Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
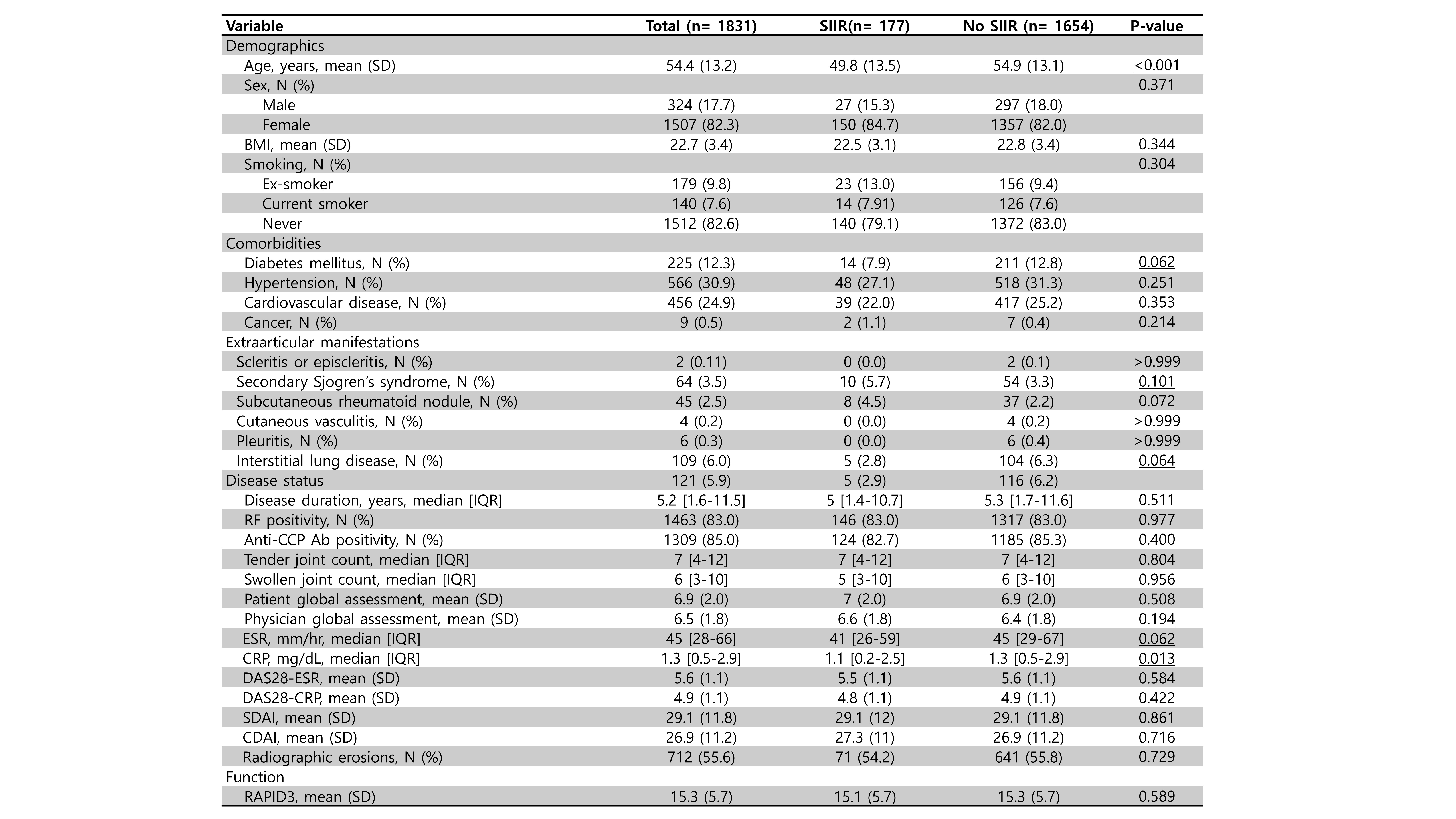
Background/Purpose: The use of biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) has revolutionized the management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), despite their efficacy being occasionally limited by infusion-related reactions (IRRs). This study aimed to investigate demographic and clinical characteristics between RA patients with and without IRR, using data from the Korean College of Rheumatology Biologics (KOBIO) registry.
