Our objective was to determine the risk and predictors of developing additional SARDs during the prospective follow-up of primary aPL-positive patients with/without antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) classification (primary aPL/APS).
Methods: A web-based data capturing system is used to store patient demographics, aPL-related history, 1997 Updated ACR Lupus Classification Criteria, and medications. The inclusion criteria for the registry are positive aPL according to the Revised Sapporo Classification Criteria, tested within one year prior to enrollment. Patients are followed every 12±3 months with clinical data and blood collection. In this prospective analysis, based on primary aPL/APS patients who had at least one-year follow-up visits, we report the incident risk and predictors of new SARDs using Cox proportional hazards model.
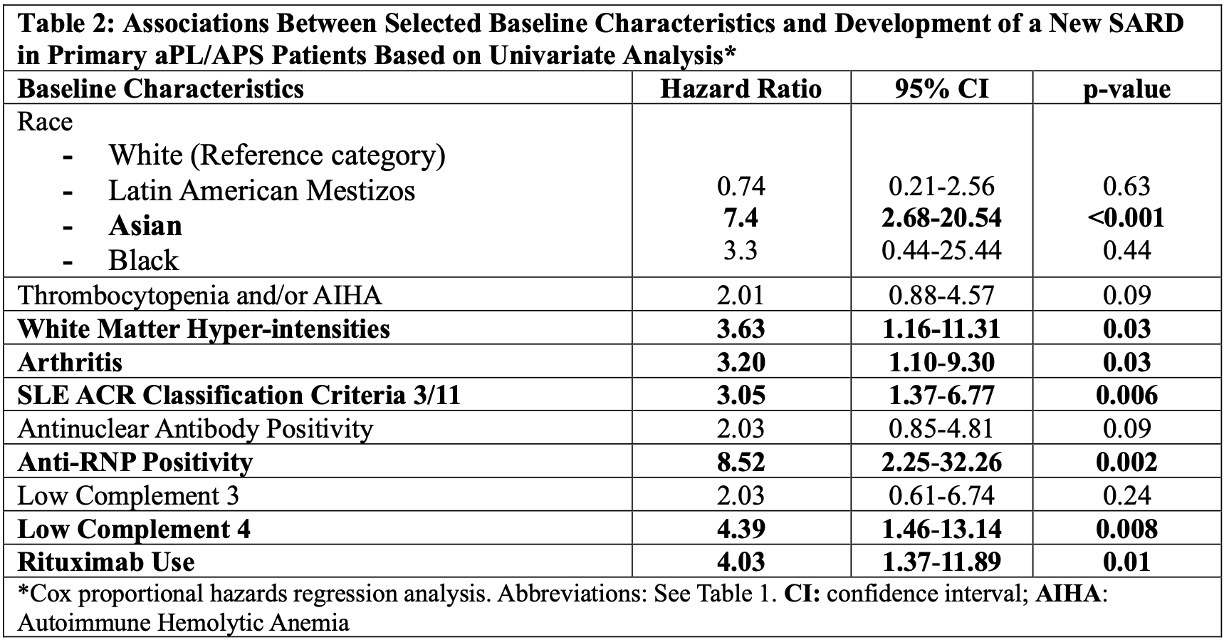
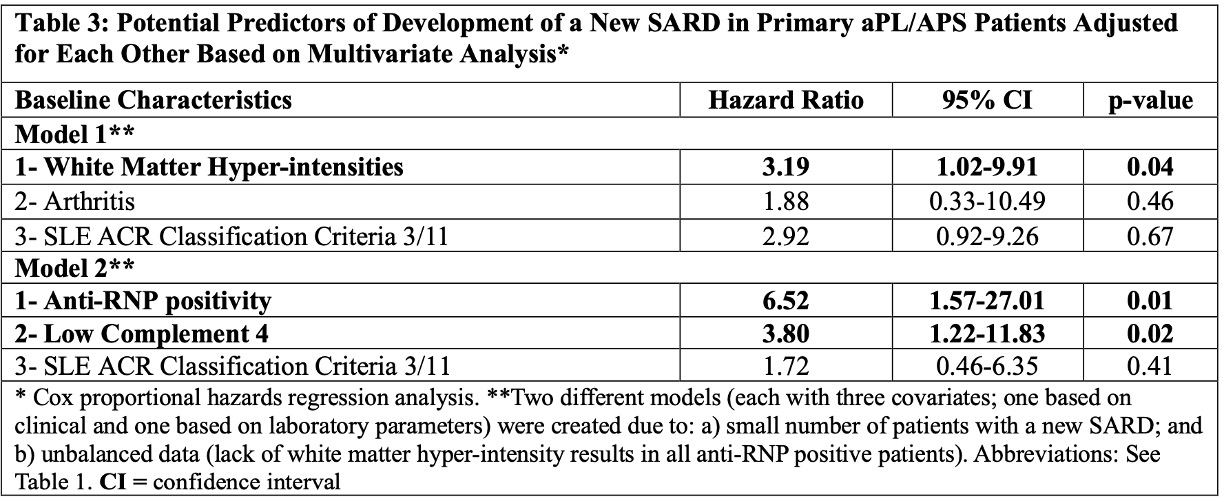
Results: As of March 2024, of 1,209 patients recruited, 487 (40%) were excluded due to concomitant SARDs at baseline, and 108 (9%) due to incomplete follow-up data. Of the remaining 614 patients (median age at registry entry: 46.9 [interquartile range 17.9-78.7], female: 442 [72%] and white: 434/570 [76%]), 28 (5%) developed a new SARD (lupus 17, other 11) during the median follow-up of six years (interquartile range 1.9 to 8.7) (longer in patients with new SARDs [Table 1]). The incident SARD risk was 0.76 per 100 patient-years based on 3,684 patient year follow-up. Based on the univariate Cox regression analysis, Asian race, brain white matter hyper-intensities, arthritis, lupus-like disease (3 of 11 ACR 1997 lupus classification criteria), anti-ribonuclear antibody (anti-RNP) positivity, low C4 levels, and rituximab (RTX) use were significantly associated with a new SARD development (Table 2). Based on the multivariate Cox regression analyses adjusted for confounders in two different models (clinical and laboratory), brain white matter hyper-intensities (Hazard Ratio [HR] 3.19, 95% Confidence Interval [CI] 1.02-9.91, p=0.04), anti-RNP positivity (HR 6.52, 95% CI 1.57-27.01, p=0.01), and low C4 levels (HR 3.80, 95% CI 1.22-11.83, p=0.02) remained significant (Table 3).
