Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Adalimumab is an effective and safe treatment for RA, however a substantial proportion of RA patients discontinue its use due to inefficacy. Upon failure, guidelines recommend switching to another TNF inhibitor (TNFi) or a biological or targeted syntetic DMARD (b/tsDMARD) with a different mode of action (non-TNFi). Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM), i.e. assessment of serum drug concentrations or anti-drug antibodies, may aid in determining the most optimal subsequent treatment choice. However, the clinical effectiveness of TDM in the setting of RA patients failing adalimumab treatment due to inefficacy has not been tested in a controlled trial. Therefore, our study aimed to assess whether a switching strategy based on adalimumab trough serum concentration at the time of failure is superior to random switching in this setting.
Methods: This 24-week, multicenter, triple-blinded, randomized controlled superiority test treatment trial enrolled RA patients who discontinued adalimumab (40 mg subcutaneously every other week for ≥ 10 weeks) due to inefficacy (defined as DAS28-CRP >2.9). (1) Participants were randomized 1:1 to a TDM based or random switching strategy, and allocation remained fully blinded during the study and analyses. In the TDM group, patients with adalimumab concentrations < 1.0 mg/L were switched to etanercept (TNFi), while those with concentrations ≥ 1.0 mg/L were switched to a non-TNFi b/tsDMARD. Control group patients were randomly assigned to a second TNFi or non-TNFi, following the same relative proportions as the TDM group. In both groups the specific non-TNFi b/tsDMARD, chosen at the discretion of the treating physician, could be abatacept, rituximab, sarilumab, tocilizumab, or a Janus kinase inhibitor. The primary outcome was the between-group difference in mean time-weighted DAS in 28 joints (DAS28-CRP) at 24 weeks, analyzed with student’s t-test in the intention-to-treat population. Secondary outcomes included per-protocol analysis of the primary outcome, and between-group differences in proportions of patients meeting EULAR response criteria, achieving DAS28-CRP < 2.9, and the total number of flares at 24 weeks.
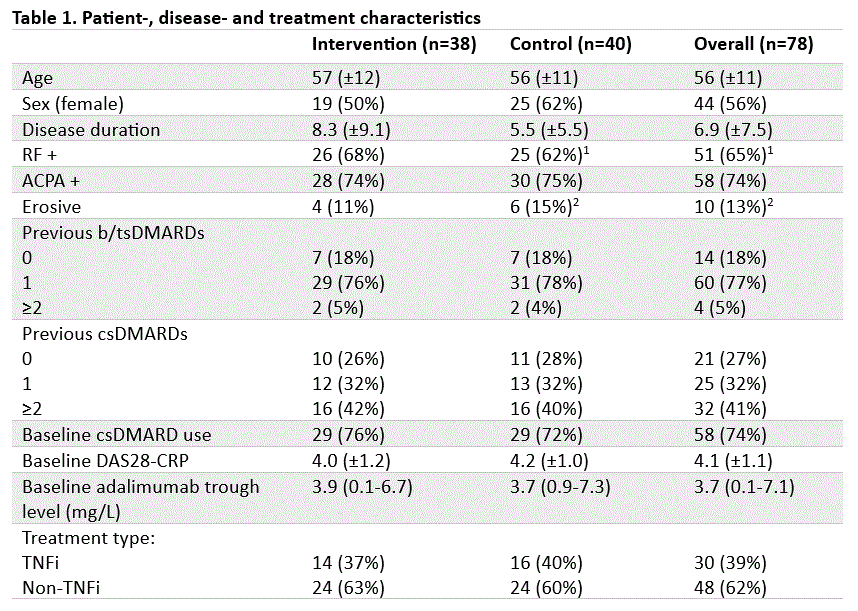
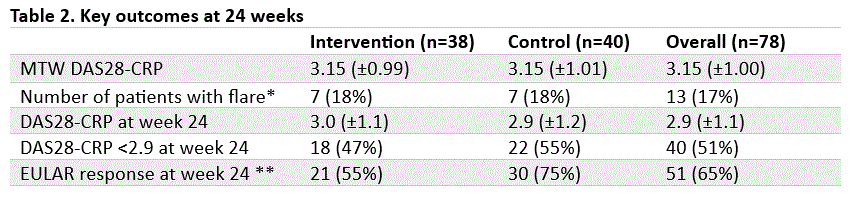
Results: Between July 31, 2020, and November 6, 2023, 83 consecutive RA patients were included, of whom 78 started a new b/tsDMARD based on random assignment to either the intervention (n=38) or control (n=40) group (Table 1). Mean time weighted DAS28-CRP over 24 weeks was 3.15 (SD: 0.99) and 3.15 (SD: 1.01) in the intervention and control group respectively (p = 0.98, 95% CI -0.46 to 0.47). Per protocol analyses did not show substantial differences. Key secondary outcomes are presented in Table 2.
Conclusion: A switching strategy based on adalimumab trough serum concentration was not superior to random switching in RA patients failing adalimumab treatment.
References:
1: Wientjes MHM, Atiqi S, Wolbink GJ, et al. Trials. 2021 Jun 19;22(1):406.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wientjes M, Atiqi S, Wolbink G, Nurmohamed M, Boers M, Hooijberg F, Rispens T, De Vries A, Loeff F, Van Vollenhoven R, Ramiro S, van Herwaarden N, van den Bemt B, den Broeder A. Using Adalimumab Serum Concentration to Choose a Subsequent DMARD in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Failing Adalimumab Treatment (ADDORA-switch): Results of a Blinded Randomized Test Treatment Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/using-adalimumab-serum-concentration-to-choose-a-subsequent-dmard-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-failing-adalimumab-treatment-addora-switch-results-of-a-blinded-randomized-test-treatment-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/using-adalimumab-serum-concentration-to-choose-a-subsequent-dmard-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-failing-adalimumab-treatment-addora-switch-results-of-a-blinded-randomized-test-treatment-trial/