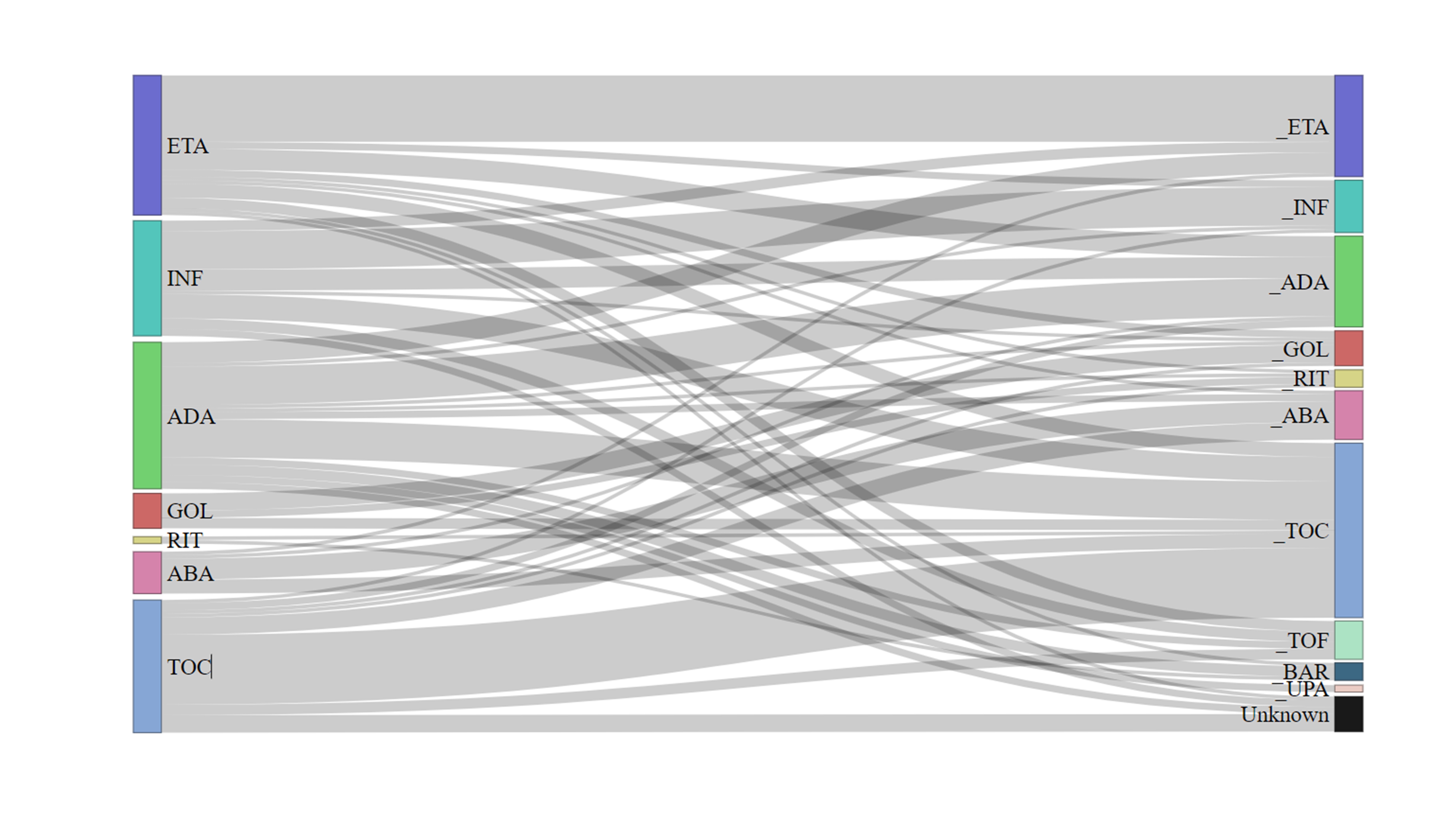
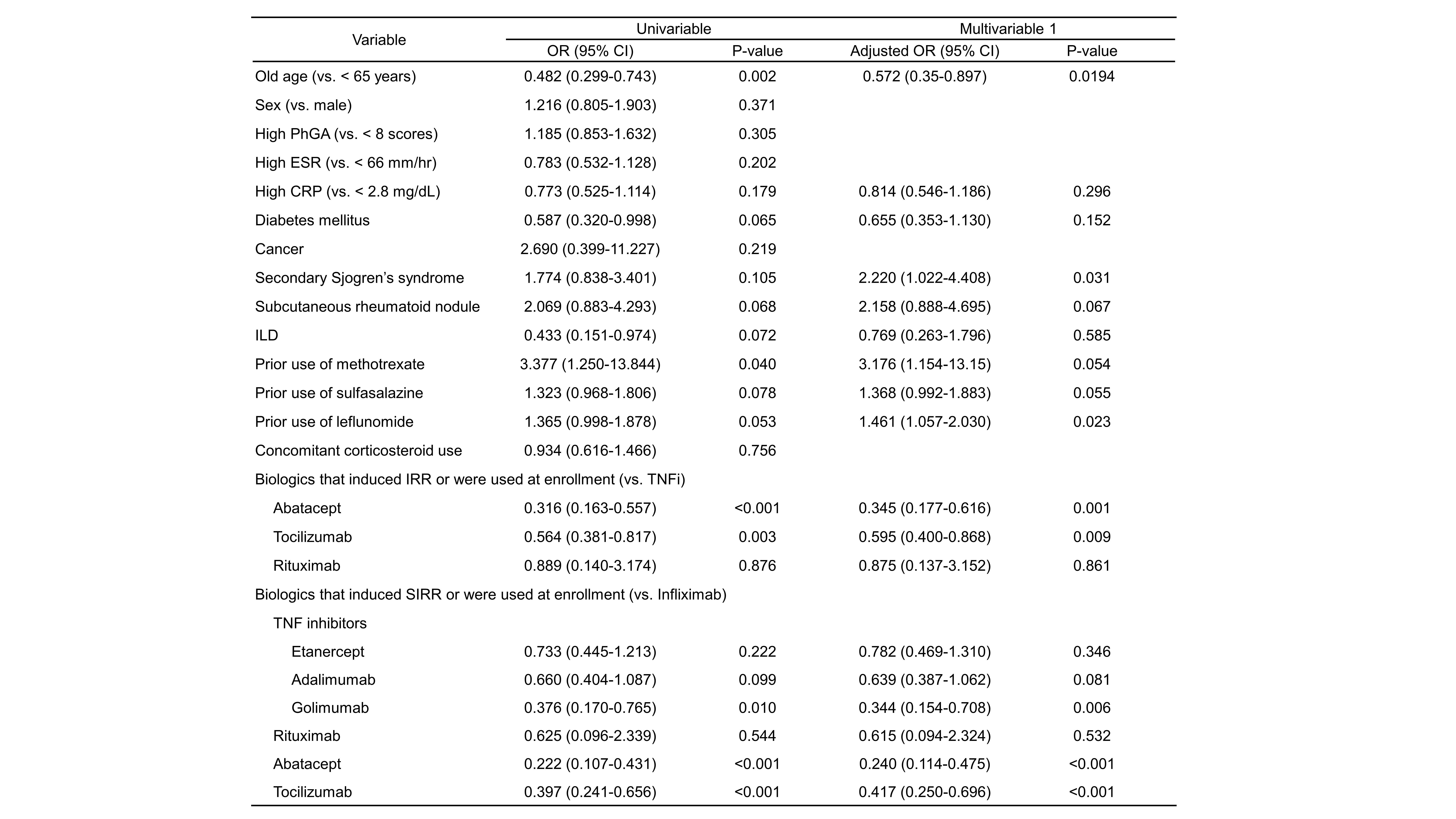
Methods: We analyzed data from 1,831 patients with RA enrolled in the KOBIO registry, categorizing them into groups with and without IRR. Patient demographics, disease characteristics, and treatment details were compared to identify factors associated with IRR. Furthermore, we visualized the patterns of switching between bDMARDs over time, using a Sankey plot. Multivariate logistic regression was used to identify independent predictors of IRR.
Results: Among the 1,831 RA patients, 177 (9.7%) experienced IRRs. Significant differences were observed in mean age (IRR: 49.8 years; no IRR: 54.9 years; p< 0.001), CRP level (IRR: 1.1mg/dL; no IRR: 1.3mg/dL; p=0.013), and prior use of methotrexate (IRR: 98.3%; no IRR: 94.5%; p=0.029). Multivariable analysis revealed that older age was associated with a decreased odds ratio (OR = 0.564, P = 0.016). Additionally, the presence of secondary Sjogren’s syndrome (OR = 2.220, p = 0.031) and prior use of leflunomide (OR 1.461, p=0.023) were identified as independent risk factors. bDMARDs such as abatacept (OR 0.240, p< 0.001) and tocilizumab (OR 0.417, p< 0.001) showed significantly decreased IRR compared to TNF inhibitors. Among TNF inhibitors, golimumab (OR = 0.344, p = 0.006) was found to reduce the risk of IRR. Following IRR, the use of etanercept, infliximab, and adalimumab decreased, while the use of tocilizumab and Janus kinase pathway inhibitors increased.
Conclusion: This study reveals a significant incidence of IRRs in patients with RA using bDMARDs, with younger age and prior use of specific conventional DMARDs posing higher risks. For patients with these risk factors, abatacept or tocilizumab may be considered as preferred options. These findings underscore the need for careful monitoring and tailored therapeutic strategies to enhance patient outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim J, Jung J, Suh C, Kim H. Characterizing Infusion-Related Reactions in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Biologic DMARDs: Observations from the KOBIO Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterizing-infusion-related-reactions-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-biologic-dmards-observations-from-the-kobio-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterizing-infusion-related-reactions-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-biologic-dmards-observations-from-the-kobio-registry/