Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs) are at higher risk of general infection due to the presence of comorbidities, underlying disease activity, and use of targeted immune-modulating therapies. Some laboratory parameters play a crucial role in assessing infection risk.
Objective: To evaluate risk factors associated with severe infection during B-lymphocyte targeted therapy in vaccinated patients and the relationship between neutrophil–to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and severe infections.
Methods: A retrospective longitudinal study of 158 SARD patients treated with rituximab (RTX) and Belimumab (BLM) was conducted. Immunoglobulin levels and NLR were measured between December 2019 and February 2020 (before the pandemic period). All severe infections (infection requiring hospitalisation) due to COVID-19 or other microorganism were collected between 1st March 2020 to 1st January 2024. Frequency and percentage were calculated for qualitative variables. Student’s t test or Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the means or medians between two groups according to the sample size. Spearman’s correlation coefficient was used to test the association between numerical variables. Multivariate analysis was performed to assess risk factors associated with severe infection and the relationship of NLR to COVID-19 infection. P-values of less than 0.05 were considered significant. The statistical program used was STATA MP-Parallel Edition 17.0.
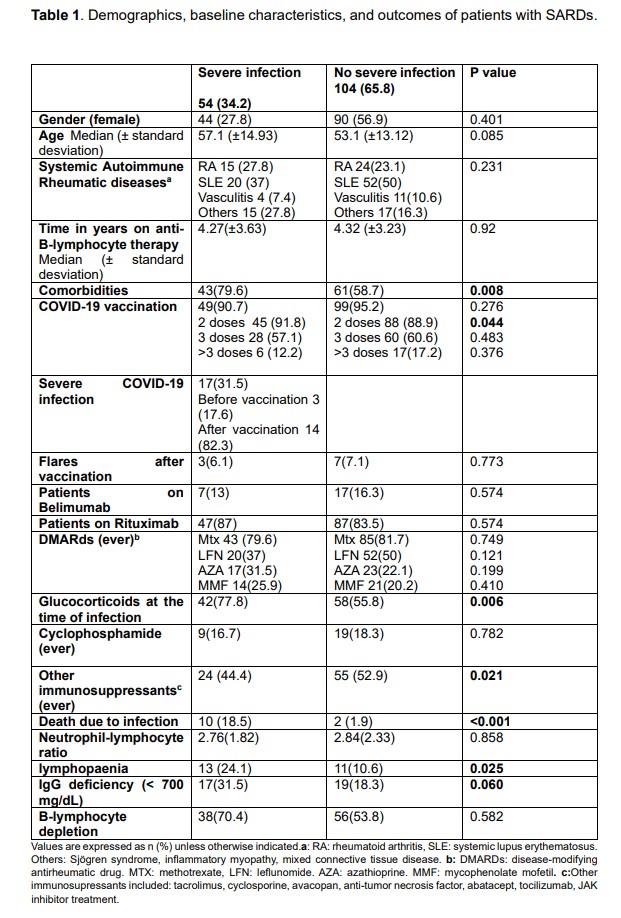
Results: 158 patients with SARDs were included: 84.8% females (n=134) and 15.2% males (n=24). The mean age was 54 (±13.8). 24 patients were on belimumab (28%) and 134 patients on rituximab (84.8%). The SARDs included were: 72 systemic lupus erythematosus (45.6%), 15 ANCA vasculitis (9.5%),39 rheumatoid arthritis (24.7)% and 32 were other connective tissue diseases (20.2%). More than half of the patients had other comorbidities (65.8%).
There were 92 (41.7%) COVID-19 infections of which 17 (10.7%) required hospitalisation. Ten percent (n=16) had concurrent infection with another microorganism. Almost a third of patients (29.1%, n=46) developed severe infection other than COVID-19. Twelve patients (7.6%) died due to severe infection.
Table 1 shows demographic, clinical and laboratory differences between patients with severe infection (COVID-19 or other) and no severe infection.
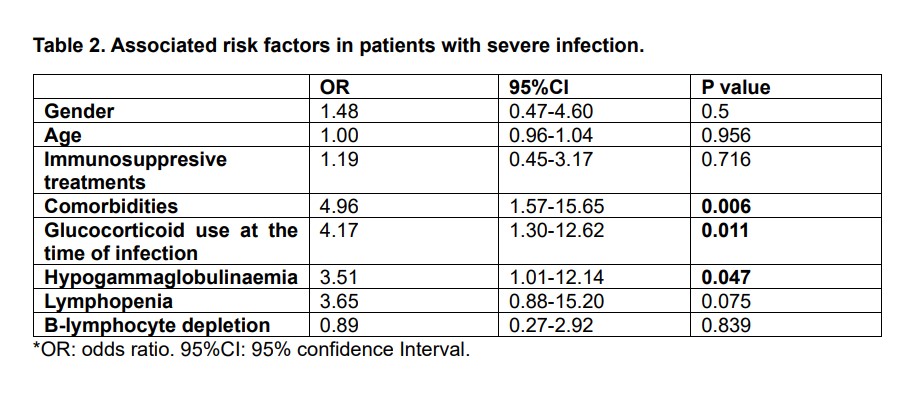
Table 2 shows the multivariate analysis adjusted for age, sex and immunosuppressive treatments between patients with and without severe infection. Comorbidities, glucocorticoid use at the time of infection and hypogammaglobulinaemia were associated with severe infection.
NLR was statistically significant associated with the development of COVID-19 infection (OR 1.79 [CI 95% 1.64-2.98] p=0.035) but no with any type of severe infection (OR 1.1 95% [CI 0.98-5.94] p=0.678).
Conclusion: During the COVID-19 period, patients on anti-B cell therapies developed more serious infections with micro-organisms other than COVID-19. Risk factors for severe infection were comorbidities, hypogammagglublinaemia and glucorticoids. NLR was significantly associated with COVID-19 infection.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Garcia Olivas d, Hernández Sánchez J, Bausá Gimeno l, Nóvoa Medina J, Machín S, Acosta-Mérida M, Botello-Corzo D, Batista Perdomo d, Hernández Beriain J, Tejera Segura B. Severe Infection in COVID-19 Vaccinated Patients with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases on B Cell Targeted Therapies: Association with Neutrophil-lymphocyte Ratio [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/severe-infection-in-covid-19-vaccinated-patients-with-systemic-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases-on-b-cell-targeted-therapies-association-with-neutrophil-lymphocyte-ratio/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/severe-infection-in-covid-19-vaccinated-patients-with-systemic-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases-on-b-cell-targeted-therapies-association-with-neutrophil-lymphocyte-ratio/