Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Leukopenia is an established adverse effect associated with tocilizumab(TCZ) therapy. Nevertheless, the extent of risk and its correlation with infection rates among Asian rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients remain ambiguous. This study seeks to ascertain the incidence of leukopenia following tocilizumab administration and evaluate its impact on infection rates and remission outcomes in RA patients.
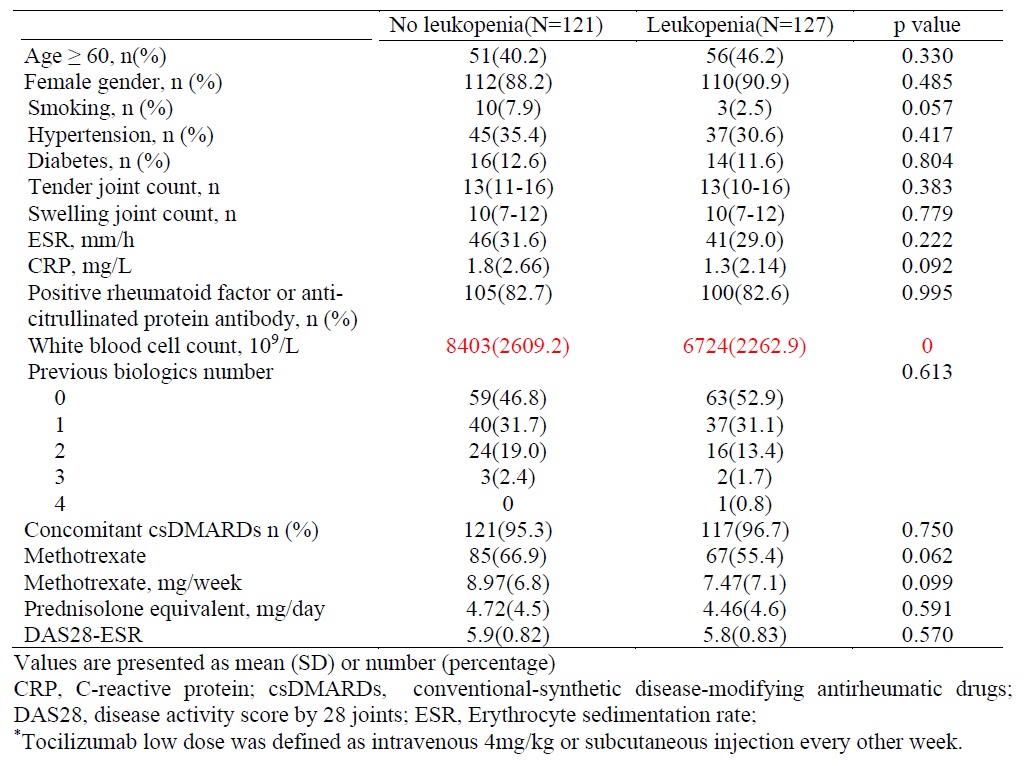
Methods: This retrospective cohort study enrolled RA patients undergoing TCZ treatment between 2012 and 2020. White blood cell counts were measured at baseline and at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months post-initiation of TCZ therapy. Leukopenia was defined as white blood cell < 4000 /uL and patients with baseline leukopenia were excluded . Baseline clinical characteristics and laboratory data were compared between RA patients who developed leukopenia during TCZ treatment and those who did not. Risk factors associated with leukopenia and infections were analyzed. The percentage of RA patients achieving DAS28-low disease activity(LDA), DAS28-remission and EULAR response were documented.
