Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Macrophages play key roles in the pathogenesis of various inflammatory vascular diseases, such as Takayasu’s arteritis (TAK) and atherosclerosis. However, limited data on the difference in compositional characterizations and transcriptomic profile of macrophages across these diseases was reported.
Methods: Single-cell RNA-Seq (scRNA-Seq) were performed on artery tissues from 5 active patients with TAK. As control, single-cell transcriptomic data on the control vascular samples including 3 calcified atherosclerotic core plaques (AC) and 3 patient-matched proximal adjacent portions of carotid artery tissue (PA), was obtained from the database Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened after quality control and clustering. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) were conducted for DEGs enrichment analysis. Differentiation trajectory and status of macrophage were determined by Monocle2 pseudotime analysis and CytoTRACE. CellPhoneDB was performed to identify ligand-receptor pairs between the macrophages and vascular cells in artery tissues.
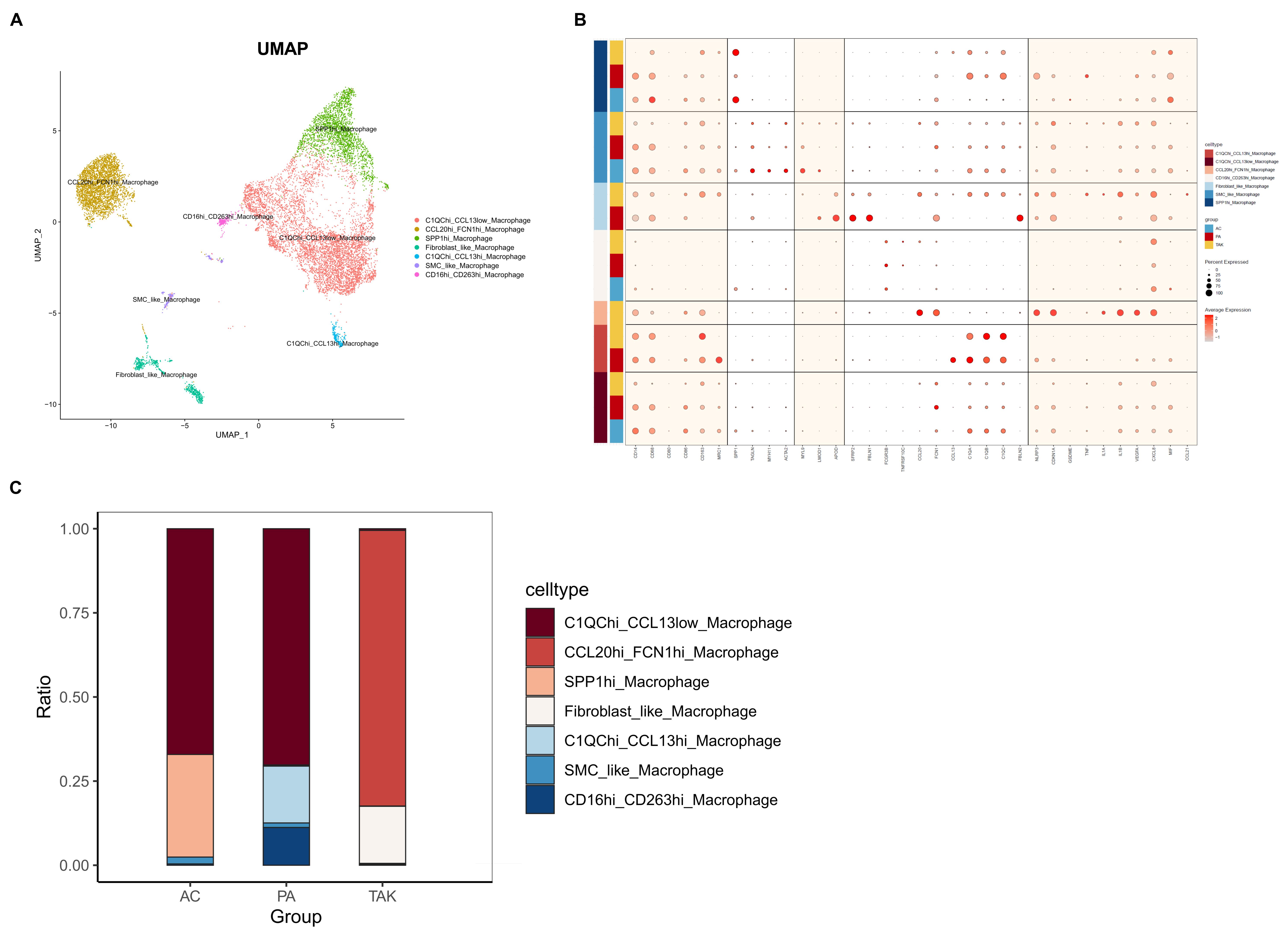
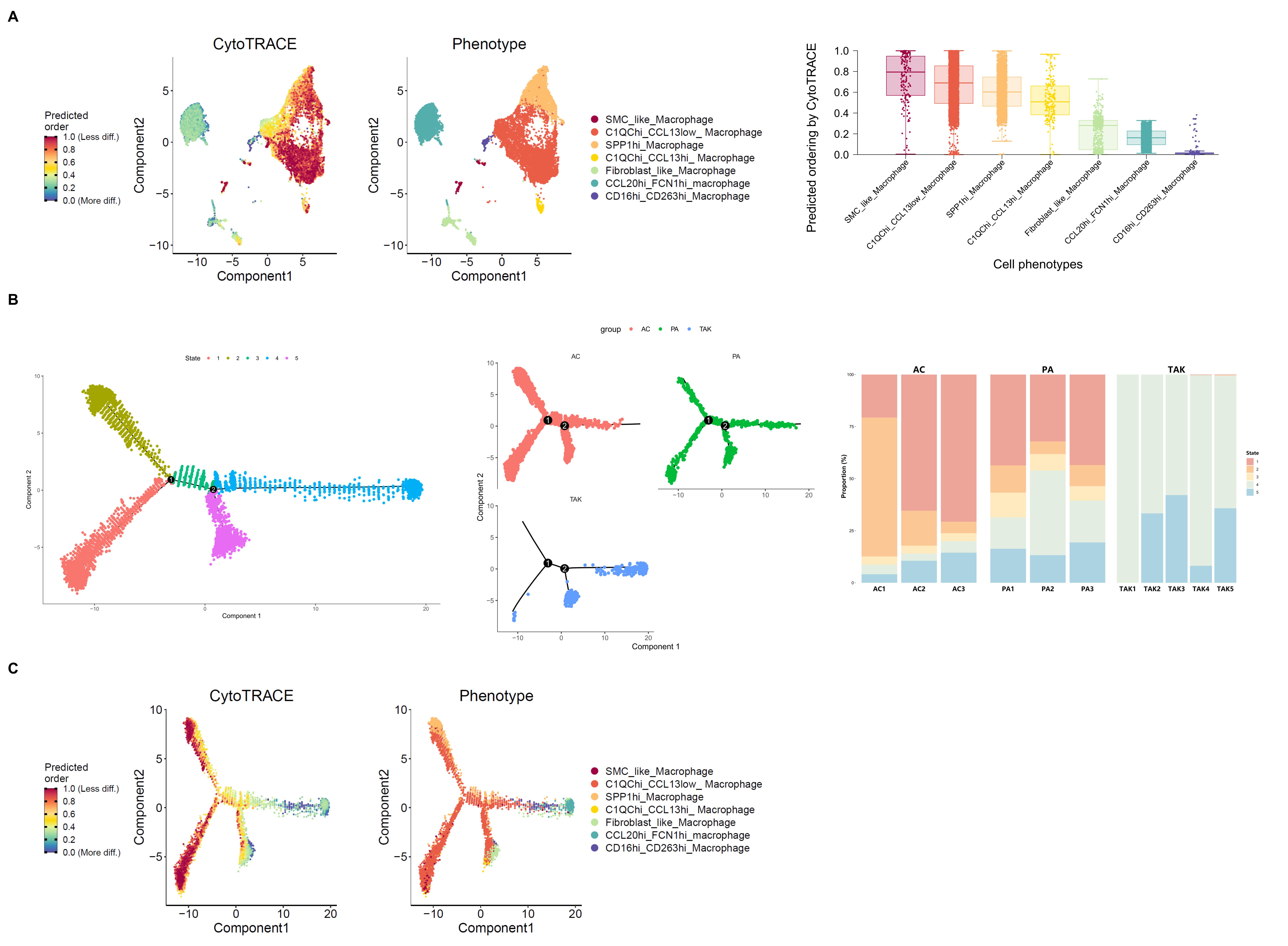