Conclusion: In primary aPL-positive patients with/without APS classification, based on 3,684 patient years of prospective follow-up, the incident SARD development rate was 5% (0.76 per 100 patient-years). Baseline white matter hyper-intensities, anti-RNP positivity, and low C4 levels, were associated with a new SARD development. Future registry analyses using standardized core laboratory lupus-related autoantibody results, and with longer follow-up times and larger numbers of new SARD, will help better define predictors of new SARD development in primary aPL/APS patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kose Cobanoglu R, Willis R, Paredes-Ruiz D, Tektonidou M, Pengo V, Sciascia S, Nalli C, Signorelli F, Fortin P, Efthymiou M, Belmont H, Petri M, Cervera R, Barber M, ATSUMI T, Lopez-Pedrera C, Knight J, Branch D, Kello N, Ji L, Rodriguez-Almaraz E, Artim Esen B, Pardos Gea J, Quintana R, Pazzola G, Shi H, Duarte-Garcia A, Meroni P, Roubey R, Bertolaccini M, Cohen H, Andrade D, Erkan D. The Incident Risk and Predictors of Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease (SARD) Development in Persistently Antiphospholipid Antibody Positive Patients Without SARDs: Prospective Results from the APS ACTION Clinical Database and Repository (“Registry”) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-incident-risk-and-predictors-of-systemic-autoimmune-rheumatic-disease-sard-development-in-persistently-antiphospholipid-antibody-positive-patients-without-sards-prospective-results-from-the-aps/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-incident-risk-and-predictors-of-systemic-autoimmune-rheumatic-disease-sard-development-in-persistently-antiphospholipid-antibody-positive-patients-without-sards-prospective-results-from-the-aps/