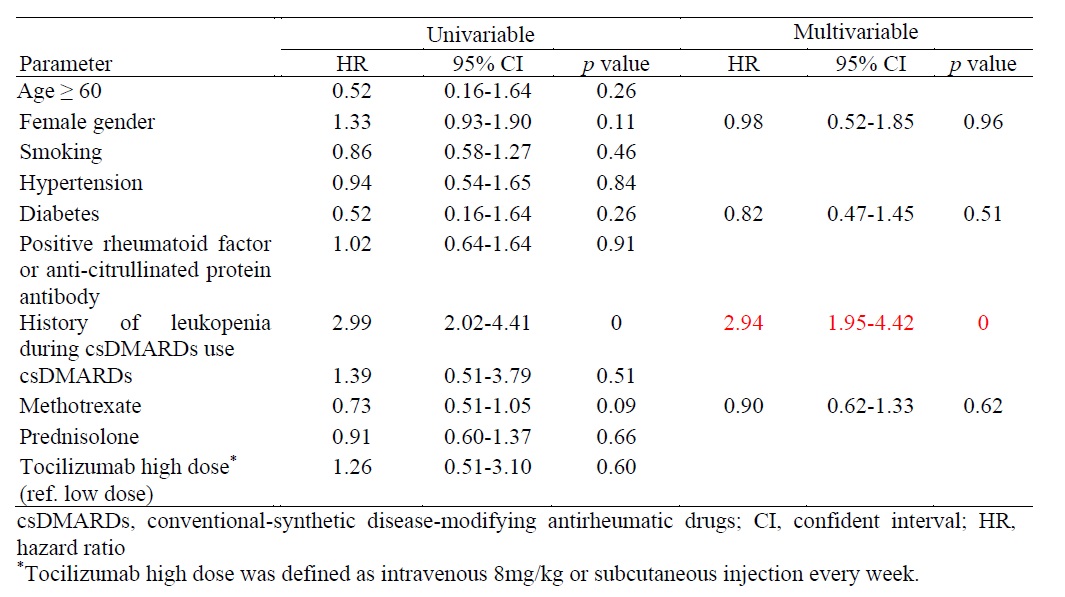
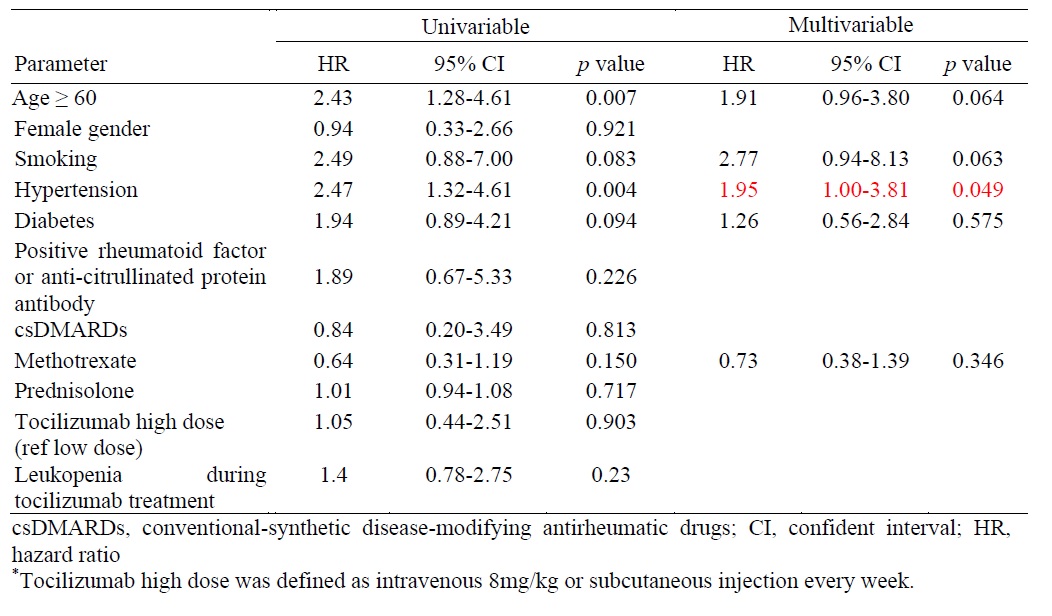
Results: In this study, a total of 248 RA patients were enrolled, predominantly female (89.5%, n=222). During treatment with TCZ, 127 patients (48.8%) developed leukopenia, and 40 patients (16.1%) experienced severe infections requiring hospitalization during the follow-up period. Multivariable analysis revealed that a history of leukopenia with conventional-synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) significantly increased the risk of developing leukopenia in RA patients treated with TCZ.(hazard ratio 2.94, 95% CI 1.95-4.42, p=0). The occurrence of leukopenia following TCZ administration and different TCZ dosage did not significantly influence the risk of infections, rates of DAS28-LDA, DAS28-remission, or EULAR response at six and twelve months.
Conclusion: Leukopenia is a recognized adverse effect observed in RA patients treated with tocilizumab. A history of leukopenia during csDMARDs usage is identified as a risk factor for developing leukopenia. The occurrence of leukopenia subsequent to tocilizumab therapy did not significantly affect the incidence of infections. Continuation of tocilizumab treatment may be considered despite the presence of leukopenia.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kuo P, Fang P, Chen M. Risk Factors for Leukopenia in Asian Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Undergoing Tocilizumab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-factors-for-leukopenia-in-asian-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-undergoing-tocilizumab/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-factors-for-leukopenia-in-asian-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-undergoing-tocilizumab/