Background/Purpose:
Chronic inflammation in RA may contribute to an unstable atherosclerotic plaque phenotype. Dynamic contrast enhanced MRI (DCE MRI) can be used to image carotid plaque neovascularisation and vascular permeability. Contrast agent distribution into the plaque, measured via the transfer constant (Ktrans), correlates with macrophage content and microvessel density on non-RA carotid endarterectomy specimens. Positron emission tomography with fludeoxyglucose (18F) (FDG-PET) can be used to quantify inflammation in carotid plaque and also correlates well with macrophage content. We aimed to employ these imaging techniques to assess plaque inflammation, for the first time, in RA.
Methods:
RA patients, aged 40-65 years old were recruited and underwent a clinical and serological evaluation of RA disease and cardiovascular risk. All patients were screened for carotid plaque using B-mode Doppler ultrasound (US). Patients with plaque >2mm thickness had a carotid DCE MRI on a 3 Tesla scanner. Images were analysed by 2 blinded readers at the Vascular Imaging Laboratory, University of Washington, using a semi-automated analysis software package (Cascade; University of Washington, Seattle, WA). Patients with no history of cancer or recent infection underwent a carotid FDG-PET-CT scan. Plaque was localised using MR and CT then FDG uptake in the region of interest (ROI) was measured by calculating the standardised uptake value (SUVmax).
Results:
57 patients were screened, of whom 29 (51%) had ultrasound evidence of carotid plaque and 12 (21%) had a plaque >2mm. 2 MR scans were incomplete (1 due to pain, 1 due to claustrophobia) so MRI data were available on 10 patients; 5 patients also had FDG-PET-CT. The median (IQR) age and disease duration of the 10 patients undergoing imaging was 57 (55,59) and 9 (2, 20) years respectively. The median (IQR) DAS28 score was 5.15 (4.69, 6.55) and all patients were seropositive. No patients had a history of cerebrovascular disease.
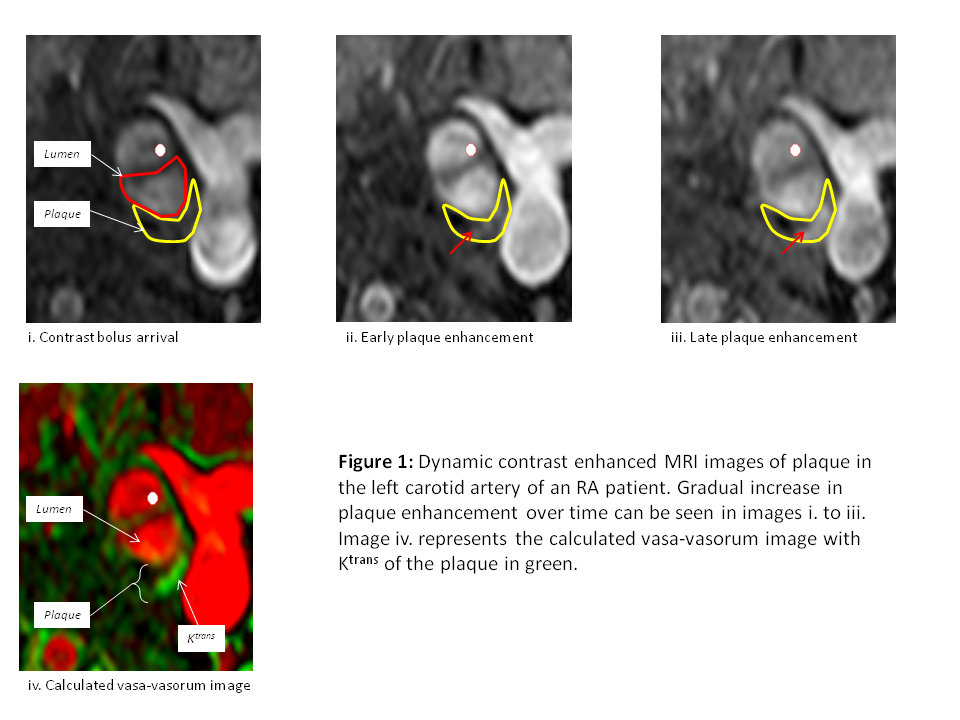
On MRI, plaque >2mm thick was confirmed in 6 (60%) cases. The median (IQR) vessel stenosis was 54.5 (42,70)% and contrast enhancement was seen in all 6 cases (see figure 1), with a median Ktrans value of 0.046 (0.023, 0.105)min-1. Preliminary analysis of PET images demonstrated uptake in all cases with a median (IQR) SUVmax= 2.22 (1.67, 2.95). There was no significant correlation between imaging and clinical parameters.
Conclusion:
Our preliminary study shows that atherosclerotic plaque inflammation can be detected using both 3T MRI and PET in RA patients. The discrepancy between MRI and US findings may be due to measurement error on US or flow artefact on MRI. A larger sample size and a comparator cohort will enable us to further determine the characteristics of atherosclerotic plaque inflammation in RA patients.
Disclosure:
S. Skeoch,
None;
P. Hubbard,
None;
H. Williams,
None;
D. Xu,
VP. Diagnostics Inc.,
5;
S. Jie,
None;
N. Balu,
None;
W. Zhang,
None;
J. James,
None;
T. Hatsukami,
National Institute of Health and Philips Healthcare,
2;
C. Yuan,
NIH, Philips Healthcare, and VPDiagnostics Inc. .,
2,
ImagePace and Boehringer-Ingelheim,
5;
M. Y. Alexander,
None;
P. Hockings,
None;
J. Waterton,
None;
I. N. Bruce,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/imaging-atherosclerotic-plaque-inflammation-in-ra-methodology-and-initial-findings-in-a-single-centre-cohort/