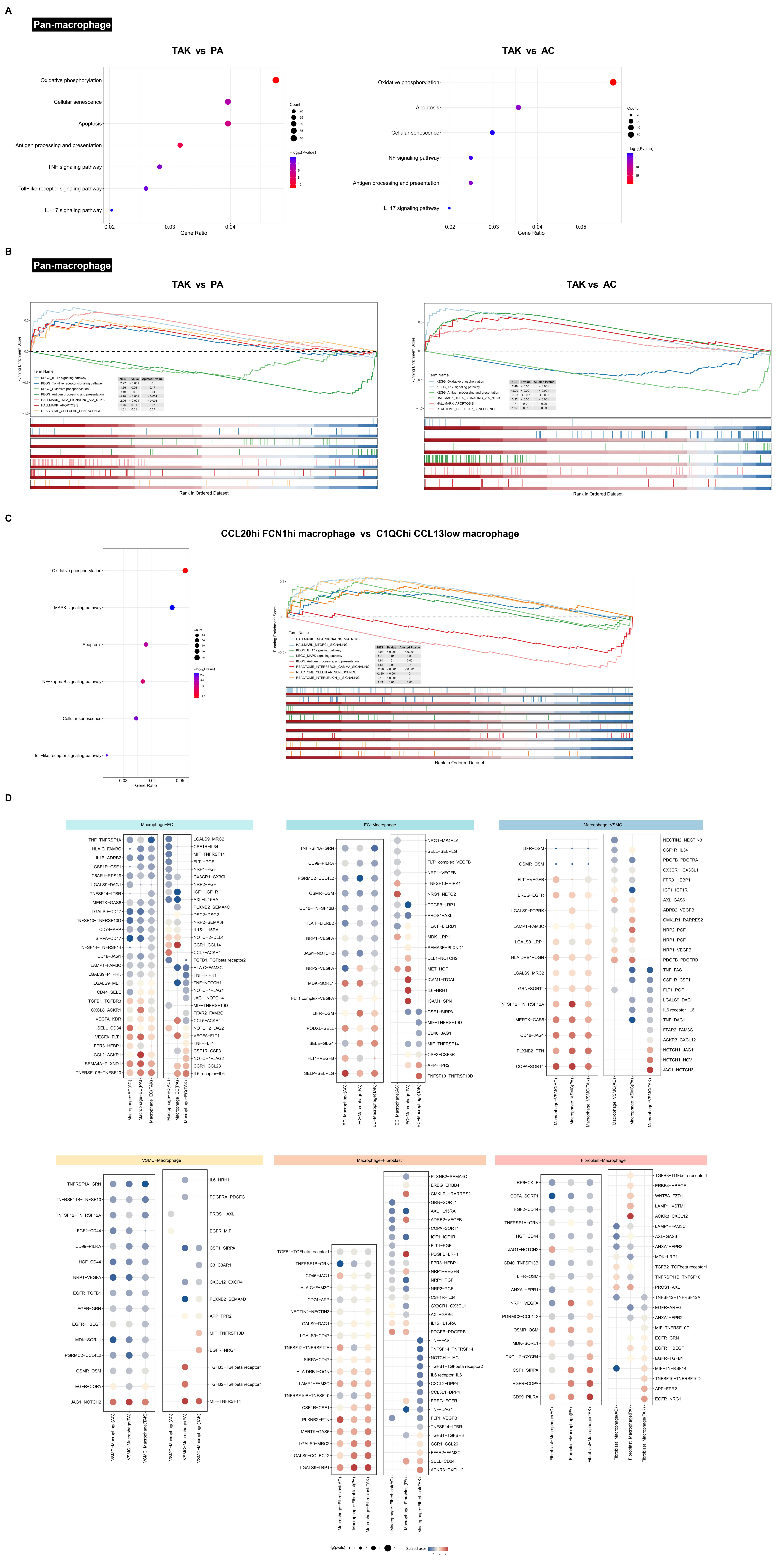
Results: Unsupervised dimensionality reduction and clustering for pan–macrophage populations revealed distinct subgroups, including C1QChi CCL13low macrophage, CCL20hi FCN1hi macrophage, SPP1hi macrophage, fibroblast-like macrophage, C1QChi CCL13hi macrophage, SMC-like macrophage, CD16hi CD263hi macrophage across samples. Of particular note, CCL20hi FCN1hi subsets and fibroblast-like subsets virtually account for all macrophages and were present only in vascular lesions of TAK, while the vast majority of macrophages in PA and AC were C1QChi CCL13low subsets (Figure 1). Monocle peusdotime trajectory analysis, together with CytoTRACE suggested that macrophages of patients with TAK were more highly differentiated (Figure 2). Differential gene enrichment analysis suggested that IL-17 signaling pathway, TNF signaling via NF-kB pathway, apoptosis pathway and cellular senescence pathway were significantly upregulated, while Oxidative phosphorylation pathway and antigen processing and presentation pathway in macrophage were downregulated in both macrophages of TAK versus PA or AC, and CCL20hi FCN1hi macrophage versus C1QChi CCL13low macrophage (Figure 3). Unexpectedly, cell–cell communication analysis by CellPhoneDB showed that vascular cells (VSMCs, endothelial cells and fibroblast) provided multiple signaling that regulate differentiation and functional status of macrophages in TAK (Figure 3).
Conclusion: TAK has distinct compositional characterizations, transcriptomic profiles, and differentiation status of macrophages in vascular lesion. CCL20hi FCN1hi and fibroblast-like subsets are the main and disease-specific subpopulations of macrophages in TAK. Vascular cells may be significant determinants of macrophages function in inflamed artery of TAK.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
du L, Fang C, Gao s, Chen z, Li Y. Single-cell RNA-Seq Analysis Reveals Distinct Compositional Characterizations and Transcriptomic Profiles of Macrophages in Takayasu’s Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-rna-seq-analysis-reveals-distinct-compositional-characterizations-and-transcriptomic-profiles-of-macrophages-in-takayasus-arteritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-rna-seq-analysis-reveals-distinct-compositional-characterizations-and-transcriptomic-profiles-of-macrophages-in-takayasus-arteritis/