Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with spondyloarthritis (SpA) can present with several phenotypes (i.e., axial SpA (axSpA), peripheral SpA (pSpA) and Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)) and peripheral arthritis can occur either concomitantly with the axial disease or independently. Peripheral arthritis can impact disease activity outcomes, but data is lacking on the potentially different magnitude of this effect across the phenotypes of the disease. The objectives of this study were: a) to determine the independent impact of the presence of peripheral arthritis on disease activity outcomes across all SpA phenotypes; b) to investigate differences in this impact across SpA phenotypes (axSpA, pSpA and PsA).
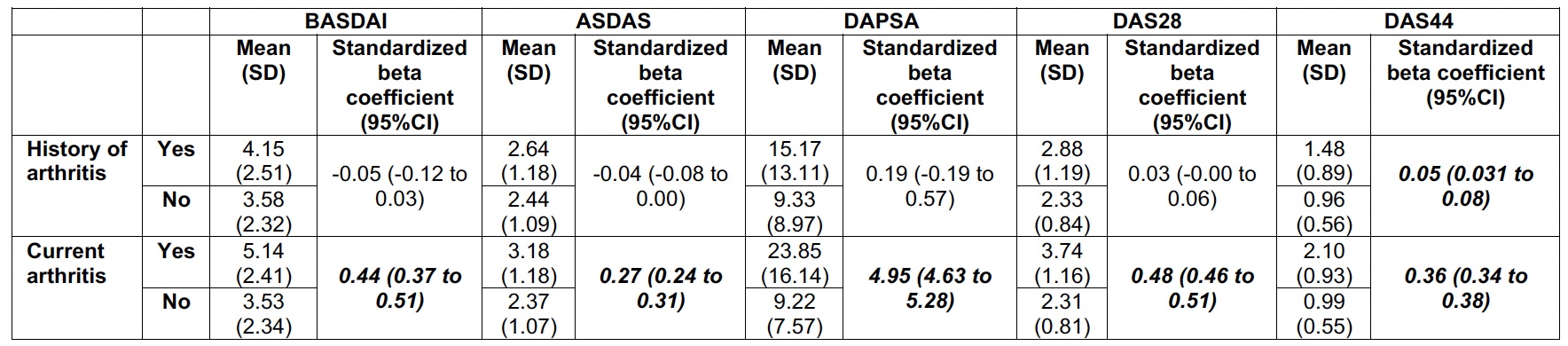
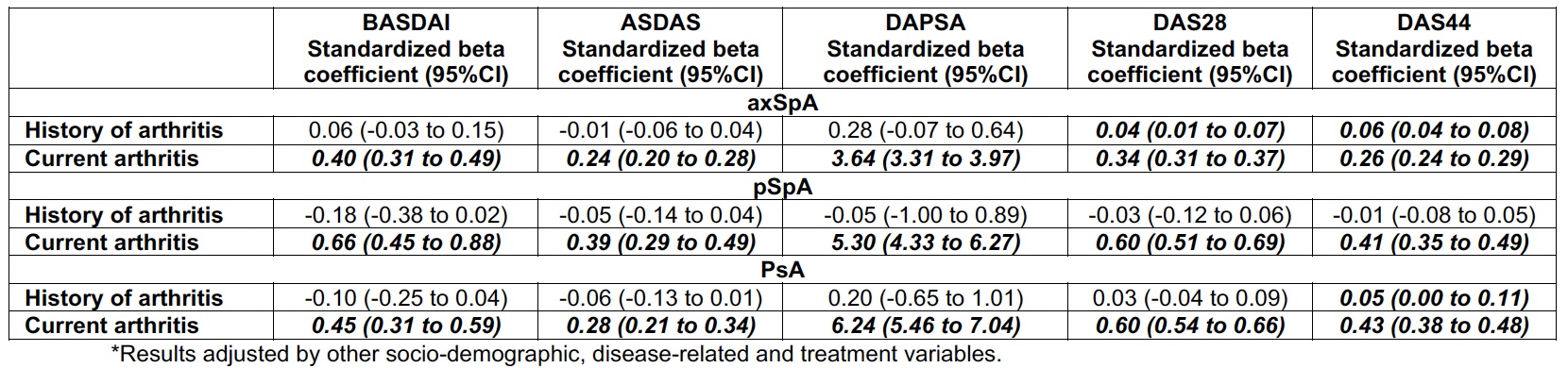
Methods: This analysis is derived from the cross-sectional ASAS-PerSpA study. The impact of peripheral arthritis (i.e., history of peripheral arthritis and current peripheral arthritis) on BASDAI, ASDAS, DAPSA, DAS28 and DAS44 was initially explored using multivariable models encompassing the other peripheral manifestations (enthesitis), as well as socio-demographic, disease-related and treatment variables. Then, analyses were stratified by phenotype. All the obtained regression coefficients were standardized to allow for comparisons across the different disease activity measures.
Results: A total of 4185 patients (2719 axSpA, 433 pSpA, 1033 PsA) were included. Multivariabçe analyses in the overall population revealed that a history of arthritis exclusively affected DAS44, while current arthritis influenced all disease activity outcomes, with a more pronounced effect on DAPSA than on BASDAI, ASDAS, DAS28 or DAS44 (Table 1). Multivariable analyses across phenotypes showed very similar results. Current arthritis significantly impacted BASDAI, ASDAS, DAPSA, DAS28 and DAS44 in the three subtypes. However, this effect was larger for DAPSA than for the other outcomes (Table 2).
Conclusion: Peripheral arthritis, particularly its current presence, significantly impacts disease activity outcome measures in SpA patients. Notably, this impact remains consistent across the different phenotypes of SpA, but with a larger impact on DAPSA compared to the remaining disease activity measurement instruments.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
López Medina C, Ramiro S, Capelusnik D, Molto A. Impact of Peripheral Arthritis on Disease Activity Outcomes in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis, Peripheral Spondyloarthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Data from the ASAS-PerSpA Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-peripheral-arthritis-on-disease-activity-outcomes-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-peripheral-spondyloarthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-data-from-the-asas-perspa-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-peripheral-arthritis-on-disease-activity-outcomes-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-peripheral-spondyloarthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-data-from-the-asas-perspa-study/